Felix Neutatz
AutoML in Heavily Constrained Applications
Jun 29, 2023Abstract:Optimizing a machine learning pipeline for a task at hand requires careful configuration of various hyperparameters, typically supported by an AutoML system that optimizes the hyperparameters for the given training dataset. Yet, depending on the AutoML system's own second-order meta-configuration, the performance of the AutoML process can vary significantly. Current AutoML systems cannot automatically adapt their own configuration to a specific use case. Further, they cannot compile user-defined application constraints on the effectiveness and efficiency of the pipeline and its generation. In this paper, we propose Caml, which uses meta-learning to automatically adapt its own AutoML parameters, such as the search strategy, the validation strategy, and the search space, for a task at hand. The dynamic AutoML strategy of Caml takes user-defined constraints into account and obtains constraint-satisfying pipelines with high predictive performance.
ED2: Two-stage Active Learning for Error Detection -- Technical Report
Aug 17, 2019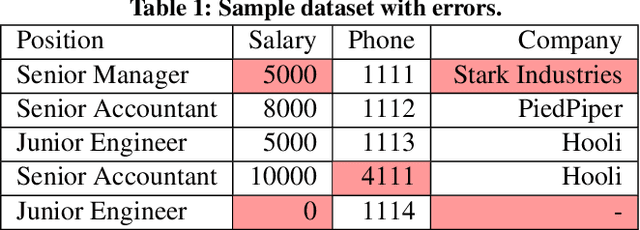
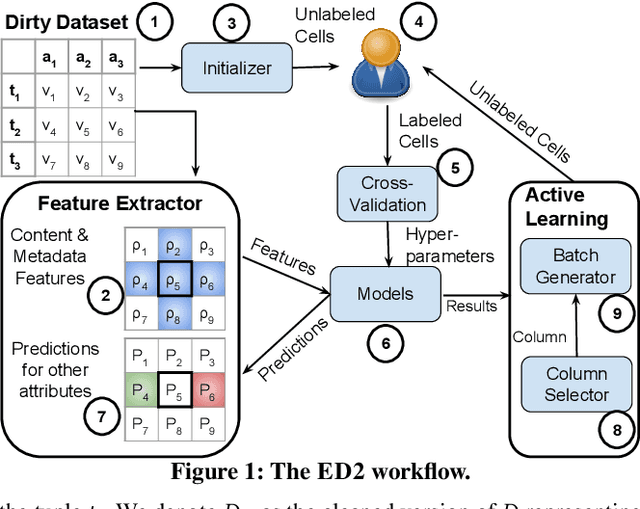
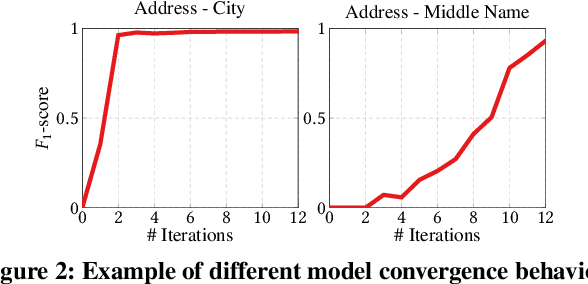
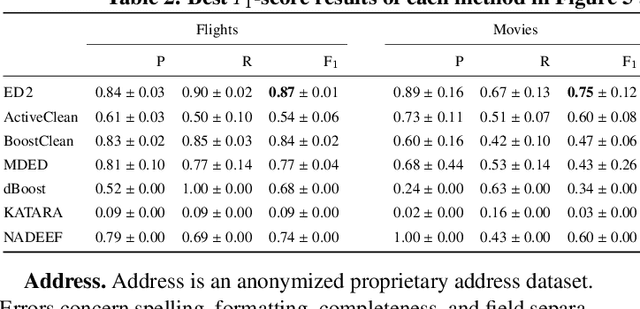
Abstract:Traditional error detection approaches require user-defined parameters and rules. Thus, the user has to know both the error detection system and the data. However, we can also formulate error detection as a semi-supervised classification problem that only requires domain expertise. The challenges for such an approach are twofold: (1) to represent the data in a way that enables a classification model to identify various kinds of data errors, and (2) to pick the most promising data values for learning. In this paper, we address these challenges with ED2, our new example-driven error detection method. First, we present a new two-dimensional multi-classifier sampling strategy for active learning. Second, we propose novel multi-column features. The combined application of these techniques provides fast convergence of the classification task with high detection accuracy. On several real-world datasets, ED2 requires, on average, less than 1% labels to outperform existing error detection approaches. This report extends the peer-reviewed paper "ED2: A Case for Active Learning in Error Detection". All source code related to this project is available on GitHub.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge