Mingyue Fan
Trajectory optimization of tail-sitter considering speed constraints
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:Tail-sitters combine the advantages of fixed-wing unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and vertical take-off and landing UAVs, and have been widely designed and researched in recent years. With the change in modern UAV application scenarios, it is required that UAVs have fast maneuverable three-dimensional flight capabilities. Due to the highly nonlinear aerodynamics produced by the fuselage and wings of the tail-sitter, how to quickly generate a smooth and executable trajectory is a problem that needs to be solved urgently. We constrain the speed of the tail-sitter, eliminate the differential dynamics constraints in the trajectory generation process of the tail-sitter through differential flatness, and allocate the time variable of the trajectory through the state-of-the-art trajectory generation method named MINCO. Because we discretize the trajectory in time, we convert the speed constraint on the vehicle into a soft constraint, thereby achieving the time-optimal trajectory for the tail-sitter to fly through any given waypoints.
Detecting COVID-19 Conspiracy Theories with Transformers and TF-IDF
May 01, 2022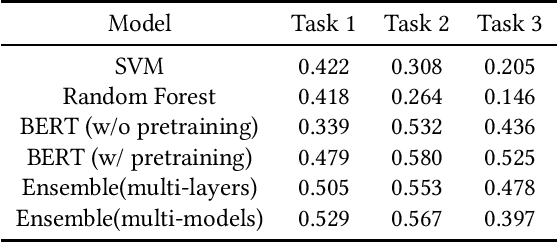
Abstract:The sharing of fake news and conspiracy theories on social media has wide-spread negative effects. By designing and applying different machine learning models, researchers have made progress in detecting fake news from text. However, existing research places a heavy emphasis on general, common-sense fake news, while in reality fake news often involves rapidly changing topics and domain-specific vocabulary. In this paper, we present our methods and results for three fake news detection tasks at MediaEval benchmark 2021 that specifically involve COVID-19 related topics. We experiment with a group of text-based models including Support Vector Machines, Random Forest, BERT, and RoBERTa. We find that a pre-trained transformer yields the best validation results, but a randomly initialized transformer with smart design can also be trained to reach accuracies close to that of the pre-trained transformer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge