Nafisa Hussain
Multimodal Language Models for Domain-Specific Procedural Video Summarization
Jul 07, 2024



Abstract:Videos serve as a powerful medium to convey ideas, tell stories, and provide detailed instructions, especially through long-format tutorials. Such tutorials are valuable for learning new skills at one's own pace, yet they can be overwhelming due to their length and dense content. Viewers often seek specific information, like precise measurements or step-by-step execution details, making it essential to extract and summarize key segments efficiently. An intelligent, time-sensitive video assistant capable of summarizing and detecting highlights in long videos is highly sought after. Recent advancements in Multimodal Large Language Models offer promising solutions to develop such an assistant. Our research explores the use of multimodal models to enhance video summarization and step-by-step instruction generation within specific domains. These models need to understand temporal events and relationships among actions across video frames. Our approach focuses on fine-tuning TimeChat to improve its performance in specific domains: cooking and medical procedures. By training the model on domain-specific datasets like Tasty for cooking and MedVidQA for medical procedures, we aim to enhance its ability to generate concise, accurate summaries of instructional videos. We curate and restructure these datasets to create high-quality video-centric instruction data. Our findings indicate that when finetuned on domain-specific procedural data, TimeChat can significantly improve the extraction and summarization of key instructional steps in long-format videos. This research demonstrates the potential of specialized multimodal models to assist with practical tasks by providing personalized, step-by-step guidance tailored to the unique aspects of each domain.
Directed Domain Fine-Tuning: Tailoring Separate Modalities for Specific Training Tasks
Jun 24, 2024

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) and large visual language models (LVLMs) have been at the forefront of the artificial intelligence field, particularly for tasks like text generation, video captioning, and question-answering. Typically, it is more applicable to train these models on broader knowledge bases or datasets to increase generalizability, learn relationships between topics, and recognize patterns. Instead, we propose to provide instructional datasets specific to the task of each modality within a distinct domain and then fine-tune the parameters of the model using LORA. With our approach, we can eliminate all noise irrelevant to the given task while also ensuring that the model generates with enhanced precision. For this work, we use Video-LLaVA to generate recipes given cooking videos without transcripts. Video-LLaVA's multimodal architecture allows us to provide cooking images to its image encoder, cooking videos to its video encoder, and general cooking questions to its text encoder. Thus, we aim to remove all noise unrelated to cooking while improving our model's capabilities to generate specific ingredient lists and detailed instructions. As a result, our approach to fine-tuning Video-LLaVA leads to gains over the baseline Video-LLaVA by 2% on the YouCook2 dataset. While this may seem like a marginal increase, our model trains on an image instruction dataset 2.5% the size of Video-LLaVA's and a video instruction dataset 23.76% of Video-LLaVA's.
A Survey on Human-AI Teaming with Large Pre-Trained Models
Mar 07, 2024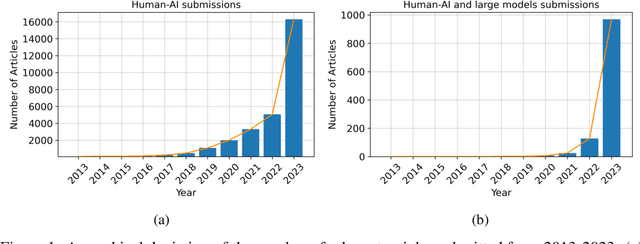
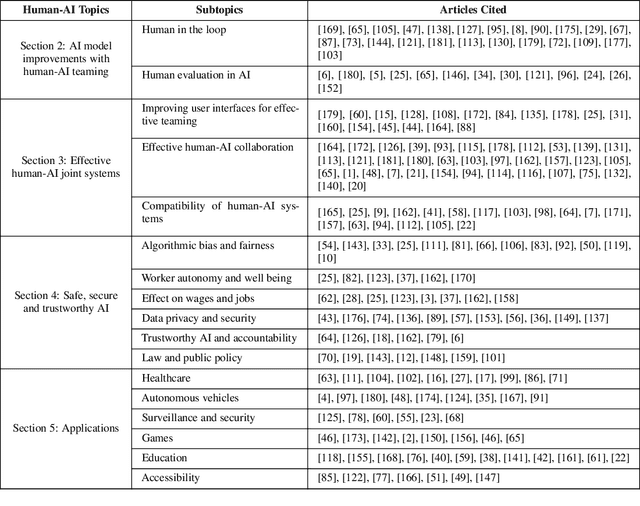
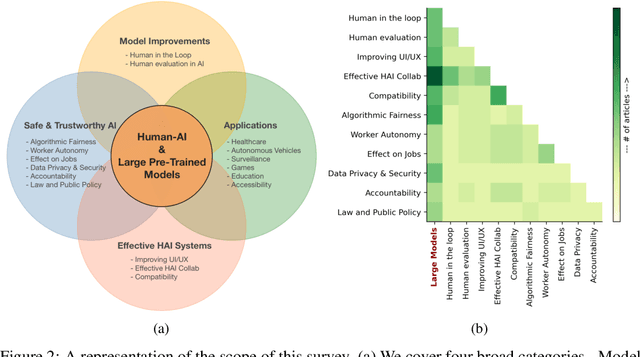
Abstract:In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence (AI), the collaboration between human intelligence and AI systems, known as Human-AI (HAI) Teaming, has emerged as a cornerstone for advancing problem-solving and decision-making processes. The advent of Large Pre-trained Models (LPtM) has significantly transformed this landscape, offering unprecedented capabilities by leveraging vast amounts of data to understand and predict complex patterns. This paper surveys the pivotal integration of LPtMs with HAI, emphasizing how these models enhance collaborative intelligence beyond traditional approaches. It examines the synergistic potential of LPtMs in augmenting human capabilities, discussing this collaboration for AI model improvements, effective teaming, ethical considerations, and their broad applied implications in various sectors. Through this exploration, the study sheds light on the transformative impact of LPtM-enhanced HAI Teaming, providing insights for future research, policy development, and strategic implementations aimed at harnessing the full potential of this collaboration for research and societal benefit.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge