Ahmed Hosny
Deep learning-based detection of intravenous contrast in computed tomography scans
Oct 19, 2021



Abstract:Purpose: Identifying intravenous (IV) contrast use within CT scans is a key component of data curation for model development and testing. Currently, IV contrast is poorly documented in imaging metadata and necessitates manual correction and annotation by clinician experts, presenting a major barrier to imaging analyses and algorithm deployment. We sought to develop and validate a convolutional neural network (CNN)-based deep learning (DL) platform to identify IV contrast within CT scans. Methods: For model development and evaluation, we used independent datasets of CT scans of head, neck (HN) and lung cancer patients, totaling 133,480 axial 2D scan slices from 1,979 CT scans manually annotated for contrast presence by clinical experts. Five different DL models were adopted and trained in HN training datasets for slice-level contrast detection. Model performances were evaluated on a hold-out set and on an independent validation set from another institution. DL models was then fine-tuned on chest CT data and externally validated on a separate chest CT dataset. Results: Initial DICOM metadata tags for IV contrast were missing or erroneous in 1,496 scans (75.6%). The EfficientNetB4-based model showed the best overall detection performance. For HN scans, AUC was 0.996 in the internal validation set (n = 216) and 1.0 in the external validation set (n = 595). The fine-tuned model on chest CTs yielded an AUC: 1.0 for the internal validation set (n = 53), and AUC: 0.980 for the external validation set (n = 402). Conclusion: The DL model could accurately detect IV contrast in both HN and chest CT scans with near-perfect performance.
ModelHub.AI: Dissemination Platform for Deep Learning Models
Nov 26, 2019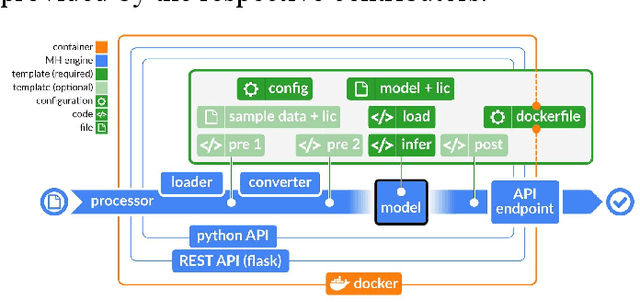
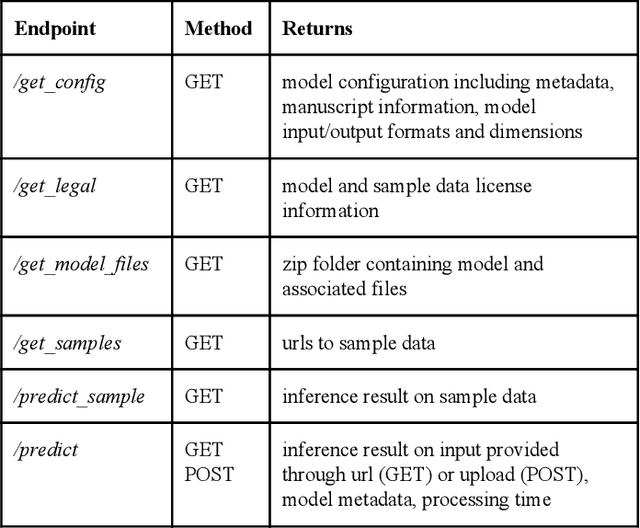
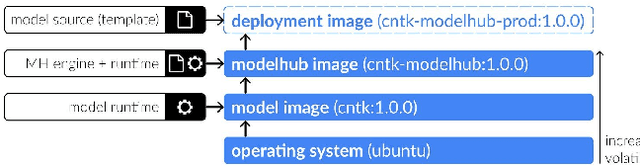
Abstract:Recent advances in artificial intelligence research have led to a profusion of studies that apply deep learning to problems in image analysis and natural language processing among others. Additionally, the availability of open-source computational frameworks has lowered the barriers to implementing state-of-the-art methods across multiple domains. Albeit leading to major performance breakthroughs in some tasks, effective dissemination of deep learning algorithms remains challenging, inhibiting reproducibility and benchmarking studies, impeding further validation, and ultimately hindering their effectiveness in the cumulative scientific progress. In developing a platform for sharing research outputs, we present ModelHub.AI (www.modelhub.ai), a community-driven container-based software engine and platform for the structured dissemination of deep learning models. For contributors, the engine controls data flow throughout the inference cycle, while the contributor-facing standard template exposes model-specific functions including inference, as well as pre- and post-processing. Python and RESTful Application programming interfaces (APIs) enable users to interact with models hosted on ModelHub.AI and allows both researchers and developers to utilize models out-of-the-box. ModelHub.AI is domain-, data-, and framework-agnostic, catering to different workflows and contributors' preferences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge