Nanda Kishore Sreenivas
Multi-Modal Discussion Transformer: Integrating Text, Images and Graph Transformers to Detect Hate Speech on Social Media
Jul 18, 2023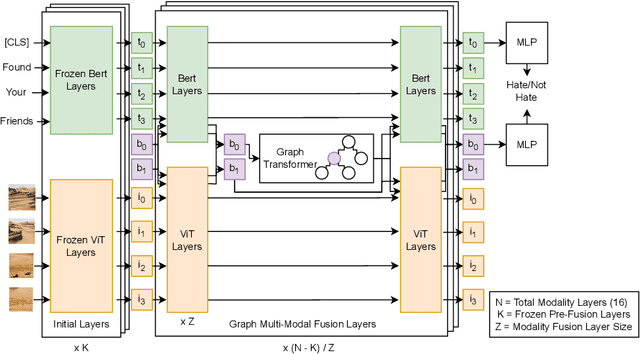

Abstract:We present the Multi-Modal Discussion Transformer (mDT), a novel multi-modal graph-based transformer model for detecting hate speech in online social networks. In contrast to traditional text-only methods, our approach to labelling a comment as hate speech centers around the holistic analysis of text and images. This is done by leveraging graph transformers to capture the contextual relationships in the entire discussion that surrounds a comment, with interwoven fusion layers to combine text and image embeddings instead of processing different modalities separately. We compare the performance of our model to baselines that only process text; we also conduct extensive ablation studies. We conclude with future work for multimodal solutions to deliver social value in online contexts, arguing that capturing a holistic view of a conversation greatly advances the effort to detect anti-social behavior.
Egocentric Bias and Doubt in Cognitive Agents
Mar 01, 2019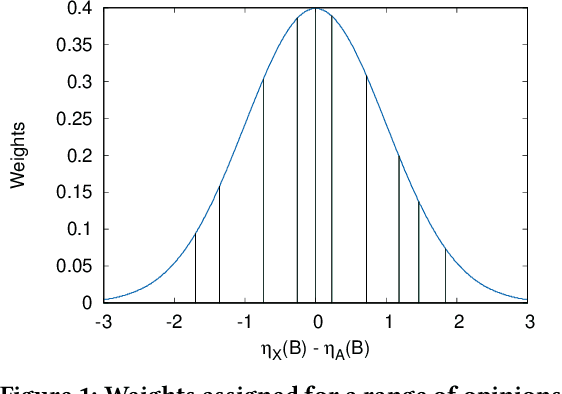
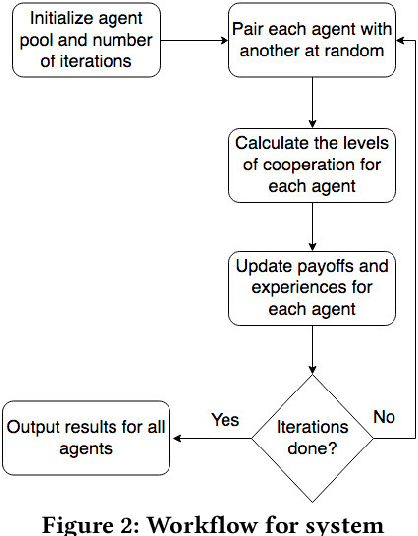
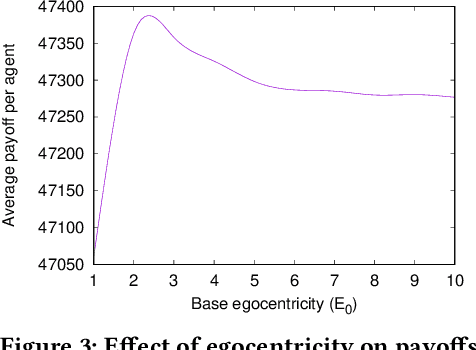
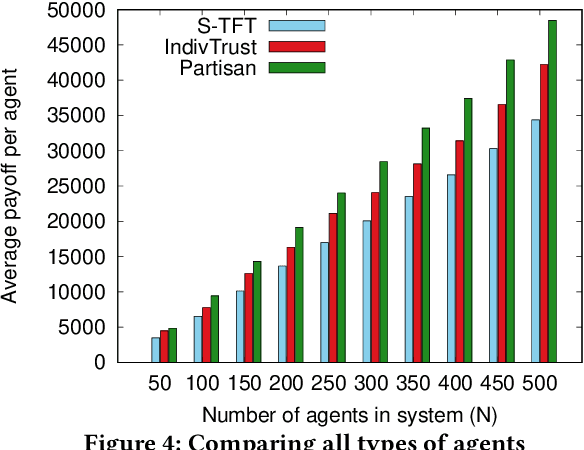
Abstract:Modeling social interactions based on individual behavior has always been an area of interest, but prior literature generally presumes rational behavior. Thus, such models may miss out on capturing the effects of biases humans are susceptible to. This work presents a method to model egocentric bias, the real-life tendency to emphasize one's own opinion heavily when presented with multiple opinions. We use a symmetric distribution centered at an agent's own opinion, as opposed to the Bounded Confidence (BC) model used in prior work. We consider a game of iterated interactions where an agent cooperates based on its opinion about an opponent. Our model also includes the concept of domain-based self-doubt, which varies as the interaction succeeds or not. An increase in doubt makes an agent reduce its egocentricity in subsequent interactions, thus enabling the agent to learn reactively. The agent system is modeled with factions not having a single leader, to overcome some of the issues associated with leader-follower factions. We find that agents belonging to factions perform better than individual agents. We observe that an intermediate level of egocentricity helps the agent perform at its best, which concurs with conventional wisdom that neither overconfidence nor low self-esteem brings benefits.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge