Muhammad Islam
Evaluation of Preprocessing Techniques for U-Net Based Automated Liver Segmentation
Mar 26, 2021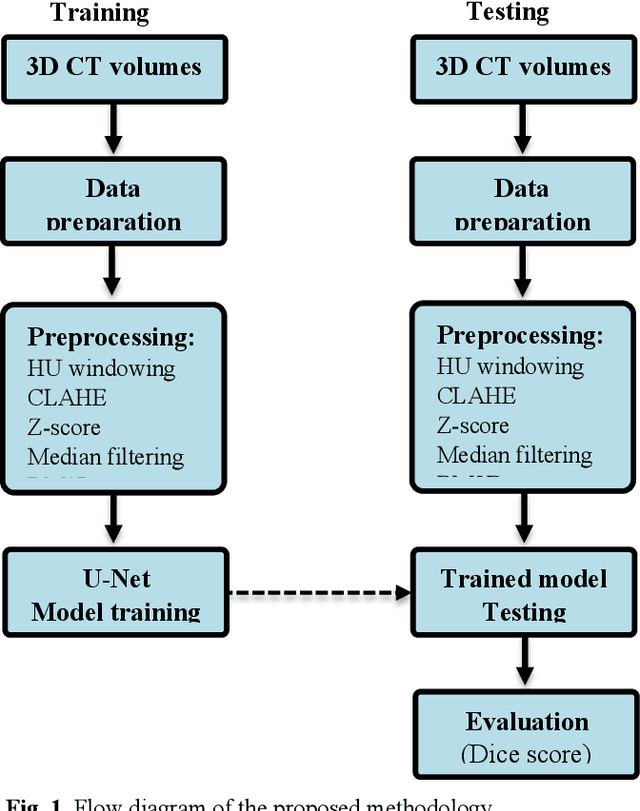
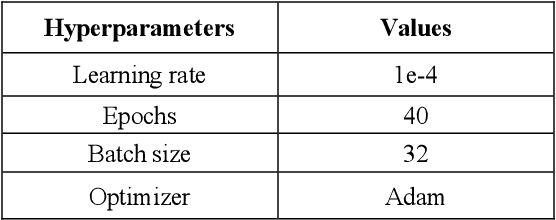
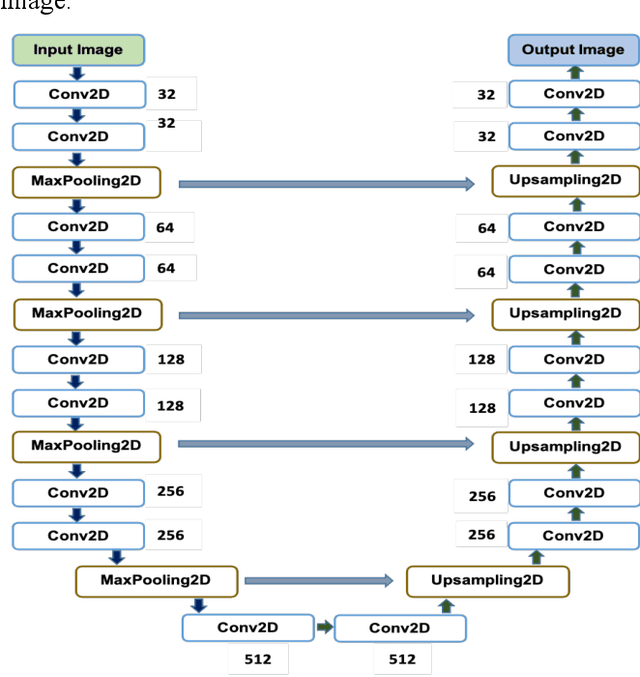
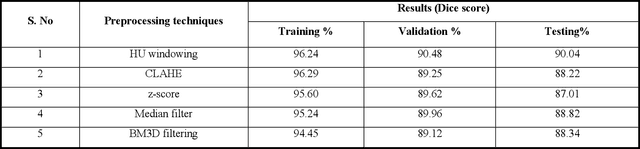
Abstract:To extract liver from medical images is a challenging task due to similar intensity values of liver with adjacent organs, various contrast levels, various noise associated with medical images and irregular shape of liver. To address these issues, it is important to preprocess the medical images, i.e., computerized tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data prior to liver analysis and quantification. This paper investigates the impact of permutation of various preprocessing techniques for CT images, on the automated liver segmentation using deep learning, i.e., U-Net architecture. The study focuses on Hounsfield Unit (HU) windowing, contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE), z-score normalization, median filtering and Block-Matching and 3D (BM3D) filtering. The segmented results show that combination of three techniques; HU-windowing, median filtering and z-score normalization achieve optimal performance with Dice coefficient of 96.93%, 90.77% and 90.84% for training, validation and testing respectively.
Fuzzy Integral = Contextual Linear Order Statistic
Jul 06, 2020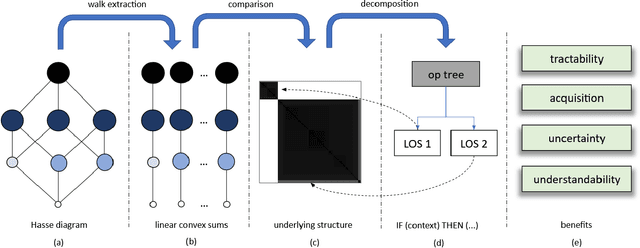
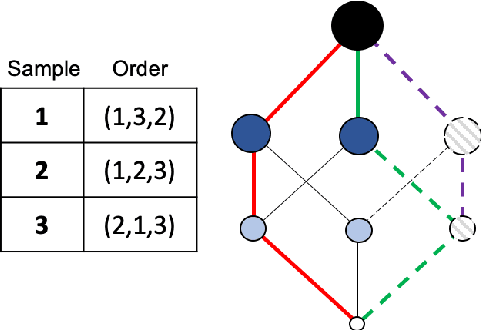
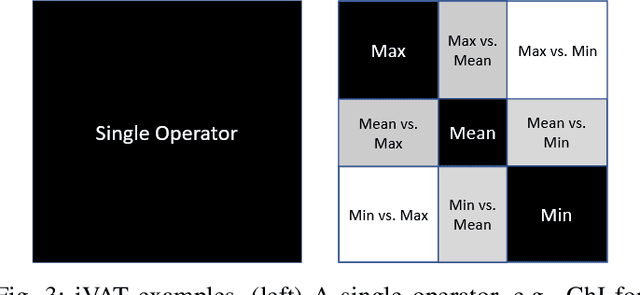
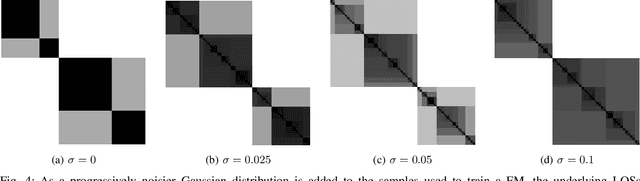
Abstract:The fuzzy integral is a powerful parametric nonlin-ear function with utility in a wide range of applications, from information fusion to classification, regression, decision making,interpolation, metrics, morphology, and beyond. While the fuzzy integral is in general a nonlinear operator, herein we show that it can be represented by a set of contextual linear order statistics(LOS). These operators can be obtained via sampling the fuzzy measure and clustering is used to produce a partitioning of the underlying space of linear convex sums. Benefits of our approach include scalability, improved integral/measure acquisition, generalizability, and explainable/interpretable models. Our methods are both demonstrated on controlled synthetic experiments, and also analyzed and validated with real-world benchmark data sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge