Nicholas E. Pacheco
Towards a Physics Engine to Simulate Robotic Laser Surgery: Finite Element Modeling of Thermal Laser-Tissue Interactions
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents a computational model, based on the Finite Element Method (FEM), that simulates the thermal response of laser-irradiated tissue. This model addresses a gap in the current ecosystem of surgical robot simulators, which generally lack support for lasers and other energy-based end effectors. In the proposed model, the thermal dynamics of the tissue are calculated as the solution to a heat conduction problem with appropriate boundary conditions. The FEM formulation allows the model to capture complex phenomena, such as convection, which is crucial for creating realistic simulations. The accuracy of the model was verified via benchtop laser-tissue interaction experiments using agar tissue phantoms and ex-vivo chicken muscle. The results revealed an average root-mean-square error (RMSE) of less than 2 degrees Celsius across most experimental conditions.
Light in the Larynx: a Miniaturized Robotic Optical Fiber for In-office Laser Surgery of the Vocal Folds
Apr 27, 2022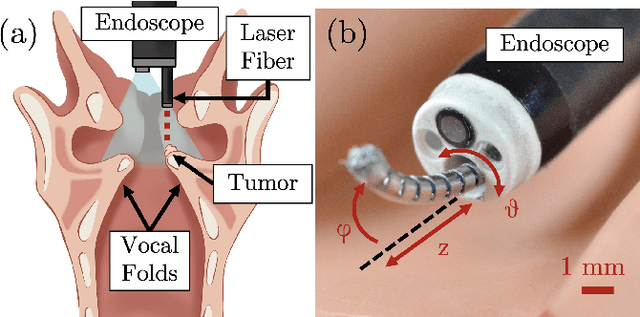
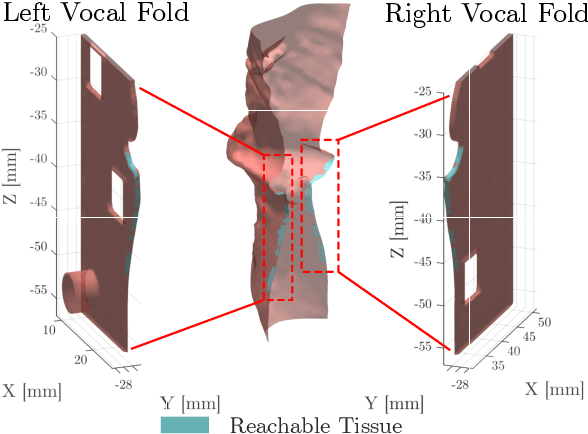
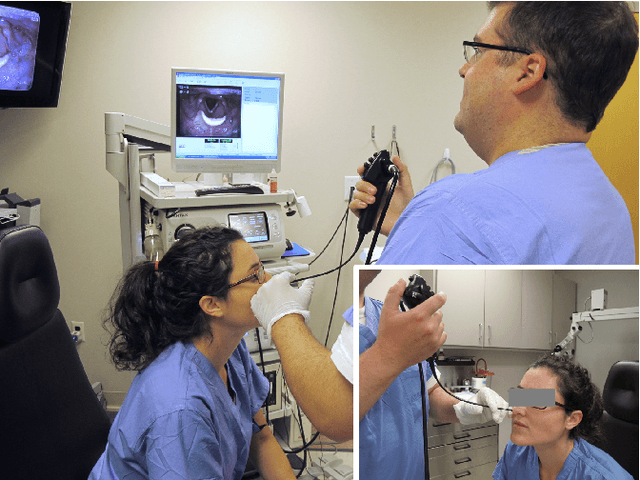
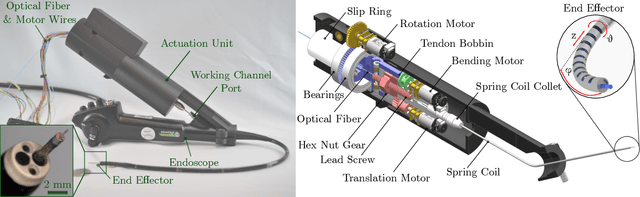
Abstract:This letter reports the design, construction, and experimental validation of a novel hand-held robot for in-office laser surgery of the vocal folds. In-office endoscopic laser surgery is an emerging trend in Laryngology: It promises to deliver the same patient outcomes of traditional surgical treatment (i.e., in the operating room), at a fraction of the cost. Unfortunately, office procedures can be challenging to perform; the optical fibers used for laser delivery can only emit light forward in a line-of-sight fashion, which severely limits anatomical access. The robot we present in this letter aims to overcome these challenges. The end effector of the robot is a steerable laser fiber, created through the combination of a thin optical fiber (0.225 mm) with a tendon-actuated Nickel-Titanium notched sheath that provides bending. This device can be seamlessly used with most commercially available endoscopes, as it is sufficiently small (1.1 mm) to pass through a working channel. To control the fiber, we propose a compact actuation unit that can be mounted on top of the endoscope handle, so that, during a procedure, the operating physician can operate both the endoscope and the steerable fiber with a single hand. We report simulation and phantom experiments demonstrating that the proposed device substantially enhances surgical access compared to current clinical fibers.
Multi Jet Fusion of Nylon-12: A Viable Method to 3D-print Concentric Tube Robots?
Apr 01, 2022
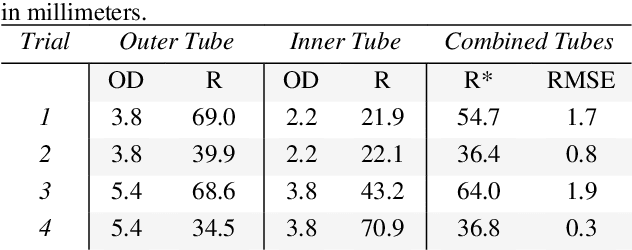
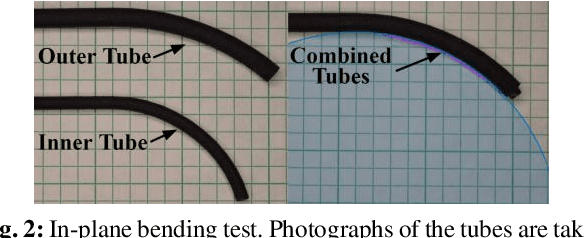
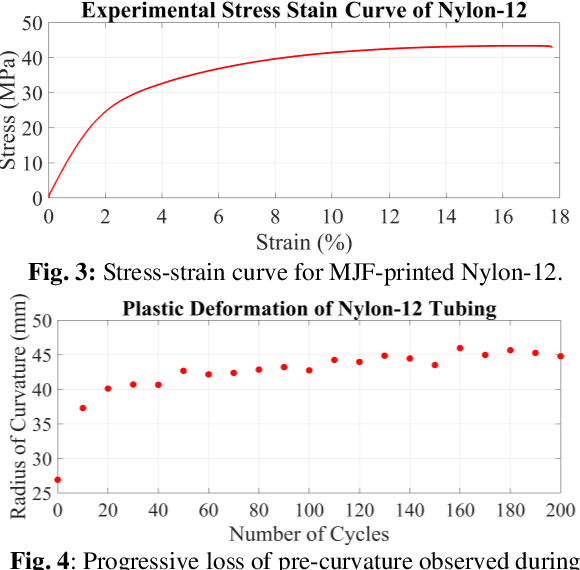
Abstract:In this paper, we present a study on the viability of fabricating Concentric Tube Robots using Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) of Nylon-12, a type of elastic polymer commonly used in additive manufacturing. We note that Nylon-12 was already evaluated for the purpose of building CTRs in prior work, but fabrication was performed with Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), which produced unsatisfactory results. Our study is the first study to evaluate the suitability of MJF to 3Dprint CTRs.
* in press
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge