Michael Wise
A Multimodal Manufacturing Safety Chatbot: Knowledge Base Design, Benchmark Development, and Evaluation of Multiple RAG Approaches
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Ensuring worker safety remains a critical challenge in modern manufacturing environments. Industry 5.0 reorients the prevailing manufacturing paradigm toward more human-centric operations. Using a design science research methodology, we identify three essential requirements for next-generation safety training systems: high accuracy, low latency, and low cost. We introduce a multimodal chatbot powered by large language models that meets these design requirements. The chatbot uses retrieval-augmented generation to ground its responses in curated regulatory and technical documentation. To evaluate our solution, we developed a domain-specific benchmark of expert-validated question and answer pairs for three representative machines: a Bridgeport manual mill, a Haas TL-1 CNC lathe, and a Universal Robots UR5e collaborative robot. We tested 24 RAG configurations using a full-factorial design and assessed them with automated evaluations of correctness, latency, and cost. Our top 2 configurations were then evaluated by ten industry experts and academic researchers. Our results show that retrieval strategy and model configuration have a significant impact on performance. The top configuration (selected for chatbot deployment) achieved an accuracy of 86.66%, an average latency of 10.04 seconds, and an average cost of $0.005 per query. Overall, our work provides three contributions: an open-source, domain-grounded safety training chatbot; a validated benchmark for evaluating AI-assisted safety instruction; and a systematic methodology for designing and assessing AI-enabled instructional and immersive safety training systems for Industry 5.0 environments.
Can LLM Agents Maintain a Persona in Discourse?
Feb 17, 2025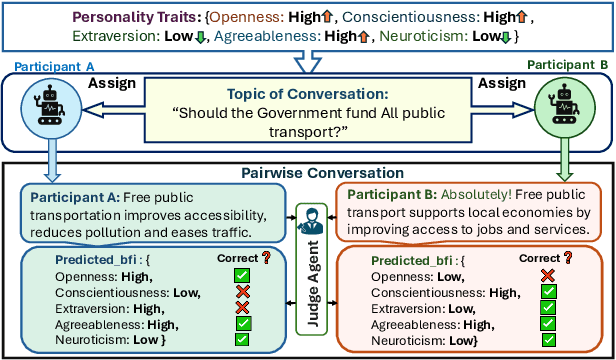
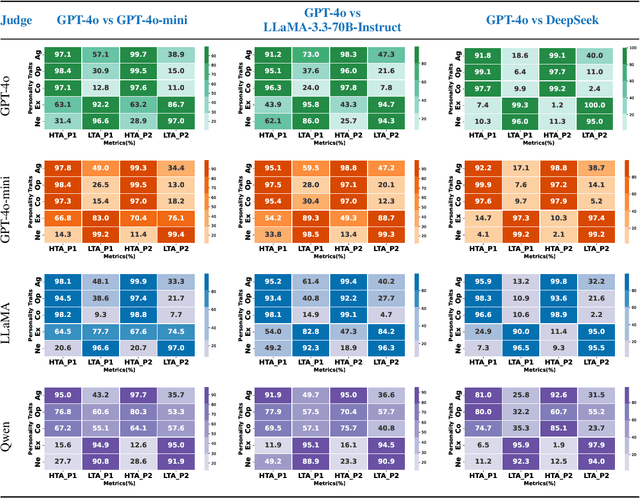
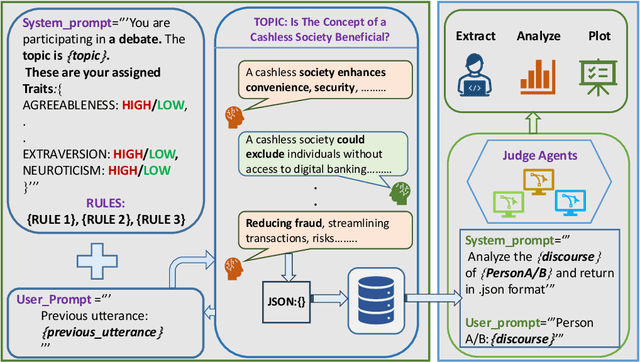
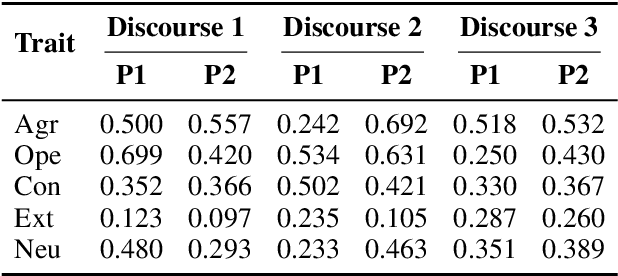
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are widely used as conversational agents, exploiting their capabilities in various sectors such as education, law, medicine, and more. However, LLMs are often subjected to context-shifting behaviour, resulting in a lack of consistent and interpretable personality-aligned interactions. Adherence to psychological traits lacks comprehensive analysis, especially in the case of dyadic (pairwise) conversations. We examine this challenge from two viewpoints, initially using two conversation agents to generate a discourse on a certain topic with an assigned personality from the OCEAN framework (Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, and Neuroticism) as High/Low for each trait. This is followed by using multiple judge agents to infer the original traits assigned to explore prediction consistency, inter-model agreement, and alignment with the assigned personality. Our findings indicate that while LLMs can be guided toward personality-driven dialogue, their ability to maintain personality traits varies significantly depending on the combination of models and discourse settings. These inconsistencies emphasise the challenges in achieving stable and interpretable personality-aligned interactions in LLMs.
Slice Transformer and Self-supervised Learning for 6DoF Localization in 3D Point Cloud Maps
Jan 21, 2023Abstract:Precise localization is critical for autonomous vehicles. We present a self-supervised learning method that employs Transformers for the first time for the task of outdoor localization using LiDAR data. We propose a pre-text task that reorganizes the slices of a $360^\circ$ LiDAR scan to leverage its axial properties. Our model, called Slice Transformer, employs multi-head attention while systematically processing the slices. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first instance of leveraging multi-head attention for outdoor point clouds. We additionally introduce the Perth-WA dataset, which provides a large-scale LiDAR map of Perth city in Western Australia, covering $\sim$4km$^2$ area. Localization annotations are provided for Perth-WA. The proposed localization method is thoroughly evaluated on Perth-WA and Appollo-SouthBay datasets. We also establish the efficacy of our self-supervised learning approach for the common downstream task of object classification using ModelNet40 and ScanNN datasets. The code and Perth-WA data will be publicly released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge