Mohamed Jarraya
MoEDiff-SR: Mixture of Experts-Guided Diffusion Model for Region-Adaptive MRI Super-Resolution
Apr 09, 2025



Abstract:Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) at lower field strengths (e.g., 3T) suffers from limited spatial resolution, making it challenging to capture fine anatomical details essential for clinical diagnosis and neuroimaging research. To overcome this limitation, we propose MoEDiff-SR, a Mixture of Experts (MoE)-guided diffusion model for region-adaptive MRI Super-Resolution (SR). Unlike conventional diffusion-based SR models that apply a uniform denoising process across the entire image, MoEDiff-SR dynamically selects specialized denoising experts at a fine-grained token level, ensuring region-specific adaptation and enhanced SR performance. Specifically, our approach first employs a Transformer-based feature extractor to compute multi-scale patch embeddings, capturing both global structural information and local texture details. The extracted feature embeddings are then fed into an MoE gating network, which assigns adaptive weights to multiple diffusion-based denoisers, each specializing in different brain MRI characteristics, such as centrum semiovale, sulcal and gyral cortex, and grey-white matter junction. The final output is produced by aggregating the denoised results from these specialized experts according to dynamically assigned gating probabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that MoEDiff-SR outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of quantitative image quality metrics, perceptual fidelity, and computational efficiency. Difference maps from each expert further highlight their distinct specializations, confirming the effective region-specific denoising capability and the interpretability of expert contributions. Additionally, clinical evaluation validates its superior diagnostic capability in identifying subtle pathological features, emphasizing its practical relevance in clinical neuroimaging. Our code is available at https://github.com/ZWang78/MoEDiff-SR.
Distillation-Driven Diffusion Model for Multi-Scale MRI Super-Resolution: Make 1.5T MRI Great Again
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) offers critical insights into microstructural details, however, the spatial resolution of standard 1.5T imaging systems is often limited. In contrast, 7T MRI provides significantly enhanced spatial resolution, enabling finer visualization of anatomical structures. Though this, the high cost and limited availability of 7T MRI hinder its widespread use in clinical settings. To address this challenge, a novel Super-Resolution (SR) model is proposed to generate 7T-like MRI from standard 1.5T MRI scans. Our approach leverages a diffusion-based architecture, incorporating gradient nonlinearity correction and bias field correction data from 7T imaging as guidance. Moreover, to improve deployability, a progressive distillation strategy is introduced. Specifically, the student model refines the 7T SR task with steps, leveraging feature maps from the inference phase of the teacher model as guidance, aiming to allow the student model to achieve progressively 7T SR performance with a smaller, deployable model size. Experimental results demonstrate that our baseline teacher model achieves state-of-the-art SR performance. The student model, while lightweight, sacrifices minimal performance. Furthermore, the student model is capable of accepting MRI inputs at varying resolutions without the need for retraining, significantly further enhancing deployment flexibility. The clinical relevance of our proposed method is validated using clinical data from Massachusetts General Hospital. Our code is available at https://github.com/ZWang78/SR.
Few-Shot Adaptation of Training-Free Foundation Model for 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Jan 15, 2025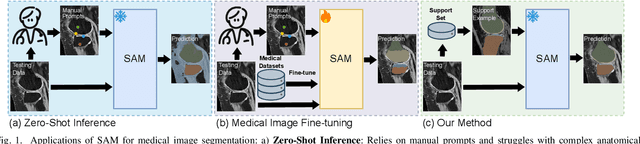
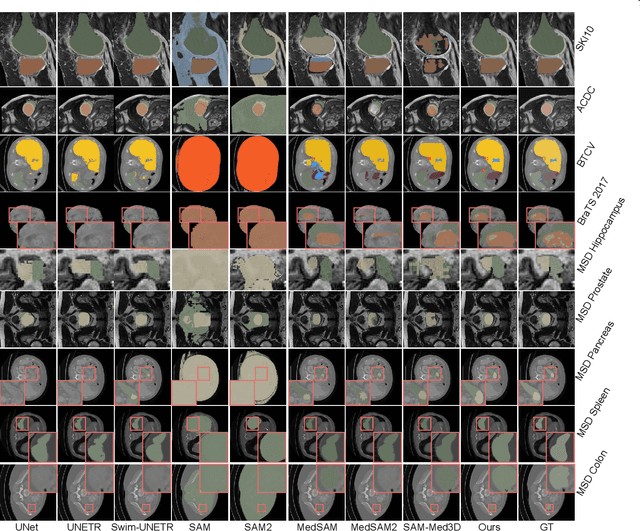
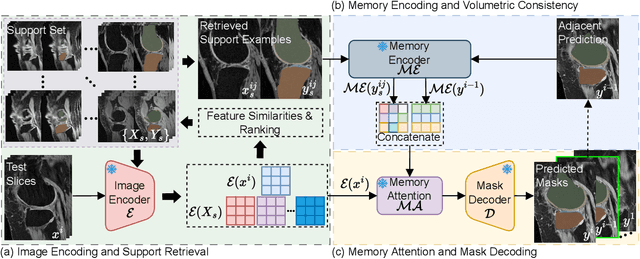
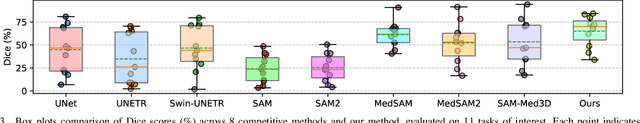

Abstract:Vision foundation models have achieved remarkable progress across various image analysis tasks. In the image segmentation task, foundation models like the Segment Anything Model (SAM) enable generalizable zero-shot segmentation through user-provided prompts. However, SAM primarily trained on natural images, lacks the domain-specific expertise of medical imaging. This limitation poses challenges when applying SAM to medical image segmentation, including the need for extensive fine-tuning on specialized medical datasets and a dependency on manual prompts, which are both labor-intensive and require intervention from medical experts. This work introduces the Few-shot Adaptation of Training-frEe SAM (FATE-SAM), a novel method designed to adapt the advanced Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) for 3D medical image segmentation. FATE-SAM reassembles pre-trained modules of SAM2 to enable few-shot adaptation, leveraging a small number of support examples to capture anatomical knowledge and perform prompt-free segmentation, without requiring model fine-tuning. To handle the volumetric nature of medical images, we incorporate a Volumetric Consistency mechanism that enhances spatial coherence across 3D slices. We evaluate FATE-SAM on multiple medical imaging datasets and compare it with supervised learning methods, zero-shot SAM approaches, and fine-tuned medical SAM methods. Results show that FATE-SAM delivers robust and accurate segmentation while eliminating the need for large annotated datasets and expert intervention. FATE-SAM provides a practical, efficient solution for medical image segmentation, making it more accessible for clinical applications.
A Diffusion-based Xray2MRI Model: Generating Pseudo-MRI Volumes From one Single X-ray
Oct 09, 2024



Abstract:Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is a prevalent musculoskeletal disorder, and X-rays are commonly used for its diagnosis due to their cost-effectiveness. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), on the other hand, offers detailed soft tissue visualization and has become a valuable supplementary diagnostic tool for KOA. Unfortunately, the high cost and limited accessibility of MRI hinder its widespread use, leaving many patients with KOA reliant solely on X-ray imaging. In this study, we introduce a novel diffusion-based Xray2MRI model capable of generating pseudo-MRI volumes from one single X-ray image. In addition to using X-rays as conditional input, our model integrates target depth, KOA probability distribution, and image intensity distribution modules to guide the synthesis process, ensuring that the generated corresponding slices accurately correspond to the anatomical structures. Experimental results demonstrate that by integrating information from X-rays with additional input data, our proposed approach is capable of generating pseudo-MRI sequences that approximate real MRI scans. Moreover, by increasing the inference times, the model achieves effective interpolation, further improving the continuity and smoothness of the generated MRI sequences, representing one promising initial attempt for cost-effective medical imaging solutions.
Temporal Evolution of Knee Osteoarthritis: A Diffusion-based Morphing Model for X-ray Medical Image Synthesis
Aug 01, 2024



Abstract:Knee Osteoarthritis (KOA) is a common musculoskeletal disorder that significantly affects the mobility of older adults. In the medical domain, images containing temporal data are frequently utilized to study temporal dynamics and statistically monitor disease progression. While deep learning-based generative models for natural images have been widely researched, there are comparatively few methods available for synthesizing temporal knee X-rays. In this work, we introduce a novel deep-learning model designed to synthesize intermediate X-ray images between a specific patient's healthy knee and severe KOA stages. During the testing phase, based on a healthy knee X-ray, the proposed model can produce a continuous and effective sequence of KOA X-ray images with varying degrees of severity. Specifically, we introduce a Diffusion-based Morphing Model by modifying the Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model. Our approach integrates diffusion and morphing modules, enabling the model to capture spatial morphing details between source and target knee X-ray images and synthesize intermediate frames along a geodesic path. A hybrid loss consisting of diffusion loss, morphing loss, and supervision loss was employed. We demonstrate that our proposed approach achieves the highest temporal frame synthesis performance, effectively augmenting data for classification models and simulating the progression of KOA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge