Mouloud Kharoune
DRUID
The Advantage of Evidential Attributes in Social Networks
Sep 05, 2017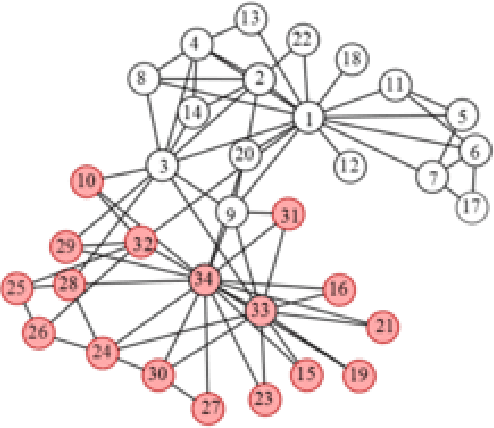
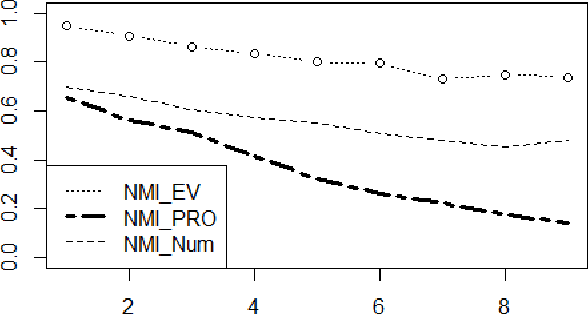
Abstract:Nowadays, there are many approaches designed for the task of detecting communities in social networks. Among them, some methods only consider the topological graph structure, while others take use of both the graph structure and the node attributes. In real-world networks, there are many uncertain and noisy attributes in the graph. In this paper, we will present how we detect communities in graphs with uncertain attributes in the first step. The numerical, probabilistic as well as evidential attributes are generated according to the graph structure. In the second step, some noise will be added to the attributes. We perform experiments on graphs with different types of attributes and compare the detection results in terms of the Normalized Mutual Information (NMI) values. The experimental results show that the clustering with evidential attributes gives better results comparing to those with probabilistic and numerical attributes. This illustrates the advantages of evidential attributes.
* 20th International Conference on Information Fusion, Jul 2017, Xi'an, China
Une mesure d'expertise pour le crowdsourcing
Jan 17, 2017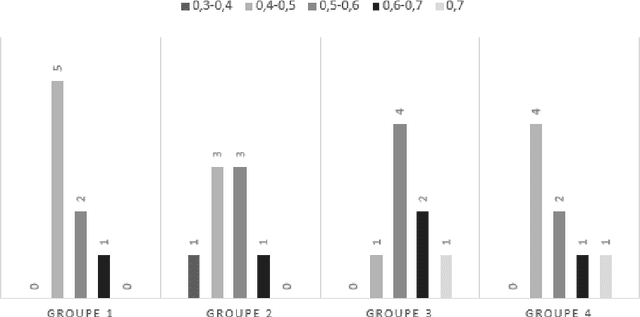
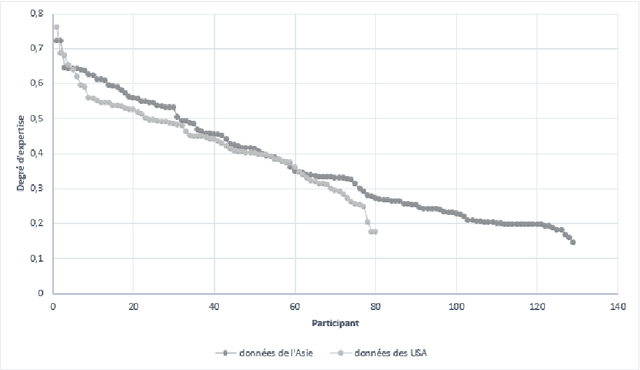
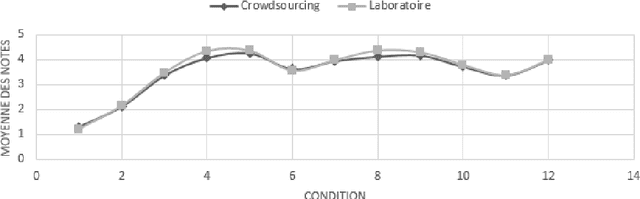
Abstract:Crowdsourcing, a major economic issue, is the fact that the firm outsources internal task to the crowd. It is a form of digital subcontracting for the general public. The evaluation of the participants work quality is a major issue in crowdsourcing. Indeed, contributions must be controlled to ensure the effectiveness and relevance of the campaign. We are particularly interested in small, fast and not automatable tasks. Several methods have been proposed to solve this problem, but they are applicable when the "golden truth" is not always known. This work has the particularity to propose a method for calculating the degree of expertise in the presence of gold data in crowdsourcing. This method is based on the belief function theory and proposes a structuring of data using graphs. The proposed approach will be assessed and applied to the data.
* in French
Characterization of experts in crowdsourcing platforms
Sep 30, 2016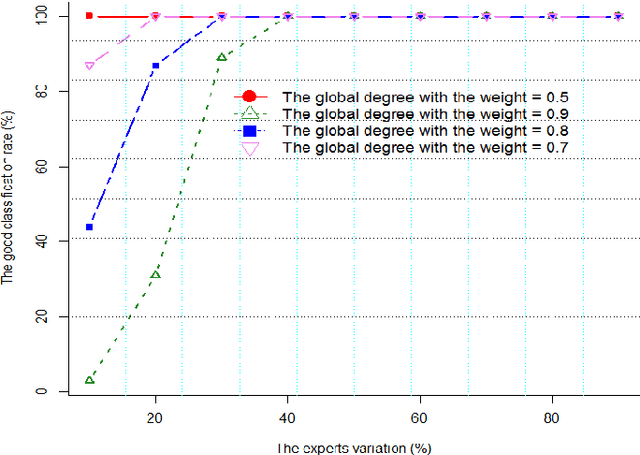
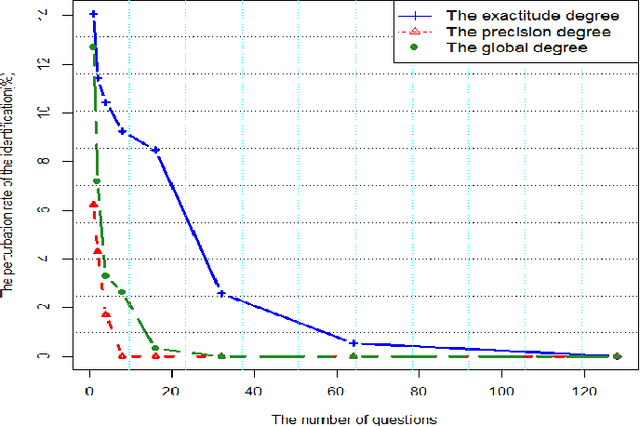
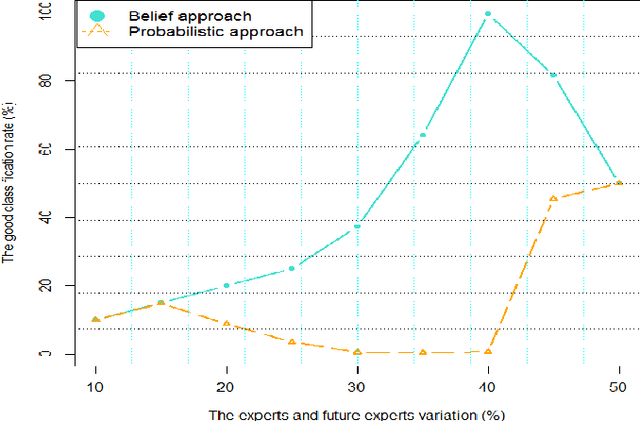
Abstract:Crowdsourcing platforms enable to propose simple human intelligence tasks to a large number of participants who realise these tasks. The workers often receive a small amount of money or the platforms include some other incentive mechanisms, for example they can increase the workers reputation score, if they complete the tasks correctly. We address the problem of identifying experts among participants, that is, workers, who tend to answer the questions correctly. Knowing who are the reliable workers could improve the quality of knowledge one can extract from responses. As opposed to other works in the literature, we assume that participants can give partial or incomplete responses, in case they are not sure that their answers are correct. We model such partial or incomplete responses with the help of belief functions, and we derive a measure that characterizes the expertise level of each participant. This measure is based on precise and exactitude degrees that represent two parts of the expertise level. The precision degree reflects the reliability level of the participants and the exactitude degree reflects the knowledge level of the participants. We also analyze our model through simulation and demonstrate that our richer model can lead to more reliable identification of experts.
Int{é}gration d'une mesure d'ind{é}pendance pour la fusion d'informations
Jan 22, 2015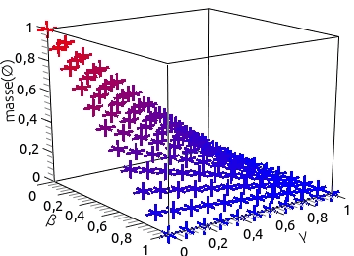
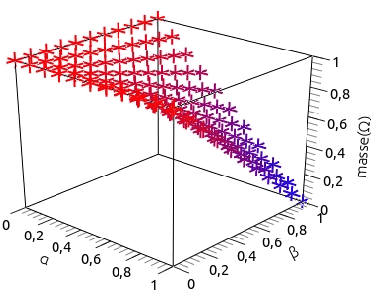
Abstract:Many information sources are considered into data fusion in order to improve the decision in terms of uncertainty and imprecision. For each technique used for data fusion, the asumption on independance is usually made. We propose in this article an approach to take into acount an independance measure befor to make the combination of information in the context of the theory of belief functions.
Belief Approach for Social Networks
Jan 20, 2015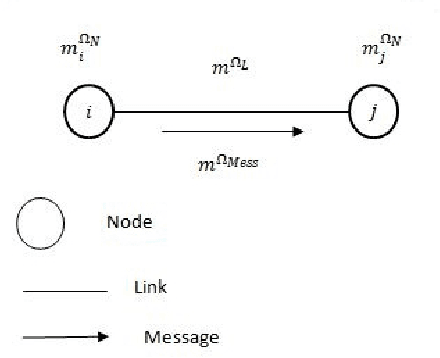
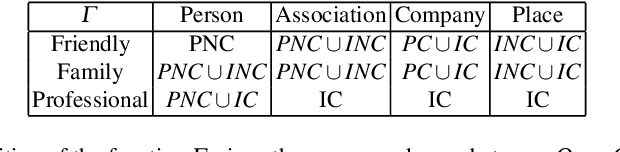

Abstract:Nowadays, social networks became essential in information exchange between individuals. Indeed, as users of these networks, we can send messages to other people according to the links connecting us. Moreover, given the large volume of exchanged messages, detecting the true nature of the received message becomes a challenge. For this purpose, it is interesting to consider this new tendency with reasoning under uncertainty by using the theory of belief functions. In this paper, we tried to model a social network as being a network of fusion of information and determine the true nature of the received message in a well-defined node by proposing a new model: the belief social network.
Consid{é}rant la d{é}pendance dans la th{é}orie des fonctions de croyance
Jan 20, 2015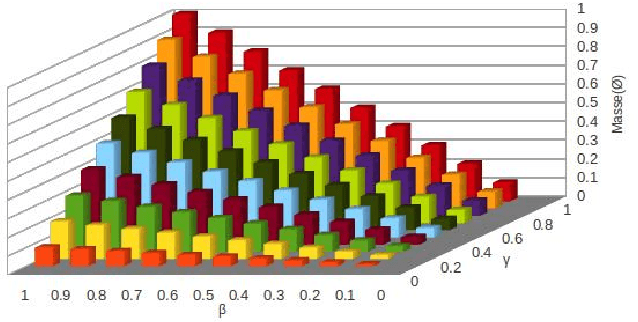
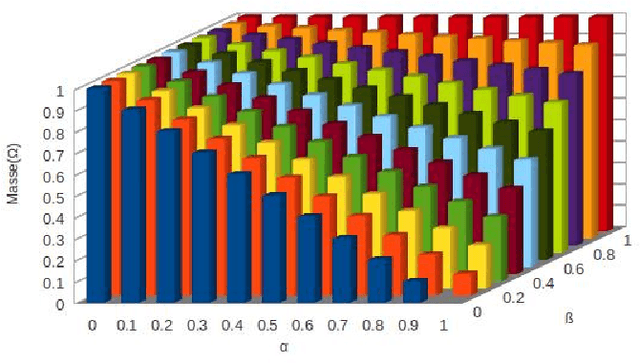
Abstract:In this paper, we propose to learn sources independence in order to choose the appropriate type of combination rules when aggregating their beliefs. Some combination rules are used with the assumption of their sources independence whereas others combine beliefs of dependent sources. Therefore, the choice of the combination rule depends on the independence of sources involved in the combination. In this paper, we propose also a measure of independence, positive and negative dependence to integrate in mass functions before the combinaision with the independence assumption.
* in French
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge