Mohammad T. Manzuri
A Bayesian Approach to the Data Description Problem
Feb 24, 2016



Abstract:In this paper, we address the problem of data description using a Bayesian framework. The goal of data description is to draw a boundary around objects of a certain class of interest to discriminate that class from the rest of the feature space. Data description is also known as one-class learning and has a wide range of applications. The proposed approach uses a Bayesian framework to precisely compute the class boundary and therefore can utilize domain information in form of prior knowledge in the framework. It can also operate in the kernel space and therefore recognize arbitrary boundary shapes. Moreover, the proposed method can utilize unlabeled data in order to improve accuracy of discrimination. We evaluate our method using various real-world datasets and compare it with other state of the art approaches of data description. Experiments show promising results and improved performance over other data description and one-class learning algorithms.
Active Learning from Positive and Unlabeled Data
Feb 24, 2016

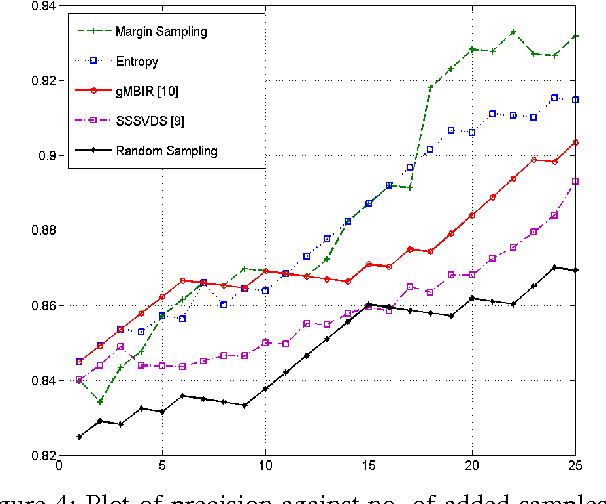

Abstract:During recent years, active learning has evolved into a popular paradigm for utilizing user's feedback to improve accuracy of learning algorithms. Active learning works by selecting the most informative sample among unlabeled data and querying the label of that point from user. Many different methods such as uncertainty sampling and minimum risk sampling have been utilized to select the most informative sample in active learning. Although many active learning algorithms have been proposed so far, most of them work with binary or multi-class classification problems and therefore can not be applied to problems in which only samples from one class as well as a set of unlabeled data are available. Such problems arise in many real-world situations and are known as the problem of learning from positive and unlabeled data. In this paper we propose an active learning algorithm that can work when only samples of one class as well as a set of unlabelled data are available. Our method works by separately estimating probability desnity of positive and unlabeled points and then computing expected value of informativeness to get rid of a hyper-parameter and have a better measure of informativeness./ Experiments and empirical analysis show promising results compared to other similar methods.
Facial Expression Representation and Recognition Using 2DHLDA, Gabor Wavelets, and Ensemble Learning
Jul 20, 2012Abstract:In this paper, a novel method for representation and recognition of the facial expressions in two-dimensional image sequences is presented. We apply a variation of two-dimensional heteroscedastic linear discriminant analysis (2DHLDA) algorithm, as an efficient dimensionality reduction technique, to Gabor representation of the input sequence. 2DHLDA is an extension of the two-dimensional linear discriminant analysis (2DLDA) approach and it removes the equal within-class covariance. By applying 2DHLDA in two directions, we eliminate the correlations between both image columns and image rows. Then, we perform a one-dimensional LDA on the new features. This combined method can alleviate the small sample size problem and instability encountered by HLDA. Also, employing both geometric and appearance features and using an ensemble learning scheme based on data fusion, we create a classifier which can efficiently classify the facial expressions. The proposed method is robust to illumination changes and it can properly represent temporal information as well as subtle changes in facial muscles. We provide experiments on Cohn-Kanade database that show the superiority of the proposed method. KEYWORDS: two-dimensional heteroscedastic linear discriminant analysis (2DHLDA), subspace learning, facial expression analysis, Gabor wavelets, ensemble learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge