Navid Hoseini Izadi
CNN AE: Convolution Neural Network combined with Autoencoder approach to detect survival chance of COVID 19 patients
Apr 18, 2021



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel method named CNN-AE to predict survival chance of COVID-19 patients using a CNN trained on clinical information. To further increase the prediction accuracy, we use the CNN in combination with an autoencoder. Our method is one of the first that aims to predict survival chance of already infected patients. We rely on clinical data to carry out the prediction. The motivation is that the required resources to prepare CT images are expensive and limited compared to the resources required to collect clinical data such as blood pressure, liver disease, etc. We evaluate our method on a publicly available clinical dataset of deceased and recovered patients which we have collected. Careful analysis of the dataset properties is also presented which consists of important features extraction and correlation computation between features. Since most of COVID-19 patients are usually recovered, the number of deceased samples of our dataset is low leading to data imbalance. To remedy this issue, a data augmentation procedure based on autoencoders is proposed. To demonstrate the generality of our augmentation method, we train random forest and Na\"ive Bayes on our dataset with and without augmentation and compare their performance. We also evaluate our method on another dataset for further generality verification. Experimental results reveal the superiority of CNN-AE method compared to the standard CNN as well as other methods such as random forest and Na\"ive Bayes. COVID-19 detection average accuracy of CNN-AE is 96.05% which is higher than CNN average accuracy of 92.49%. To show that clinical data can be used as a reliable dataset for COVID-19 survival chance prediction, CNN-AE is compared with a standard CNN which is trained on CT images.
Uncertainty-Aware Semi-supervised Method using Large Unlabelled and Limited Labeled COVID-19 Data
Feb 12, 2021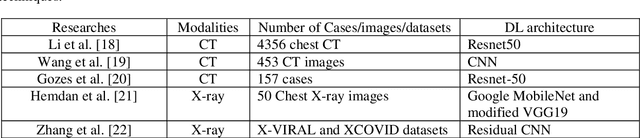
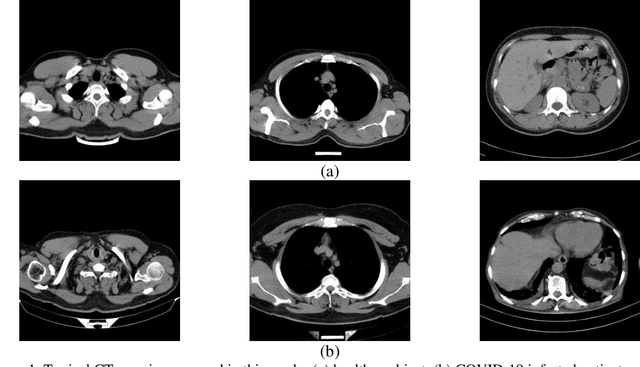
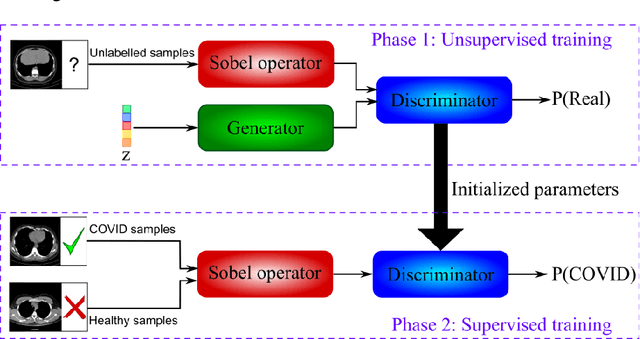
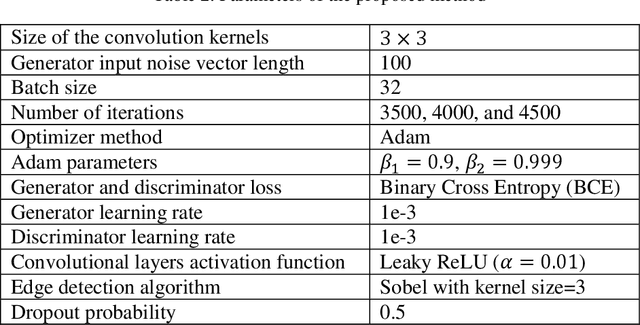
Abstract:The new coronavirus has caused more than 1 million deaths and continues to spread rapidly. This virus targets the lungs, causing respiratory distress which can be mild or severe. The X-ray or computed tomography (CT) images of lungs can reveal whether the patient is infected with COVID-19 or not. Many researchers are trying to improve COVID-19 detection using artificial intelligence. In this paper, relying on Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN), we propose a Semi-supervised Classification using Limited Labelled Data (SCLLD) for automated COVID-19 detection. Our motivation is to develop learning method which can cope with scenarios that preparing labelled data is time consuming or expensive. We further improved the detection accuracy of the proposed method by applying Sobel edge detection. The GAN discriminator output is a probability value which is used for classification in this work. The proposed system is trained using 10,000 CT scans collected from Omid hospital. Also, we validate our system using the public dataset. The proposed method is compared with other state of the art supervised methods such as Gaussian processes. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time a COVID-19 semi-supervised detection method is presented. Our method is capable of learning from a mixture of limited labelled and unlabelled data where supervised learners fail due to lack of sufficient amount of labelled data. Our semi-supervised training method significantly outperforms the supervised training of Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) in case labelled training data is scarce. Our method has achieved an accuracy of 99.60%, sensitivity of 99.39%, and specificity of 99.80% where CNN (trained supervised) has achieved an accuracy of 69.87%, sensitivity of 94%, and specificity of 46.40%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge