Michael T Lu
A Comparison of Self-Supervised Pretraining Approaches for Predicting Disease Risk from Chest Radiograph Images
Jun 15, 2023Abstract:Deep learning is the state-of-the-art for medical imaging tasks, but requires large, labeled datasets. For risk prediction, large datasets are rare since they require both imaging and follow-up (e.g., diagnosis codes). However, the release of publicly available imaging data with diagnostic labels presents an opportunity for self and semi-supervised approaches to improve label efficiency for risk prediction. Though several studies have compared self-supervised approaches in natural image classification, object detection, and medical image interpretation, there is limited data on which approaches learn robust representations for risk prediction. We present a comparison of semi- and self-supervised learning to predict mortality risk using chest x-ray images. We find that a semi-supervised autoencoder outperforms contrastive and transfer learning in internal and external validation.
ModelHub.AI: Dissemination Platform for Deep Learning Models
Nov 26, 2019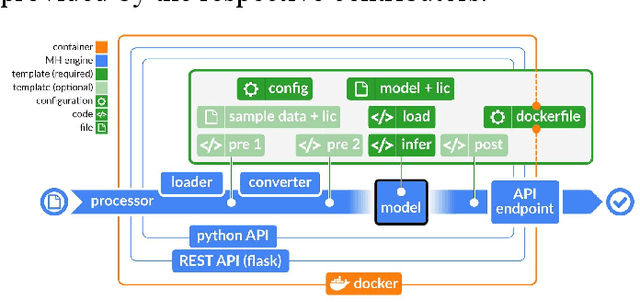
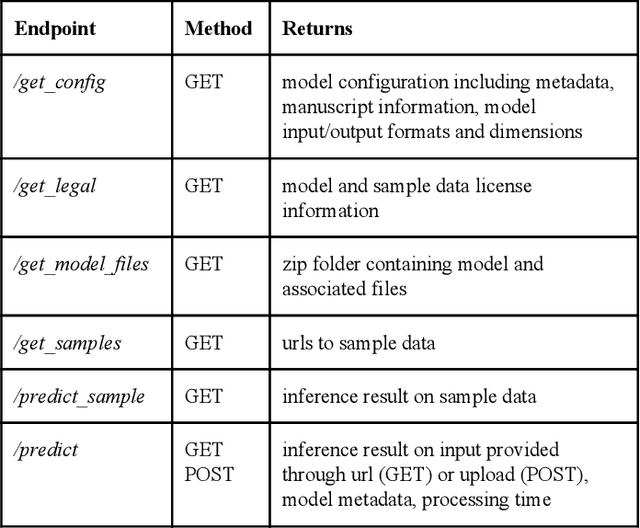
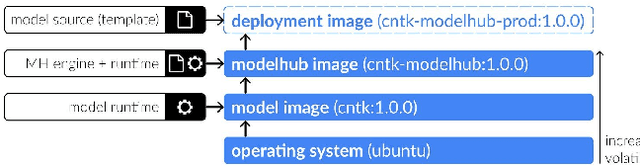
Abstract:Recent advances in artificial intelligence research have led to a profusion of studies that apply deep learning to problems in image analysis and natural language processing among others. Additionally, the availability of open-source computational frameworks has lowered the barriers to implementing state-of-the-art methods across multiple domains. Albeit leading to major performance breakthroughs in some tasks, effective dissemination of deep learning algorithms remains challenging, inhibiting reproducibility and benchmarking studies, impeding further validation, and ultimately hindering their effectiveness in the cumulative scientific progress. In developing a platform for sharing research outputs, we present ModelHub.AI (www.modelhub.ai), a community-driven container-based software engine and platform for the structured dissemination of deep learning models. For contributors, the engine controls data flow throughout the inference cycle, while the contributor-facing standard template exposes model-specific functions including inference, as well as pre- and post-processing. Python and RESTful Application programming interfaces (APIs) enable users to interact with models hosted on ModelHub.AI and allows both researchers and developers to utilize models out-of-the-box. ModelHub.AI is domain-, data-, and framework-agnostic, catering to different workflows and contributors' preferences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge