Moghis Fereidouni
Evaluating Sparse Autoencoders for Monosemantic Representation
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:A key barrier to interpreting large language models is polysemanticity, where neurons activate for multiple unrelated concepts. Sparse autoencoders (SAEs) have been proposed to mitigate this issue by transforming dense activations into sparse, more interpretable features. While prior work suggests that SAEs promote monosemanticity, there has been no quantitative comparison with their base models. This paper provides the first systematic evaluation of SAEs against base models concerning monosemanticity. We introduce a fine-grained concept separability score based on the Jensen-Shannon distance, which captures how distinctly a neuron's activation distributions vary across concepts. Using Gemma-2-2B and multiple SAE variants across five benchmarks, we show that SAEs reduce polysemanticity and achieve higher concept separability. However, greater sparsity of SAEs does not always yield better separability and often impairs downstream performance. To assess practical utility, we evaluate concept-level interventions using two strategies: full neuron masking and partial suppression. We find that, compared to base models, SAEs enable more precise concept-level control when using partial suppression. Building on this, we propose Attenuation via Posterior Probabilities (APP), a new intervention method that uses concept-conditioned activation distributions for targeted suppression. APP outperforms existing approaches in targeted concept removal.
INTERPOS: Interaction Rhythm Guided Positional Morphing for Mobile App Recommender Systems
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:The mobile app market has expanded exponentially, offering millions of apps with diverse functionalities, yet research in mobile app recommendation remains limited. Traditional sequential recommender systems utilize the order of items in users' historical interactions to predict the next item for the users. Position embeddings, well-established in transformer-based architectures for natural language processing tasks, effectively distinguish token positions in sequences. In sequential recommendation systems, position embeddings can capture the order of items in a user's historical interaction sequence. Nevertheless, this ordering does not consider the time elapsed between two interactions of the same user (e.g., 1 day, 1 week, 1 month), referred to as "user rhythm". In mobile app recommendation datasets, the time between consecutive user interactions is notably longer compared to other domains like movies, posing significant challenges for sequential recommender systems. To address this phenomenon in the mobile app domain, we introduce INTERPOS, an Interaction Rhythm Guided Positional Morphing strategy for autoregressive mobile app recommender systems. INTERPOS incorporates rhythm-guided position embeddings, providing a more comprehensive representation that considers both the sequential order of interactions and the temporal gaps between them. This approach enables a deep understanding of users' rhythms at a fine-grained level, capturing the intricacies of their interaction patterns over time. We propose three strategies to incorporate the morphed positional embeddings in two transformer-based sequential recommendation system architectures. Our extensive evaluations show that INTERPOS outperforms state-of-the-art models using 7 mobile app recommendation datasets on NDCG@K and HIT@K metrics. The source code of INTERPOS is available at https://github.com/dlgrad/INTERPOS.
* 10 pages, 8 tables, 3 figures
Improving Multi-turn Task Completion in Task-Oriented Dialog Systems via Prompt Chaining and Fine-Grained Feedback
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Task-oriented dialog (TOD) systems facilitate users in accomplishing complex, multi-turn tasks through natural language. While traditional approaches rely on extensive fine-tuning and annotated data for each domain, instruction-tuned large language models (LLMs) offer a more flexible alternative. However, LLMs struggle to reliably handle multi-turn task completion, particularly with accurately generating API calls and adapting to new domains without explicit demonstrations. To address these challenges, we propose RealTOD, a novel framework that enhances TOD systems through prompt chaining and fine-grained feedback mechanisms. Prompt chaining enables zero-shot domain adaptation via a two-stage prompting strategy, eliminating the need for human-curated demonstrations. Meanwhile, the fine-grained feedback mechanism improves task completion by verifying API calls against domain schemas and providing precise corrective feedback when errors are detected. We conduct extensive experiments on the SGD and BiTOD benchmarks using four LLMs. RealTOD improves API accuracy, surpassing AutoTOD by 37.74% on SGD and SimpleTOD by 11.26% on BiTOD. Human evaluations further confirm that LLMs integrated with RealTOD achieve superior task completion, fluency, and informativeness compared to existing methods.
Evaluating and Enhancing Out-of-Domain Generalization of Task-Oriented Dialog Systems for Task Completion without Turn-level Dialog Annotations
Feb 18, 2025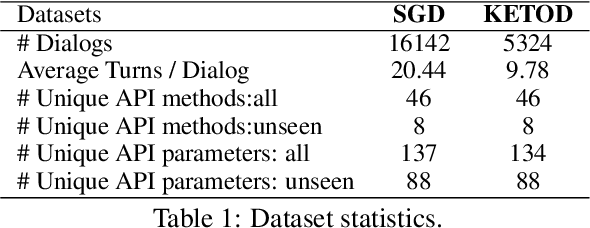
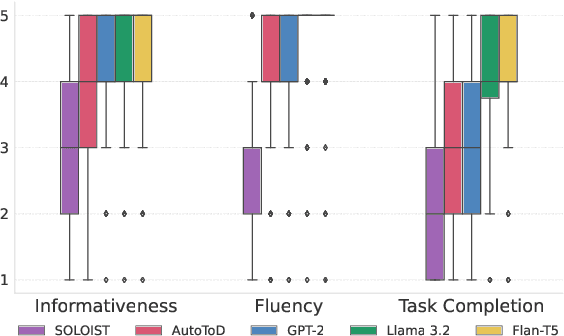
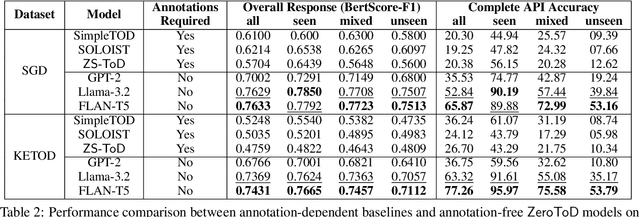
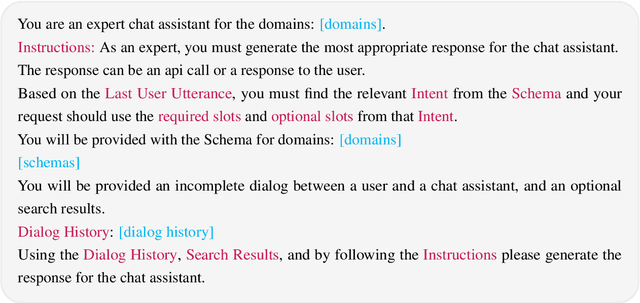
Abstract:Traditional task-oriented dialog (ToD) systems rely heavily on labor-intensive turn-level annotations, such as dialogue states and policy labels, for training. This work explores whether large language models (LLMs) can be fine-tuned solely on natural language dialogs to perform ToD tasks, without requiring such annotations. We evaluate their ability to generalize to unseen domains and compare their performance with models trained on fully annotated data. Through extensive experiments with three open-source LLMs of varying sizes and two diverse ToD datasets, we find that models fine-tuned without turn-level annotations generate coherent and contextually appropriate responses. However, their task completion performance - measured by accurate execution of API calls - remains suboptimal, with the best models achieving only around 53% success in unseen domains. To improve task completion, we propose ZeroToD, a framework that incorporates a schema augmentation mechanism to enhance API call accuracy and overall task completion rates, particularly in out-of-domain settings. We also compare ZeroToD with fine-tuning-free alternatives, such as prompting off-the-shelf LLMs, and find that our framework enables smaller, fine-tuned models that outperform large-scale proprietary LLMs in task completion. Additionally, a human study evaluating informativeness, fluency, and task completion confirms our empirical findings. These findings suggest the feasibility of developing cost-effective, scalable, and zero-shot generalizable ToD systems for real-world applications.
MobileConvRec: A Conversational Dataset for Mobile Apps Recommendations
May 28, 2024Abstract:Existing recommendation systems have focused on two paradigms: 1- historical user-item interaction-based recommendations and 2- conversational recommendations. Conversational recommendation systems facilitate natural language dialogues between users and the system, allowing the system to solicit users' explicit needs while enabling users to inquire about recommendations and provide feedback. Due to substantial advancements in natural language processing, conversational recommendation systems have gained prominence. Existing conversational recommendation datasets have greatly facilitated research in their respective domains. Despite the exponential growth in mobile users and apps in recent years, research in conversational mobile app recommender systems has faced substantial constraints. This limitation can primarily be attributed to the lack of high-quality benchmark datasets specifically tailored for mobile apps. To facilitate research for conversational mobile app recommendations, we introduce MobileConvRec. MobileConvRec simulates conversations by leveraging real user interactions with mobile apps on the Google Play store, originally captured in large-scale mobile app recommendation dataset MobileRec. The proposed conversational recommendation dataset synergizes sequential user-item interactions, which reflect implicit user preferences, with comprehensive multi-turn conversations to effectively grasp explicit user needs. MobileConvRec consists of over 12K multi-turn recommendation-related conversations spanning 45 app categories. Moreover, MobileConvRec presents rich metadata for each app such as permissions data, security and privacy-related information, and binary executables of apps, among others. We demonstrate that MobileConvRec can serve as an excellent testbed for conversational mobile app recommendation through a comparative study of several pre-trained large language models.
Search Beyond Queries: Training Smaller Language Models for Web Interactions via Reinforcement Learning
Apr 16, 2024Abstract:Traditional search systems focus on query formulation for effective results but face challenges in scenarios such as product searches where crucial product details (e.g., size, color) remain concealed until users visit specific product pages. This highlights the need for intelligent web navigation agents capable of formulating queries and navigating web pages according to users' high-level intents. In response to this need, this work introduces a Grounded Language Agent for Intelligent Web Interactions, called GLAINTEL. Drawing upon advancements in language modeling and reinforcement learning, GLAINTEL investigates the efficacy of transformer-based models in enhancing the search capabilities of interactive web environments. Given the dynamic action space for each state in web navigation, GLAINTEL employs the Flan-T5 architecture and incorporates language modeling and value estimation heads. This work focuses on training smaller language models as agents across various scenarios, systematically evaluating the impact of human demonstrations on the training process. Specifically, we investigate scenarios where no human demonstrations are available and subsequently assess the effective utilization of such demonstrations. We also explore unsupervised domain adaptation for situations where demonstrations are confined to a specific domain. Experimental evaluations across diverse setups demonstrate the effectiveness of training agents in unsupervised settings, outperforming in-context learning-based approaches that employ larger models with up to 540 billion parameters. Surprisingly, behavioral cloning-based methods that straightforwardly use human demonstrations do not outperform unsupervised learning-based methods. Additionally, combining human demonstrations with Reinforcement Learning-based training yields results comparable to models utilizing GPT-4.
Toward Open-domain Slot Filling via Self-supervised Co-training
Mar 24, 2023



Abstract:Slot filling is one of the critical tasks in modern conversational systems. The majority of existing literature employs supervised learning methods, which require labeled training data for each new domain. Zero-shot learning and weak supervision approaches, among others, have shown promise as alternatives to manual labeling. Nonetheless, these learning paradigms are significantly inferior to supervised learning approaches in terms of performance. To minimize this performance gap and demonstrate the possibility of open-domain slot filling, we propose a Self-supervised Co-training framework, called SCot, that requires zero in-domain manually labeled training examples and works in three phases. Phase one acquires two sets of complementary pseudo labels automatically. Phase two leverages the power of the pre-trained language model BERT, by adapting it for the slot filling task using these sets of pseudo labels. In phase three, we introduce a self-supervised cotraining mechanism, where both models automatically select highconfidence soft labels to further improve the performance of the other in an iterative fashion. Our thorough evaluations show that SCot outperforms state-of-the-art models by 45.57% and 37.56% on SGD and MultiWoZ datasets, respectively. Moreover, our proposed framework SCot achieves comparable performance when compared to state-of-the-art fully supervised models.
Proactive Prioritization of App Issues via Contrastive Learning
Mar 12, 2023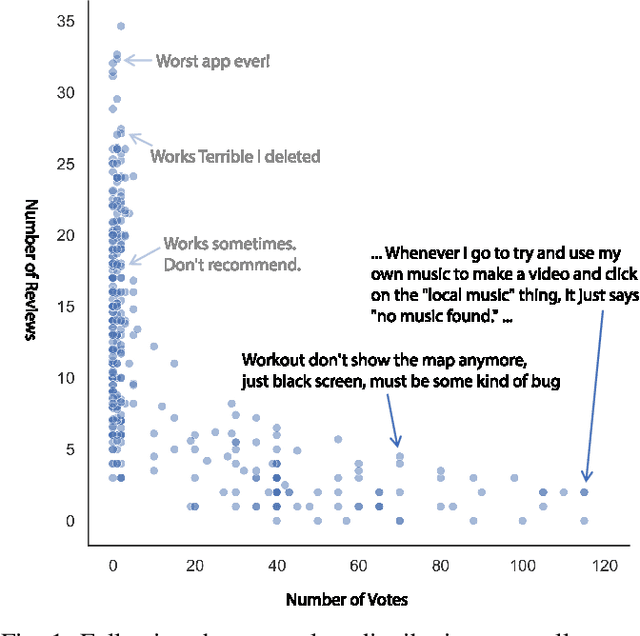
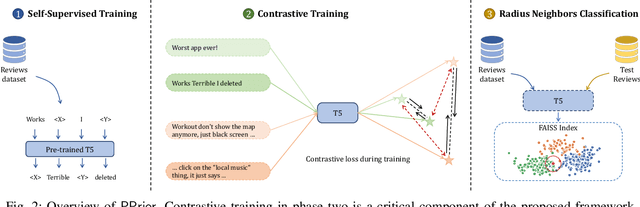
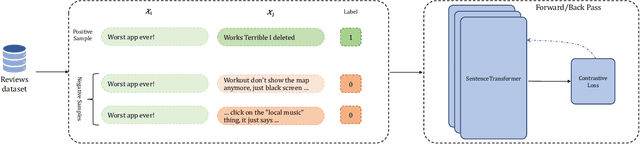
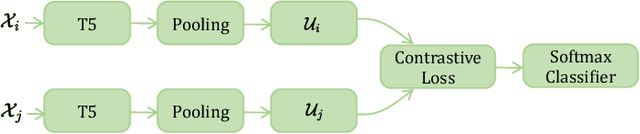
Abstract:Mobile app stores produce a tremendous amount of data in the form of user reviews, which is a huge source of user requirements and sentiments; such reviews allow app developers to proactively address issues in their apps. However, only a small number of reviews capture common issues and sentiments which creates a need for automatically identifying prominent reviews. Unfortunately, most existing work in text ranking and popularity prediction focuses on social contexts where other signals are available, which renders such works ineffective in the context of app reviews. In this work, we propose a new framework, PPrior, that enables proactive prioritization of app issues through identifying prominent reviews (ones predicted to receive a large number of votes in a given time window). Predicting highly-voted reviews is challenging given that, unlike social posts, social network features of users are not available. Moreover, there is an issue of class imbalance, since a large number of user reviews receive little to no votes. PPrior employs a pre-trained T5 model and works in three phases. Phase one adapts the pre-trained T5 model to the user reviews data in a self-supervised fashion. In phase two, we leverage contrastive training to learn a generic and task-independent representation of user reviews. Phase three uses radius neighbors classifier t o m ake t he final predictions. This phase also uses FAISS index for scalability and efficient search. To conduct extensive experiments, we acquired a large dataset of over 2.1 million user reviews from Google Play. Our experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework when compared against several state-of-the-art approaches. Moreover, the accuracy of PPrior in predicting prominent reviews is comparable to that of experienced app developers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge