Minh Trinh
Zero-Shot Parameter Learning of Robot Dynamics Using Bayesian Statistics and Prior Knowledge
Jun 24, 2025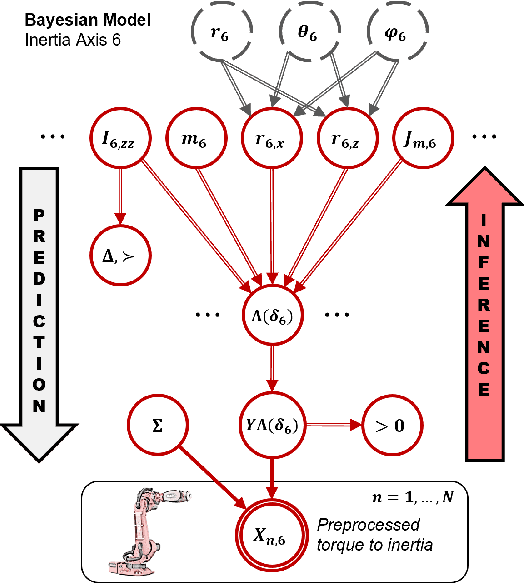
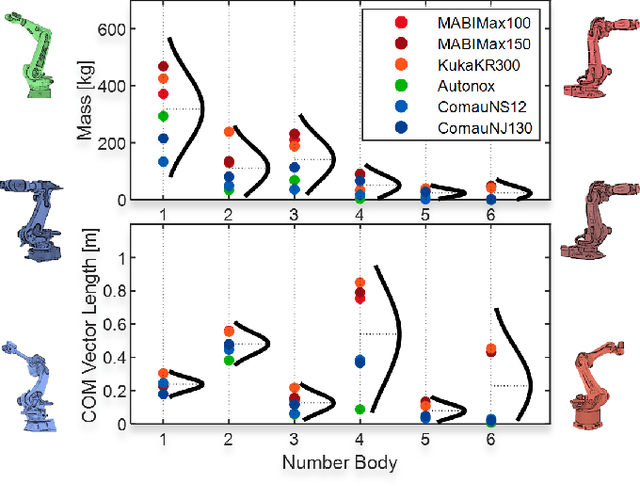
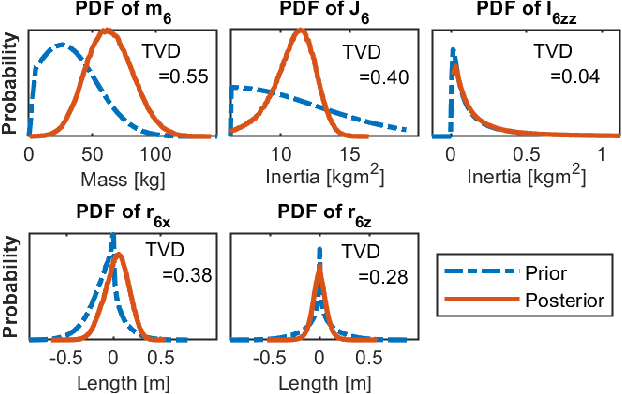
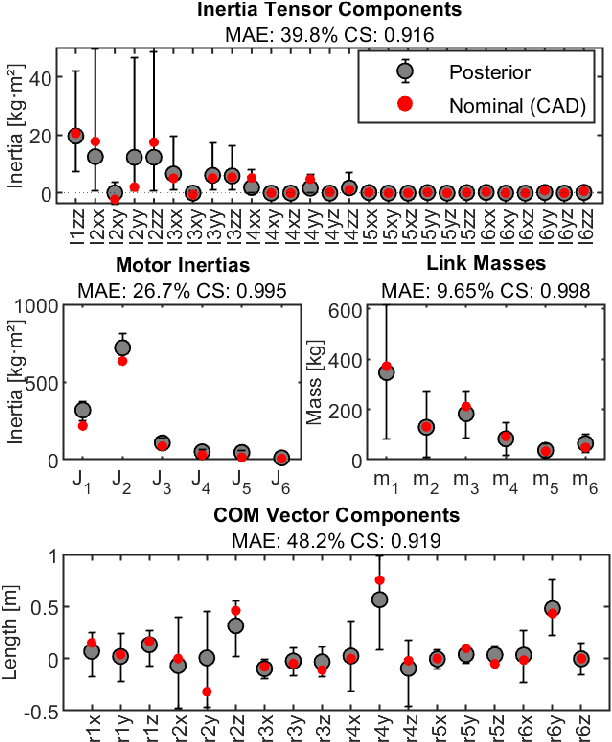
Abstract:Inertial parameter identification of industrial robots is an established process, but standard methods using Least Squares or Machine Learning do not consider prior information about the robot and require extensive measurements. Inspired by Bayesian statistics, this paper presents an identification method with improved generalization that incorporates prior knowledge and is able to learn with only a few or without additional measurements (Zero-Shot Learning). Furthermore, our method is able to correctly learn not only the inertial but also the mechanical and base parameters of the MABI Max 100 robot while ensuring physical feasibility and specifying the confidence intervals of the results. We also provide different types of priors for serial robots with 6 degrees of freedom, where datasheets or CAD models are not available.
Decoding the Narratives: Analyzing Personal Drug Experiences Shared on Reddit
Jun 17, 2024Abstract:Online communities such as drug-related subreddits serve as safe spaces for people who use drugs (PWUD), fostering discussions on substance use experiences, harm reduction, and addiction recovery. Users' shared narratives on these forums provide insights into the likelihood of developing a substance use disorder (SUD) and recovery potential. Our study aims to develop a multi-level, multi-label classification model to analyze online user-generated texts about substance use experiences. For this purpose, we first introduce a novel taxonomy to assess the nature of posts, including their intended connections (Inquisition or Disclosure), subjects (e.g., Recovery, Dependency), and specific objectives (e.g., Relapse, Quality, Safety). Using various multi-label classification algorithms on a set of annotated data, we show that GPT-4, when prompted with instructions, definitions, and examples, outperformed all other models. We apply this model to label an additional 1,000 posts and analyze the categories of linguistic expression used within posts in each class. Our analysis shows that topics such as Safety, Combination of Substances, and Mental Health see more disclosure, while discussions about physiological Effects focus on harm reduction. Our work enriches the understanding of PWUD's experiences and informs the broader knowledge base on SUD and drug use.
Assistive Robot Teleoperation Using Behavior Trees
Mar 19, 2023Abstract:Robotic assistance in robot arm teleoperation tasks has recently gained a lot of traction in industrial and domestic environment. A wide variety of input devices is used in such setups. Due to the noise in the input signals (e.g., Brain Computer Interface (BCI)) or delays due to environmental conditions (e.g., space robot teleoperation), users need assistive autonomy that keeps them in control while following predefined trajectories and avoids obstacles. This assistance calls for activity representations that are easy to define by the operator and able to take the dynamic world state into consideration. This paper represents Activities of Daily Living using Behavior Trees (BTs) whose inherent readability and modularity enables an end user to define new activities using a simple interface. To achieve this, we augment BTs with Shared Control Action Nodes, which guide the user's input on a trajectory facilitating and ensuring task execution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge