Mohamed A. Abdelsalam
Evaluating the Impact of Post-Training Quantization on Reliable VQA with Multimodal LLMs
Feb 08, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLM) are increasingly deployed in domains where both reliability and efficiency are critical. However, current models remain overconfident, producing highly certain but incorrect answers. At the same time, their large size limits deployment on edge devices, necessitating compression. We study the intersection of these two challenges by analyzing how Post-Training Quantization (PTQ) compression affects both accuracy and reliability in Visual Question Answering (VQA). We evaluate two MLLMs, Qwen2-VL-7B and Idefics3-8B, quantized with data-free (HQQ) and data-aware (MBQ) methods across multiple bit widths. To counteract the reduction in reliability caused by quantization, we adapt the Selector confidence estimator for quantized multimodal settings and test its robustness across various quantization levels and out-of-distribution (OOD) scenarios. We find that PTQ degrades both accuracy and reliability. Data-aware methods soften the effect thereof. The Selector substantially mitigates the reliability impact. The combination of int4 MBQ and the Selector achieves the best efficiency-reliability trade-off, closing in on uncompressed performance at approx. 75% less memory demand. Overall, we present the first systematic study linking quantization and reliability in multimodal settings.
CIC-BART-SSA: Controllable Image Captioning with Structured Semantic Augmentation
Jul 16, 2024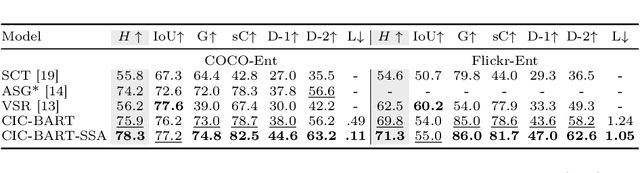
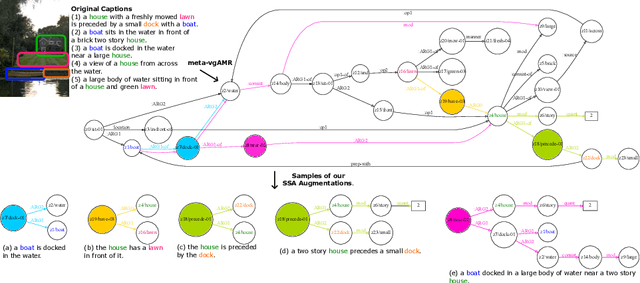
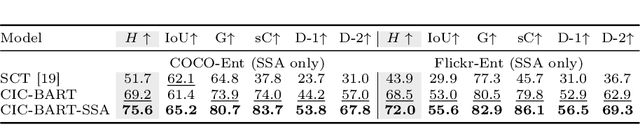

Abstract:Controllable Image Captioning (CIC) aims at generating natural language descriptions for an image, conditioned on information provided by end users, e.g., regions, entities or events of interest. However, available image--language datasets mainly contain captions that describe the entirety of an image, making them ineffective for training CIC models that can potentially attend to any subset of regions or relationships. To tackle this challenge, we propose a novel, fully automatic method to sample additional focused and visually grounded captions using a unified structured semantic representation built on top of the existing set of captions associated with an image. We leverage Abstract Meaning Representation (AMR), a cross-lingual graph-based semantic formalism, to encode all possible spatio-semantic relations between entities, beyond the typical spatial-relations-only focus of current methods. We use this Structured Semantic Augmentation (SSA) framework to augment existing image--caption datasets with the grounded controlled captions, increasing their spatial and semantic diversity and focal coverage. We then develop a new model, CIC-BART-SSA, specifically tailored for the CIC task, that sources its control signals from SSA-diversified datasets. We empirically show that, compared to SOTA CIC models, CIC-BART-SSA generates captions that are superior in diversity and text quality, are competitive in controllability, and, importantly, minimize the gap between broad and highly focused controlled captioning performance by efficiently generalizing to the challenging highly focused scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/SamsungLabs/CIC-BART-SSA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge