Salma Ben Dhaou
LARODEC, DRUID
The Advantage of Evidential Attributes in Social Networks
Sep 05, 2017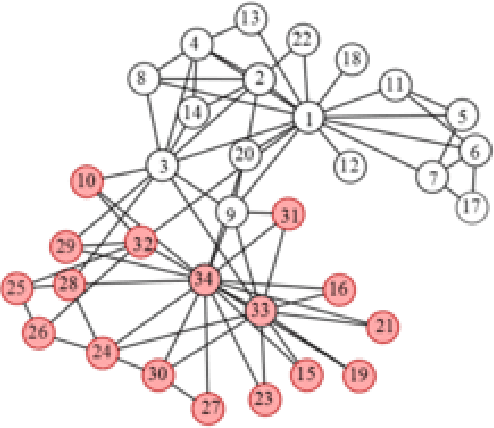
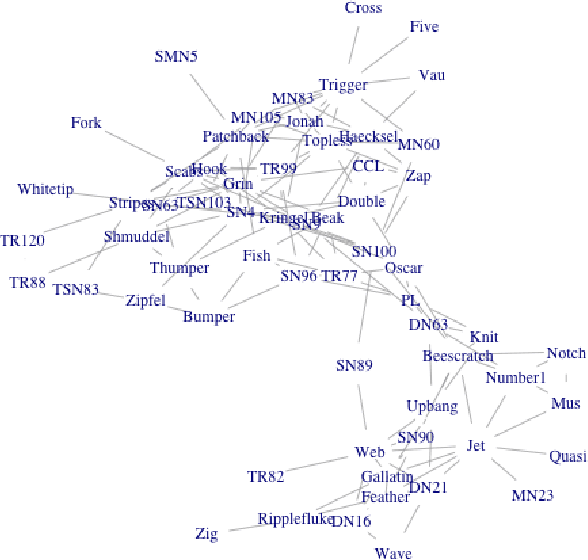
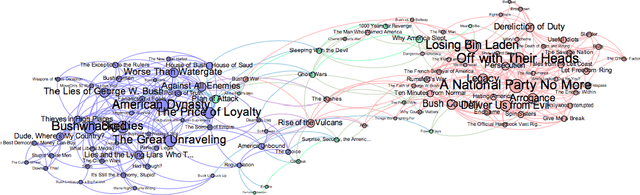
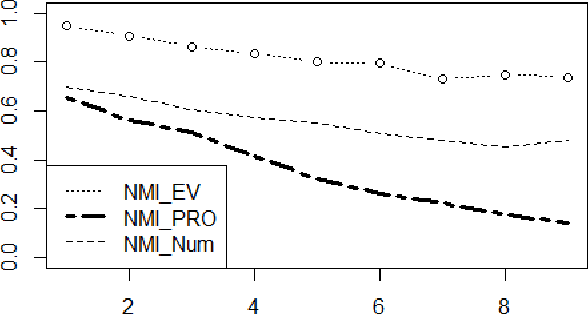
Abstract:Nowadays, there are many approaches designed for the task of detecting communities in social networks. Among them, some methods only consider the topological graph structure, while others take use of both the graph structure and the node attributes. In real-world networks, there are many uncertain and noisy attributes in the graph. In this paper, we will present how we detect communities in graphs with uncertain attributes in the first step. The numerical, probabilistic as well as evidential attributes are generated according to the graph structure. In the second step, some noise will be added to the attributes. We perform experiments on graphs with different types of attributes and compare the detection results in terms of the Normalized Mutual Information (NMI) values. The experimental results show that the clustering with evidential attributes gives better results comparing to those with probabilistic and numerical attributes. This illustrates the advantages of evidential attributes.
* 20th International Conference on Information Fusion, Jul 2017, Xi'an, China
Belief Approach for Social Networks
Jan 20, 2015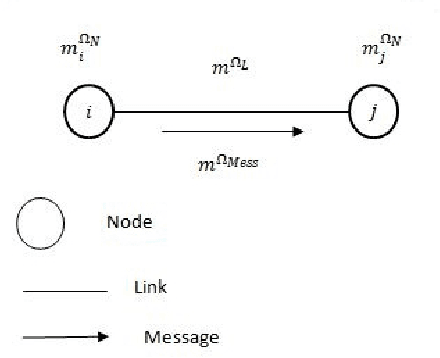

Abstract:Nowadays, social networks became essential in information exchange between individuals. Indeed, as users of these networks, we can send messages to other people according to the links connecting us. Moreover, given the large volume of exchanged messages, detecting the true nature of the received message becomes a challenge. For this purpose, it is interesting to consider this new tendency with reasoning under uncertainty by using the theory of belief functions. In this paper, we tried to model a social network as being a network of fusion of information and determine the true nature of the received message in a well-defined node by proposing a new model: the belief social network.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge