Mohit Kumar Ahuja
Testing Deep Learning Models: A First Comparative Study of Multiple Testing Techniques
Feb 24, 2022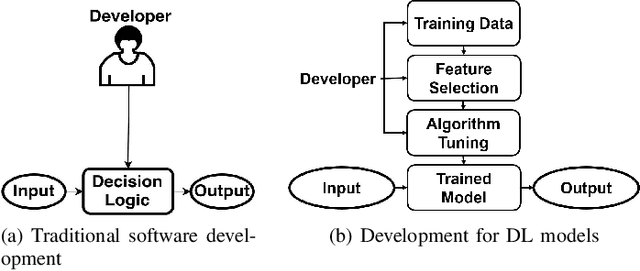

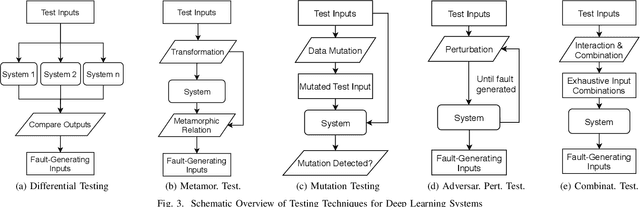
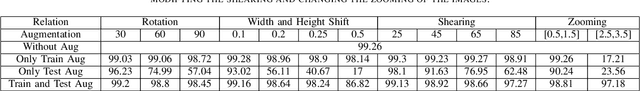
Abstract:Deep Learning (DL) has revolutionized the capabilities of vision-based systems (VBS) in critical applications such as autonomous driving, robotic surgery, critical infrastructure surveillance, air and maritime traffic control, etc. By analyzing images, voice, videos, or any type of complex signals, DL has considerably increased the situation awareness of these systems. At the same time, while relying more and more on trained DL models, the reliability and robustness of VBS have been challenged and it has become crucial to test thoroughly these models to assess their capabilities and potential errors. To discover faults in DL models, existing software testing methods have been adapted and refined accordingly. In this article, we provide an overview of these software testing methods, namely differential, metamorphic, mutation, and combinatorial testing, as well as adversarial perturbation testing and review some challenges in their deployment for boosting perception systems used in VBS. We also provide a first experimental comparative study on a classical benchmark used in VBS and discuss its results.
Opening the Software Engineering Toolbox for the Assessment of Trustworthy AI
Jul 14, 2020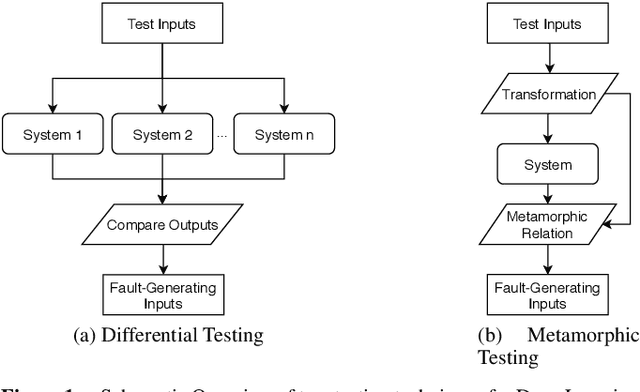
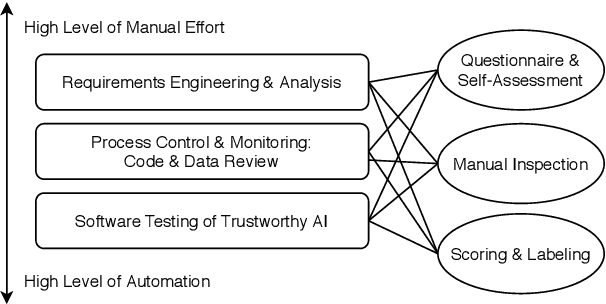
Abstract:Trustworthiness is a central requirement for the acceptance and success of human-centered artificial intelligence (AI). To deem an AI system as trustworthy, it is crucial to assess its behaviour and characteristics against a gold standard of Trustworthy AI, consisting of guidelines, requirements, or only expectations. While AI systems are highly complex, their implementations are still based on software. The software engineering community has a long-established toolbox for the assessment of software systems, especially in the context of software testing. In this paper, we argue for the application of software engineering and testing practices for the assessment of trustworthy AI. We make the connection between the seven key requirements as defined by the European Commission's AI high-level expert group and established procedures from software engineering and raise questions for future work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge