Mohammad Mahdavi
Regret Analysis of Repeated Delegated Choice
Oct 10, 2023Abstract:We present a study on a repeated delegated choice problem, which is the first to consider an online learning variant of Kleinberg and Kleinberg, EC'18. In this model, a principal interacts repeatedly with an agent who possesses an exogenous set of solutions to search for efficient ones. Each solution can yield varying utility for both the principal and the agent, and the agent may propose a solution to maximize its own utility in a selfish manner. To mitigate this behavior, the principal announces an eligible set which screens out a certain set of solutions. The principal, however, does not have any information on the distribution of solutions in advance. Therefore, the principal dynamically announces various eligible sets to efficiently learn the distribution. The principal's objective is to minimize cumulative regret compared to the optimal eligible set in hindsight. We explore two dimensions of the problem setup, whether the agent behaves myopically or strategizes across the rounds, and whether the solutions yield deterministic or stochastic utility. Our analysis mainly characterizes some regimes under which the principal can recover the sublinear regret, thereby shedding light on the rise and fall of the repeated delegation procedure in various regimes.
ED2: Two-stage Active Learning for Error Detection -- Technical Report
Aug 17, 2019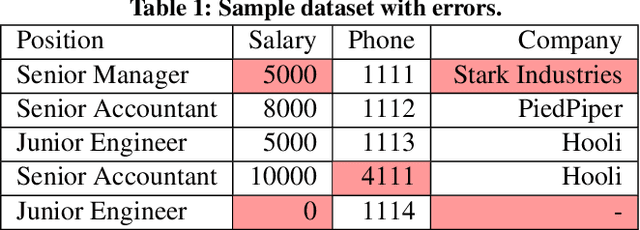
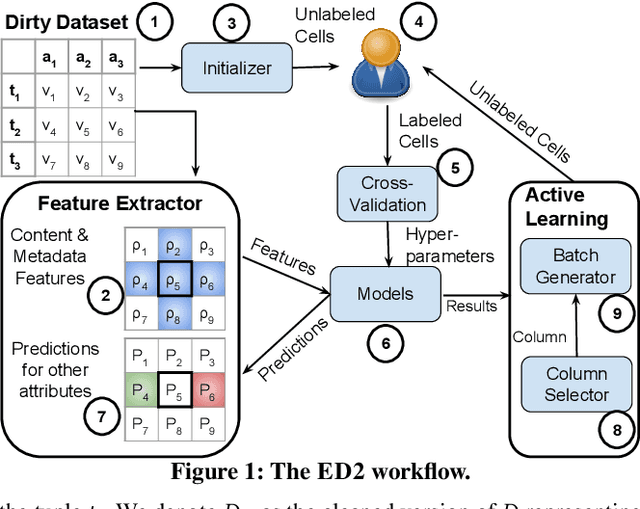
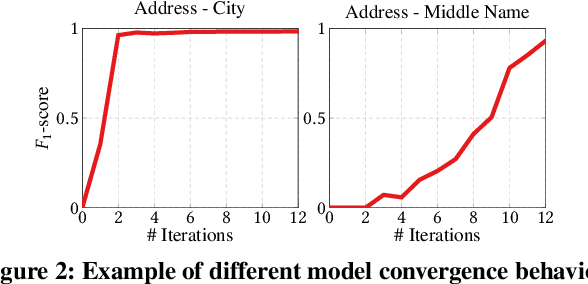
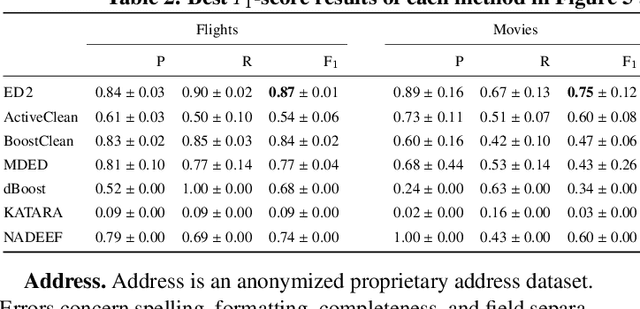
Abstract:Traditional error detection approaches require user-defined parameters and rules. Thus, the user has to know both the error detection system and the data. However, we can also formulate error detection as a semi-supervised classification problem that only requires domain expertise. The challenges for such an approach are twofold: (1) to represent the data in a way that enables a classification model to identify various kinds of data errors, and (2) to pick the most promising data values for learning. In this paper, we address these challenges with ED2, our new example-driven error detection method. First, we present a new two-dimensional multi-classifier sampling strategy for active learning. Second, we propose novel multi-column features. The combined application of these techniques provides fast convergence of the classification task with high detection accuracy. On several real-world datasets, ED2 requires, on average, less than 1% labels to outperform existing error detection approaches. This report extends the peer-reviewed paper "ED2: A Case for Active Learning in Error Detection". All source code related to this project is available on GitHub.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge