Nanjiang Jiang
Cross-TOP: Zero-Shot Cross-Schema Task-Oriented Parsing
Jun 10, 2022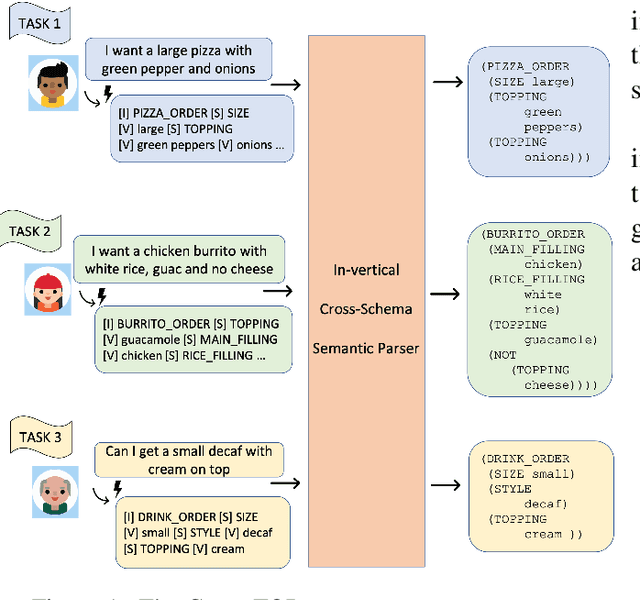


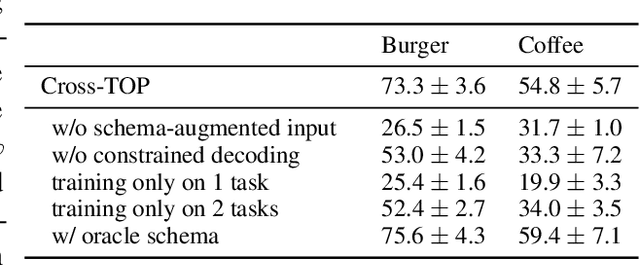
Abstract:Deep learning methods have enabled task-oriented semantic parsing of increasingly complex utterances. However, a single model is still typically trained and deployed for each task separately, requiring labeled training data for each, which makes it challenging to support new tasks, even within a single business vertical (e.g., food-ordering or travel booking). In this paper we describe Cross-TOP (Cross-Schema Task-Oriented Parsing), a zero-shot method for complex semantic parsing in a given vertical. By leveraging the fact that user requests from the same vertical share lexical and semantic similarities, a single cross-schema parser is trained to service an arbitrary number of tasks, seen or unseen, within a vertical. We show that Cross-TOP can achieve high accuracy on a previously unseen task without requiring any additional training data, thereby providing a scalable way to bootstrap semantic parsers for new tasks. As part of this work we release the FoodOrdering dataset, a task-oriented parsing dataset in the food-ordering vertical, with utterances and annotations derived from five schemas, each from a different restaurant menu.
Graph-Based Decoding for Task Oriented Semantic Parsing
Sep 09, 2021



Abstract:The dominant paradigm for semantic parsing in recent years is to formulate parsing as a sequence-to-sequence task, generating predictions with auto-regressive sequence decoders. In this work, we explore an alternative paradigm. We formulate semantic parsing as a dependency parsing task, applying graph-based decoding techniques developed for syntactic parsing. We compare various decoding techniques given the same pre-trained Transformer encoder on the TOP dataset, including settings where training data is limited or contains only partially-annotated examples. We find that our graph-based approach is competitive with sequence decoders on the standard setting, and offers significant improvements in data efficiency and settings where partially-annotated data is available.
He Thinks He Knows Better than the Doctors: BERT for Event Factuality Fails on Pragmatics
Jul 02, 2021
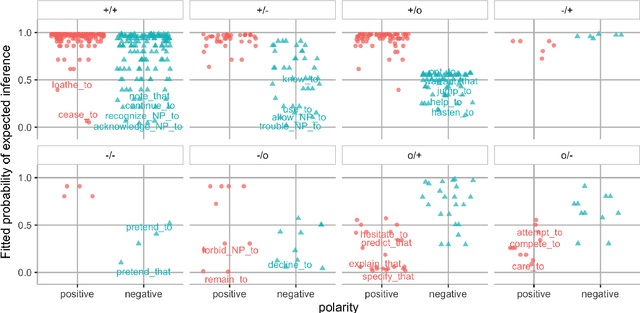
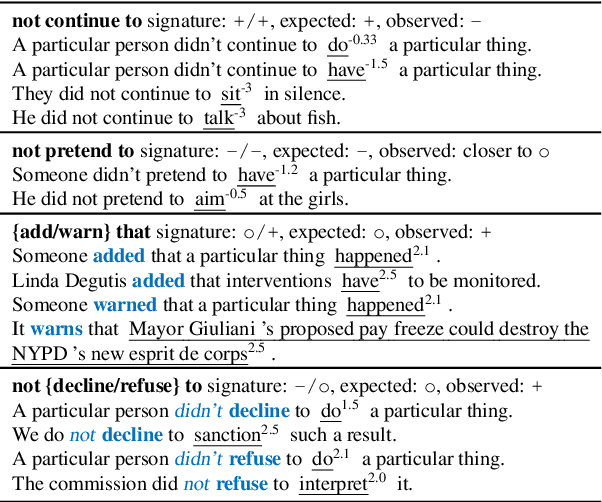
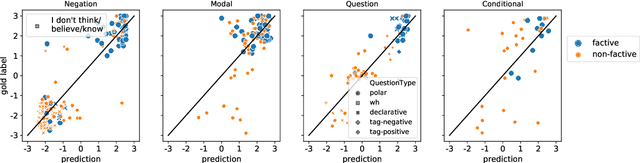
Abstract:We investigate how well BERT performs on predicting factuality in several existing English datasets, encompassing various linguistic constructions. Although BERT obtains a strong performance on most datasets, it does so by exploiting common surface patterns that correlate with certain factuality labels, and it fails on instances where pragmatic reasoning is necessary. Contrary to what the high performance suggests, we are still far from having a robust system for factuality prediction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge