Mingming Guo
Online Product Feature Recommendations with Interpretable Machine Learning
Apr 28, 2021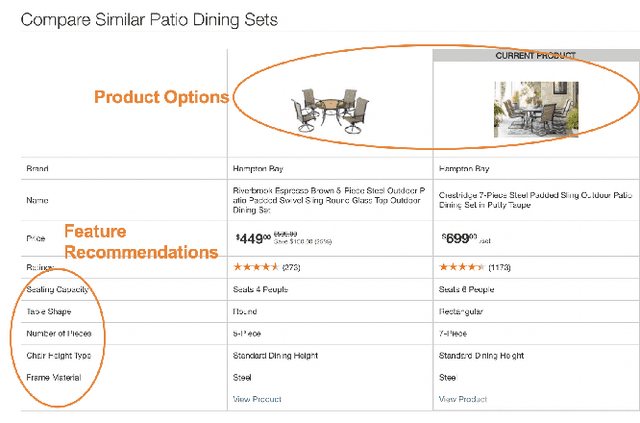
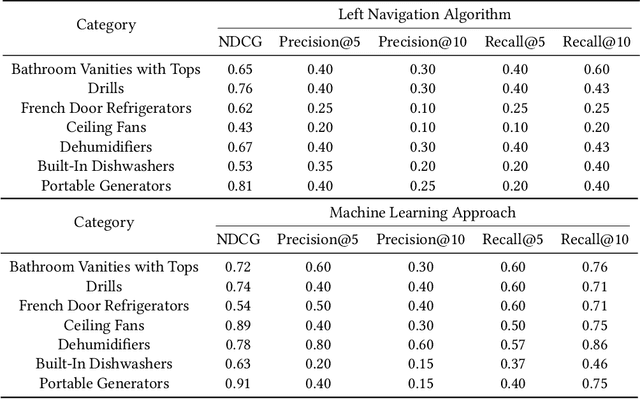
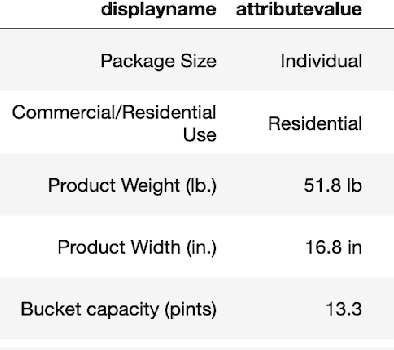
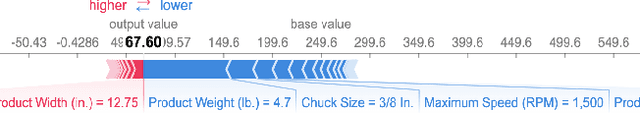
Abstract:Product feature recommendations are critical for online customers to purchase the right products based on the right features. For a customer, selecting the product that has the best trade-off between price and functionality is a time-consuming step in an online shopping experience, and customers can be overwhelmed by the available choices. However, determining the set of product features that most differentiate a particular product is still an open question in online recommender systems. In this paper, we focus on using interpretable machine learning methods to tackle this problem. First, we identify this unique product feature recommendation problem from a business perspective on a major US e-commerce site. Second, we formulate the problem into a price-driven supervised learning problem to discover the product features that could best explain the price of a product in a given product category. We build machine learning models with a model-agnostic method Shapley Values to understand the importance of each feature, rank and recommend the most essential features. Third, we leverage human experts to evaluate its relevancy. The results show that our method is superior to a strong baseline method based on customer behavior and significantly boosts the coverage by 45%. Finally, our proposed method shows comparable conversion rate against the baseline in online A/B tests.
Deep Learning-based Online Alternative Product Recommendations at Scale
Apr 15, 2021
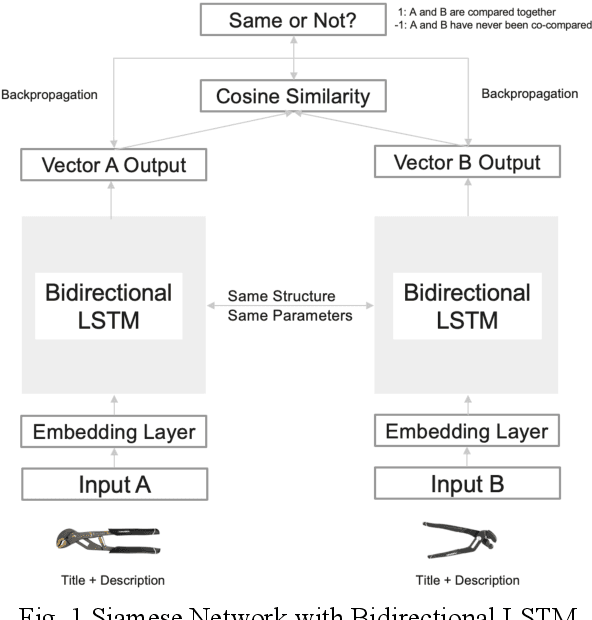
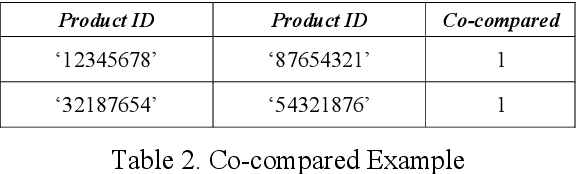
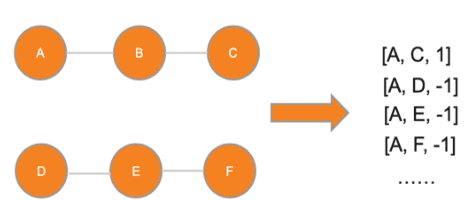
Abstract:Alternative recommender systems are critical for ecommerce companies. They guide customers to explore a massive product catalog and assist customers to find the right products among an overwhelming number of options. However, it is a non-trivial task to recommend alternative products that fit customer needs. In this paper, we use both textual product information (e.g. product titles and descriptions) and customer behavior data to recommend alternative products. Our results show that the coverage of alternative products is significantly improved in offline evaluations as well as recall and precision. The final A/B test shows that our algorithm increases the conversion rate by 12 percent in a statistically significant way. In order to better capture the semantic meaning of product information, we build a Siamese Network with Bidirectional LSTM to learn product embeddings. In order to learn a similarity space that better matches the preference of real customers, we use co-compared data from historical customer behavior as labels to train the network. In addition, we use NMSLIB to accelerate the computationally expensive kNN computation for millions of products so that the alternative recommendation is able to scale across the entire catalog of a major ecommerce site.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge