Murat Bronz
Improving Incremental Nonlinear Dynamic Inversion Robustness Using Robust Control in Aerial Robotics
Jan 13, 2025Abstract:Improving robustness to uncertainty and rejection of external disturbances represents a significant challenge in aerial robotics. Nonlinear controllers based on Incremental Nonlinear Dynamic Inversion (INDI), known for their ability in estimating disturbances through measured-filtered data, have been notably used in such applications. Typically, these controllers comprise two cascaded loops: an inner loop employing nonlinear dynamic inversion and an outer loop generating the virtual control inputs via linear controllers. In this paper, a novel methodology is introduced, that combines the advantages of INDI with the robustness of linear structured $\mathcal{H}_\infty$ controllers. A full cascaded architecture is proposed to control the dynamics of a multirotor drone, covering both stabilization and guidance. In particular, low-order $\mathcal{H}_\infty$ controllers are designed for the outer loop by properly structuring the problem and solving it through non-smooth optimization. A comparative analysis is conducted between an existing INDI/PD approach and the proposed INDI/$\mathcal{H}_\infty$ strategy, showing a notable enhancement in the rejection of external disturbances. It is carried out first using MATLAB simulations involving a nonlinear model of a Parrot Bebop quadcopter drone, and then experimentally using a customized quadcopter built by the ENAC team. The results show an improvement of more than 50\% in the rejection of disturbances such as gusts.
Guiding vector fields in Paparazzi autopilot
Jun 20, 2021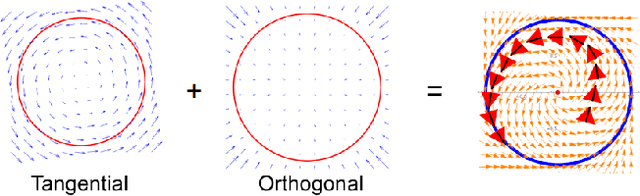

Abstract:This article is a technical report on the two different guidance systems based on vector fields that can be found in Paparazzi, a free sw/hw autopilot. Guiding vector fields allow autonomous vehicles to track paths described by the user mathematically. In particular, we allow two descriptions of the path with an implicit or a parametric function. Each description is associated with its corresponding guiding vector field algorithm. The implementations of the two algorithms are light enough to be run in a modern microcontroller. We will cover the basic theory on how they work, how a user can implement its own paths in Paparazzi, how to exploit them to coordinate multiple vehicles, and we finish with some experimental results. Although the presented implementation is focused on fixed-wing aircraft, the guidance is also applicable to other kinds of aerial vehicles such as rotorcraft.
Circular formation control of fixed-wing UAVs with constant speeds
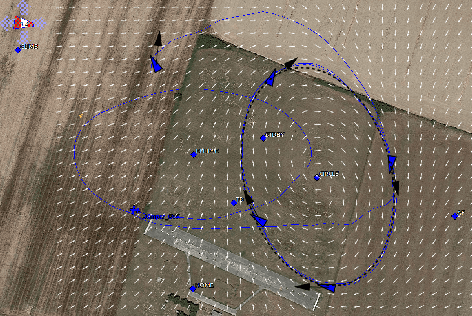
Mar 22, 2017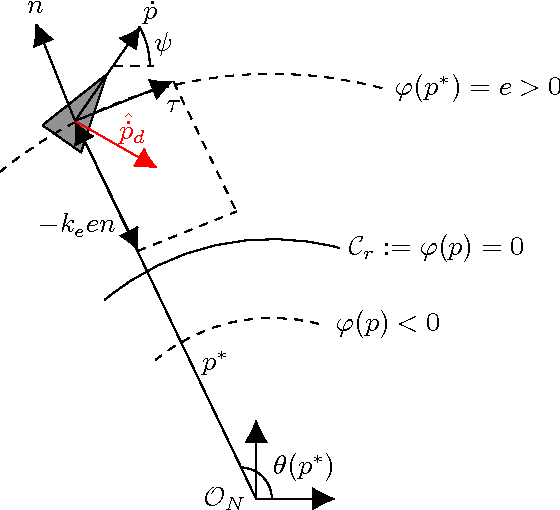

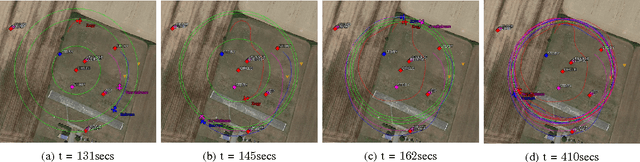
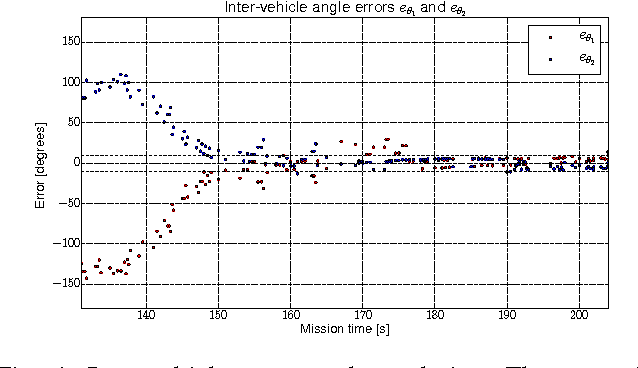
Abstract:In this paper we propose an algorithm for stabilizing circular formations of fixed-wing UAVs with constant speeds. The algorithm is based on the idea of tracking circles with different radii in order to control the inter-vehicle phases with respect to a target circumference. We prove that the desired equilibrium is exponentially stable and thanks to the guidance vector field that guides the vehicles, the algorithm can be extended to other closed trajectories. One of the main advantages of this approach is that the algorithm guarantees the confinement of the team in a specific area, even when communications or sensing among vehicles are lost. We show the effectiveness of the algorithm with an actual formation flight of three aircraft. The algorithm is ready to use for the general public in the open-source Paparazzi autopilot.
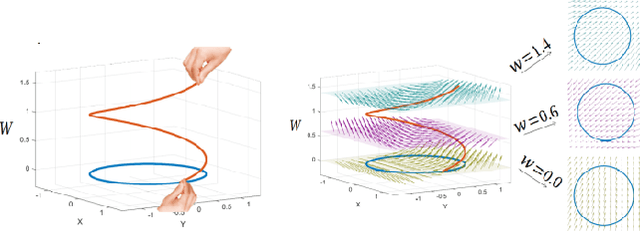
Guidance algorithm for smooth trajectory tracking of a fixed wing UAV flying in wind flows
Feb 15, 2017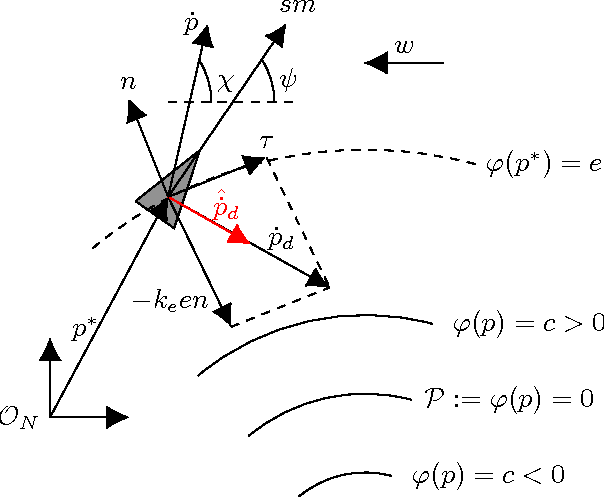
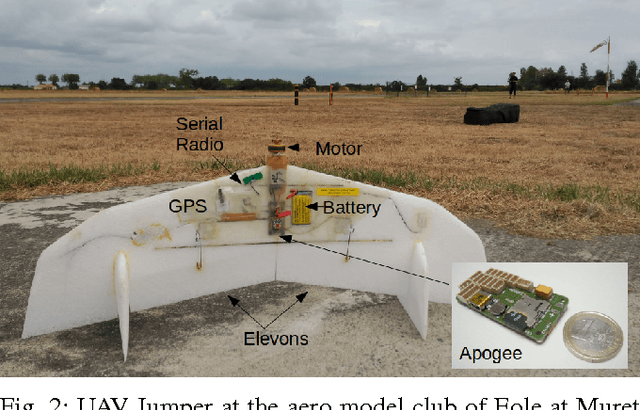
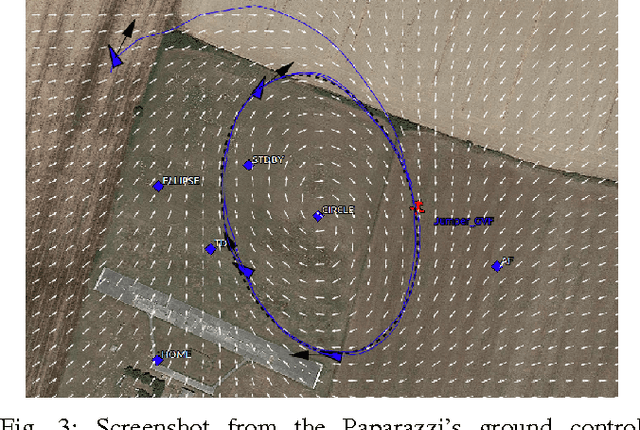
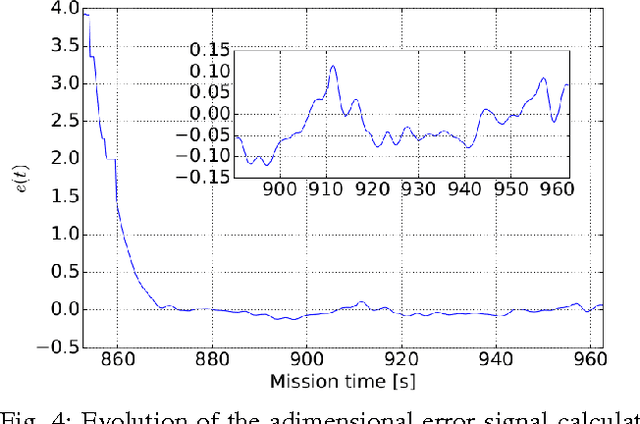
Abstract:This paper presents an algorithm for solving the problem of tracking smooth curves by a fixed wing unmanned aerial vehicle travelling with a constant airspeed and under a constant wind disturbance. The algorithm is based on the idea of following a guiding vector field which is constructed from the implicit function that describes the desired (possibly time-varying) trajectory. The output of the algorithm can be directly expressed in terms of the bank angle of the UAV in order to achieve coordinated turns. Furthermore, the algorithm can be tuned offline such that physical constraints of the UAV, e.g. the maximum bank angle, will not be violated in a neighborhood of the desired trajectory. We provide the corresponding theoretical convergence analysis and performance results from actual flights.
* 6 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge