Neil Mehta
Time-varying EEG spectral power predicts evoked and spontaneous fMRI motor brain activity
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Simultaneous EEG-fMRI recordings are increasingly used to investigate brain activity by leveraging the complementary high spatial and high temporal resolution of fMRI and EEG signals respectively. It remains unclear, however, to what degree these two imaging modalities capture shared information about neural activity. Here, we investigate whether it is possible to predict both task-evoked and spontaneous fMRI signals of motor brain networks from EEG time-varying spectral power using interpretable models trained for individual subjects with Sparse Group Lasso regularization. Critically, we test the trained models on data acquired from each subject on a different day and obtain statistical validation by comparison with appropriate null models as well as the conventional EEG sensorimotor rhythm. We find significant prediction results in most subjects, although less frequently for resting-state compared to task-based conditions. Furthermore, we interpret the model learned parameters to understand representations of EEG-fMRI coupling in terms of predictive EEG channels, frequencies, and haemodynamic delays. In conclusion, our work provides evidence of the ability to predict fMRI motor brain activity from EEG recordings alone across different days, in both task-evoked and spontaneous conditions, with statistical significance in individual subjects. These results present great potential for translation to EEG neurofeedback applications.
CuRLA: Curriculum Learning Based Deep Reinforcement Learning for Autonomous Driving
Jan 09, 2025Abstract:In autonomous driving, traditional Computer Vision (CV) agents often struggle in unfamiliar situations due to biases in the training data. Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) agents address this by learning from experience and maximizing rewards, which helps them adapt to dynamic environments. However, ensuring their generalization remains challenging, especially with static training environments. Additionally, DRL models lack transparency, making it difficult to guarantee safety in all scenarios, particularly those not seen during training. To tackle these issues, we propose a method that combines DRL with Curriculum Learning for autonomous driving. Our approach uses a Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) agent and a Variational Autoencoder (VAE) to learn safe driving in the CARLA simulator. The agent is trained using two-fold curriculum learning, progressively increasing environment difficulty and incorporating a collision penalty in the reward function to promote safety. This method improves the agent's adaptability and reliability in complex environments, and understand the nuances of balancing multiple reward components from different feedback signals in a single scalar reward function. Keywords: Computer Vision, Deep Reinforcement Learning, Variational Autoencoder, Proximal Policy Optimization, Curriculum Learning, Autonomous Driving.
Can Information Flows Suggest Targets for Interventions in Neural Circuits?
Nov 09, 2021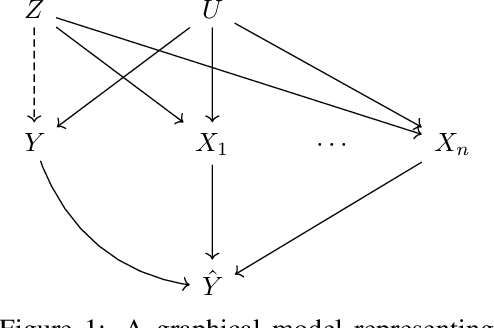
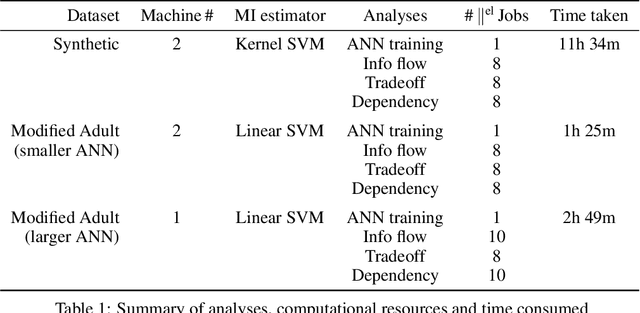
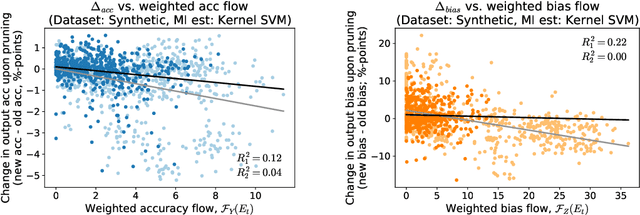

Abstract:Motivated by neuroscientific and clinical applications, we empirically examine whether observational measures of information flow can suggest interventions. We do so by performing experiments on artificial neural networks in the context of fairness in machine learning, where the goal is to induce fairness in the system through interventions. Using our recently developed $M$-information flow framework, we measure the flow of information about the true label (responsible for accuracy, and hence desirable), and separately, the flow of information about a protected attribute (responsible for bias, and hence undesirable) on the edges of a trained neural network. We then compare the flow magnitudes against the effect of intervening on those edges by pruning. We show that pruning edges that carry larger information flows about the protected attribute reduces bias at the output to a greater extent. This demonstrates that $M$-information flow can meaningfully suggest targets for interventions, answering the title's question in the affirmative. We also evaluate bias-accuracy tradeoffs for different intervention strategies, to analyze how one might use estimates of desirable and undesirable information flows (here, accuracy and bias flows) to inform interventions that preserve the former while reducing the latter.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge