Netanel Y. Tamir
What Makes for a Good Stereoscopic Image?
Dec 30, 2024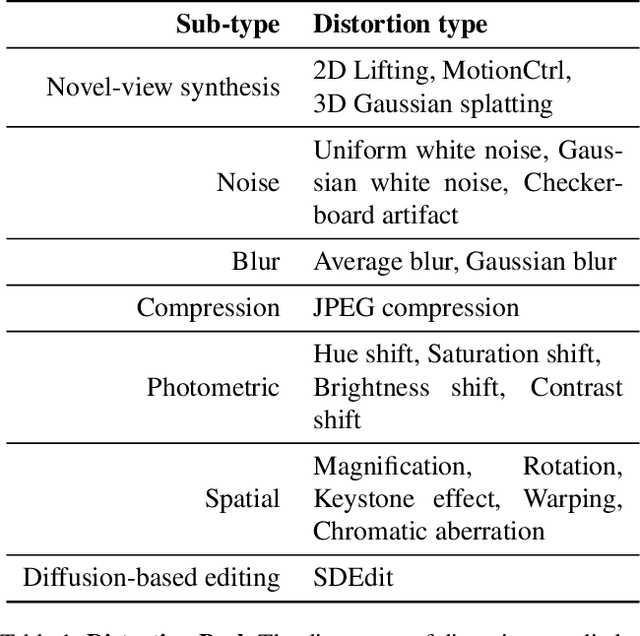
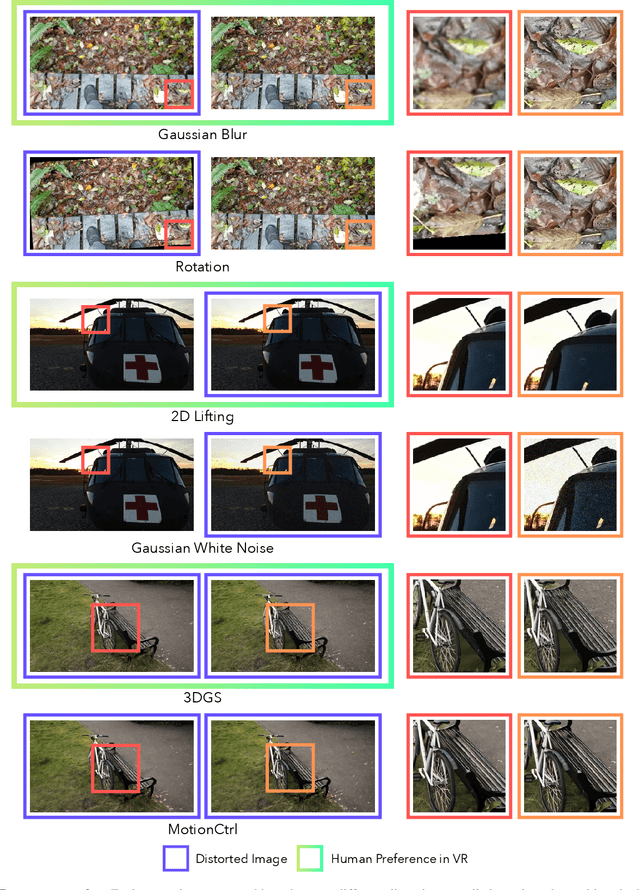
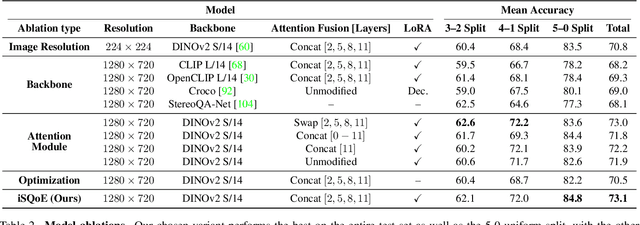
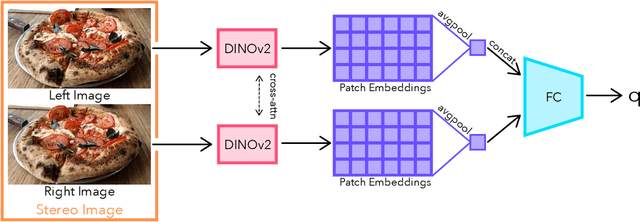
Abstract:With rapid advancements in virtual reality (VR) headsets, effectively measuring stereoscopic quality of experience (SQoE) has become essential for delivering immersive and comfortable 3D experiences. However, most existing stereo metrics focus on isolated aspects of the viewing experience such as visual discomfort or image quality, and have traditionally faced data limitations. To address these gaps, we present SCOPE (Stereoscopic COntent Preference Evaluation), a new dataset comprised of real and synthetic stereoscopic images featuring a wide range of common perceptual distortions and artifacts. The dataset is labeled with preference annotations collected on a VR headset, with our findings indicating a notable degree of consistency in user preferences across different headsets. Additionally, we present iSQoE, a new model for stereo quality of experience assessment trained on our dataset. We show that iSQoE aligns better with human preferences than existing methods when comparing mono-to-stereo conversion methods.
When Does Perceptual Alignment Benefit Vision Representations?
Oct 14, 2024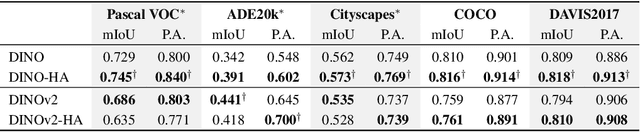
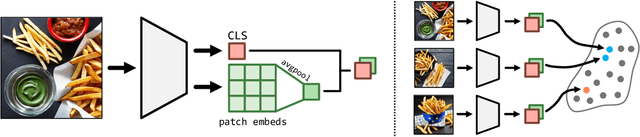
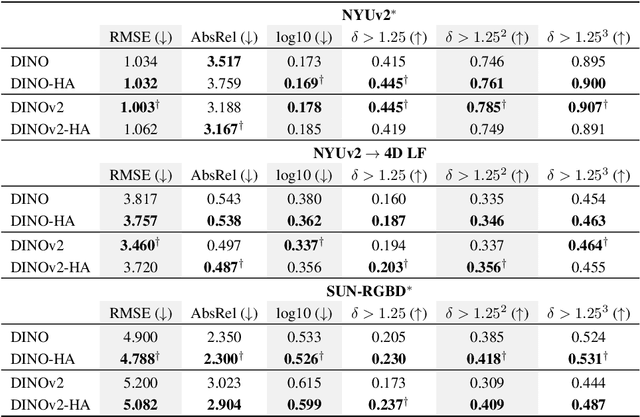
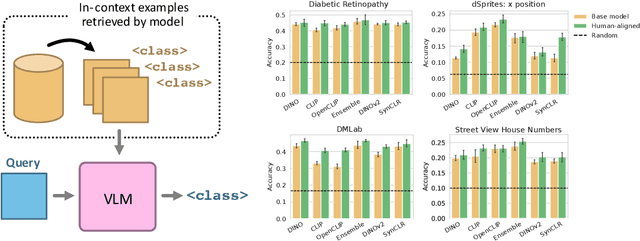
Abstract:Humans judge perceptual similarity according to diverse visual attributes, including scene layout, subject location, and camera pose. Existing vision models understand a wide range of semantic abstractions but improperly weigh these attributes and thus make inferences misaligned with human perception. While vision representations have previously benefited from alignment in contexts like image generation, the utility of perceptually aligned representations in more general-purpose settings remains unclear. Here, we investigate how aligning vision model representations to human perceptual judgments impacts their usability across diverse computer vision tasks. We finetune state-of-the-art models on human similarity judgments for image triplets and evaluate them across standard vision benchmarks. We find that aligning models to perceptual judgments yields representations that improve upon the original backbones across many downstream tasks, including counting, segmentation, depth estimation, instance retrieval, and retrieval-augmented generation. In addition, we find that performance is widely preserved on other tasks, including specialized out-of-distribution domains such as in medical imaging and 3D environment frames. Our results suggest that injecting an inductive bias about human perceptual knowledge into vision models can contribute to better representations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge