Mohammad Farhad Bulbul
Urdu text in natural scene images: a new dataset and preliminary text detection
Sep 16, 2021



Abstract:Text detection in natural scene images for content analysis is an interesting task. The research community has seen some great developments for English/Mandarin text detection. However, Urdu text extraction in natural scene images is a task not well addressed. In this work, firstly, a new dataset is introduced for Urdu text in natural scene images. The dataset comprises of 500 standalone images acquired from real scenes. Secondly, the channel enhanced Maximally Stable Extremal Region (MSER) method is applied to extract Urdu text regions as candidates in an image. Two-stage filtering mechanism is applied to eliminate non-candidate regions. In the first stage, text and noise are classified based on their geometric properties. In the second stage, a support vector machine classifier is trained to discard non-text candidate regions. After this, text candidate regions are linked using centroid-based vertical and horizontal distances. Text lines are further analyzed by a different classifier based on HOG features to remove non-text regions. Extensive experimentation is performed on the locally developed dataset to evaluate the performance. The experimental results show good performance on test set images. The dataset will be made available for research use. To the best of our knowledge, the work is the first of its kind for the Urdu language and would provide a good dataset for free research use and serve as a baseline performance on the task of Urdu text extraction.
Seizure Prediction Using Bidirectional LSTM
Dec 13, 2019



Abstract:Approximately, 50 million people in the world are affected by epilepsy. For patients, the anti-epileptic drugs are not always useful and these drugs may have undesired side effects on a patient's health. If the seizure is predicted the patients will have enough time to take preventive measures. The purpose of this work is to investigate the application of bidirectional LSTM for seizure prediction. In this paper, we trained EEG data from canines on a double Bidirectional LSTM layer followed by a fully connected layer. The data was provided in the form of a Kaggle competition by American Epilepsy Society. The main task was to classify the interictal and preictal EEG clips. Using this model, we obtained an AUC of 0.84 on the test dataset. Which shows that our classifier's performance is above chance level on unseen data. The comparison with the previous work shows that the use of bidirectional LSTM networks can achieve significantly better results than SVM and GRU networks.
An Intelligent Monitoring System of Vehicles on Highway Traffic
May 27, 2019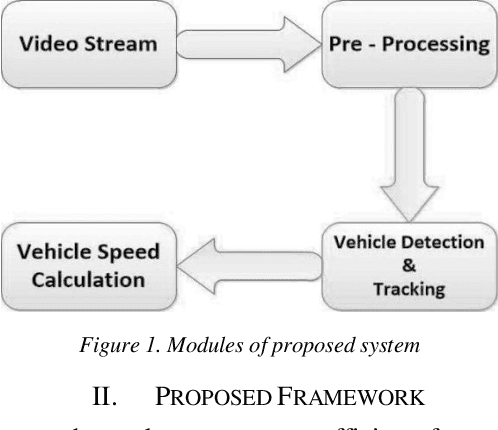
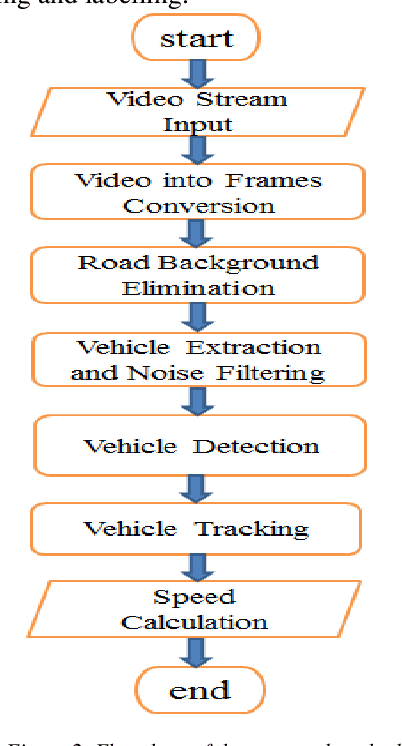

Abstract:Vehicle speed monitoring and management of highways is the critical problem of the road in this modern age of growing technology and population. A poor management results in frequent traffic jam, traffic rules violation and fatal road accidents. Using traditional techniques of RADAR, LIDAR and LASAR to address this problem is time-consuming, expensive and tedious. This paper presents an efficient framework to produce a simple, cost efficient and intelligent system for vehicle speed monitoring. The proposed method uses an HD (High Definition) camera mounted on the road side either on a pole or on a traffic signal for recording video frames. On the basis of these frames, a vehicle can be tracked by using radius growing method, and its speed can be calculated by calculating vehicle mask and its displacement in consecutive frames. The method uses pattern recognition, digital image processing and mathematical techniques for vehicle detection, tracking and speed calculation. The validity of the proposed model is proved by testing it on different highways.
* 5 pages
3D human action analysis and recognition through GLAC descriptor on 2D motion and static posture images
Mar 19, 2019
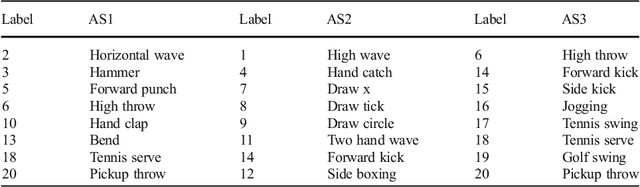
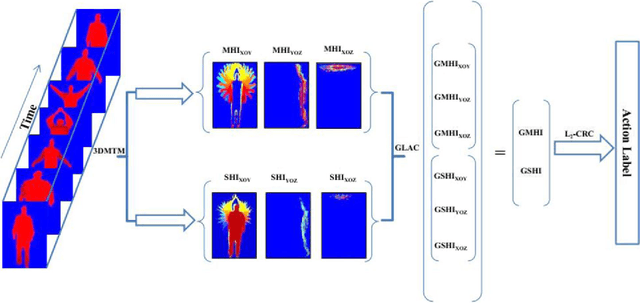

Abstract:In this paper, we present an approach for identification of actions within depth action videos. First, we process the video to get motion history images (MHIs) and static history images (SHIs) corresponding to an action video based on the use of 3D Motion Trail Model (3DMTM). We then characterize the action video by extracting the Gradient Local Auto-Correlations (GLAC) features from the SHIs and the MHIs. The two sets of features i.e., GLAC features from MHIs and GLAC features from SHIs are concatenated to obtain a representation vector for action. Finally, we perform the classification on all the action samples by using the l2-regularized Collaborative Representation Classifier (l2-CRC) to recognize different human actions in an effective way. We perform evaluation of the proposed method on three action datasets, MSR-Action3D, DHA and UTD-MHAD. Through experimental results, we observe that the proposed method performs superior to other approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge