Minjeong Shin
AttentionFlow: Visualising Influence in Networks of Time Series
Feb 03, 2021

Abstract:The collective attention on online items such as web pages, search terms, and videos reflects trends that are of social, cultural, and economic interest. Moreover, attention trends of different items exhibit mutual influence via mechanisms such as hyperlinks or recommendations. Many visualisation tools exist for time series, network evolution, or network influence; however, few systems connect all three. In this work, we present AttentionFlow, a new system to visualise networks of time series and the dynamic influence they have on one another. Centred around an ego node, our system simultaneously presents the time series on each node using two visual encodings: a tree ring for an overview and a line chart for details. AttentionFlow supports interactions such as overlaying time series of influence and filtering neighbours by time or flux. We demonstrate AttentionFlow using two real-world datasets, VevoMusic and WikiTraffic. We show that attention spikes in songs can be explained by external events such as major awards, or changes in the network such as the release of a new song. Separate case studies also demonstrate how an artist's influence changes over their career, and that correlated Wikipedia traffic is driven by cultural interests. More broadly, AttentionFlow can be generalised to visualise networks of time series on physical infrastructures such as road networks, or natural phenomena such as weather and geological measurements.
* Published in WSDM 2021. The demo is available at https://attentionflow.ml and code is available at https://github.com/alasdairtran/attentionflow
Comparative Document Summarisation via Classification
Dec 06, 2018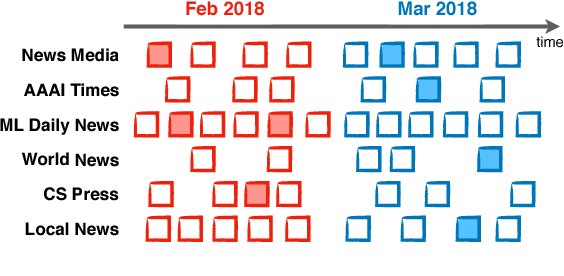

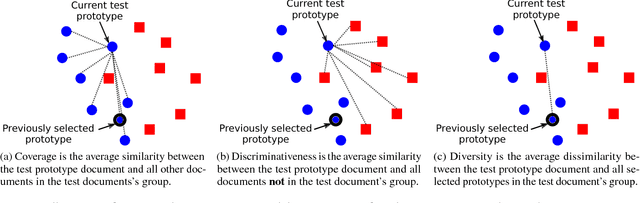
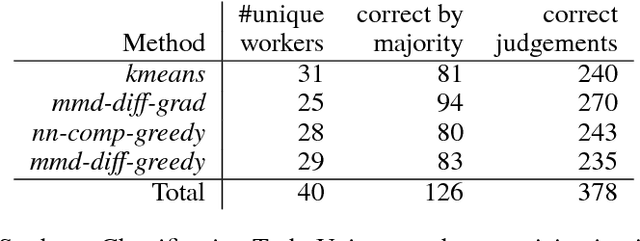
Abstract:This paper considers extractive summarisation in a comparative setting: given two or more document groups (e.g., separated by publication time), the goal is to select a small number of documents that are representative of each group, and also maximally distinguishable from other groups. We formulate a set of new objective functions for this problem that connect recent literature on document summarisation, interpretable machine learning, and data subset selection. In particular, by casting the problem as a binary classification amongst different groups, we derive objectives based on the notion of maximum mean discrepancy, as well as a simple yet effective gradient-based optimisation strategy. Our new formulation allows scalable evaluations of comparative summarisation as a classification task, both automatically and via crowd-sourcing. To this end, we evaluate comparative summarisation methods on a newly curated collection of controversial news topics over 13 months. We observe that gradient-based optimisation outperforms discrete and baseline approaches in 15 out of 24 different automatic evaluation settings. In crowd-sourced evaluations, summaries from gradient optimisation elicit 7% more accurate classification from human workers than discrete optimisation. Our result contrasts with recent literature on submodular data subset selection that favours discrete optimisation. We posit that our formulation of comparative summarisation will prove useful in a diverse range of use cases such as comparing content sources, authors, related topics, or distinct view points.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge