Michael Döbereiner
Distributed Multisensor ISAC
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Integrated Sensing and Communications (ISAC) will become a service in future mobile communication networks. It enables the detection and recognition of passive objects and environments using radar-like sensing. The ultimate advantage is the reuse of the mobile network and radio access resources for scene illumination, sensing, data transportation, computation, and fusion. It enables building a distributed, ubiquitous sensing network that can be adapted for a variety of radio sensing tasks and services. In this article, we develop the principles of multi-sensor ISAC (MS-ISAC). MS-ISAC corresponds to multi-user MIMO communication, which in radar terminology is known as distributed MIMO radar. \ First, we develop basic architectural principles for MS-ISAC and link them to example use cases. We then propose a generic MS-ISAC architecture. After a brief reference to multipath propagation and multistatic target reflectivity issues, we outline multilink access, coordination, precoding and link adaptation schemes for MS-ISAC. Moreover, we review model-based estimation and tracking of delay~/~Doppler from sparse OFDMA~/~TDMA frames. We emphasize Cooperative Passive Coherent Location (CPCL) for bistatic correlation and synchronization. Finally, issues of multisensor node synchronization and distributed data fusion are addressed.
Improving the Spatial Correlation Characteristics of Antenna Arrays using Linear Operators and Wide-band Modelling
Mar 26, 2024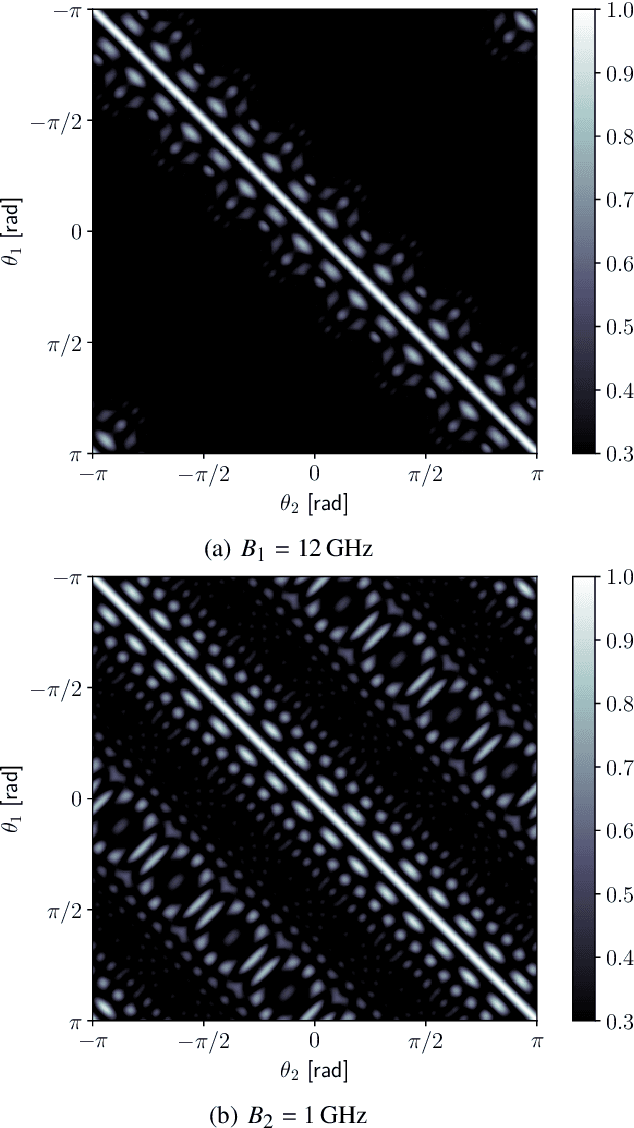

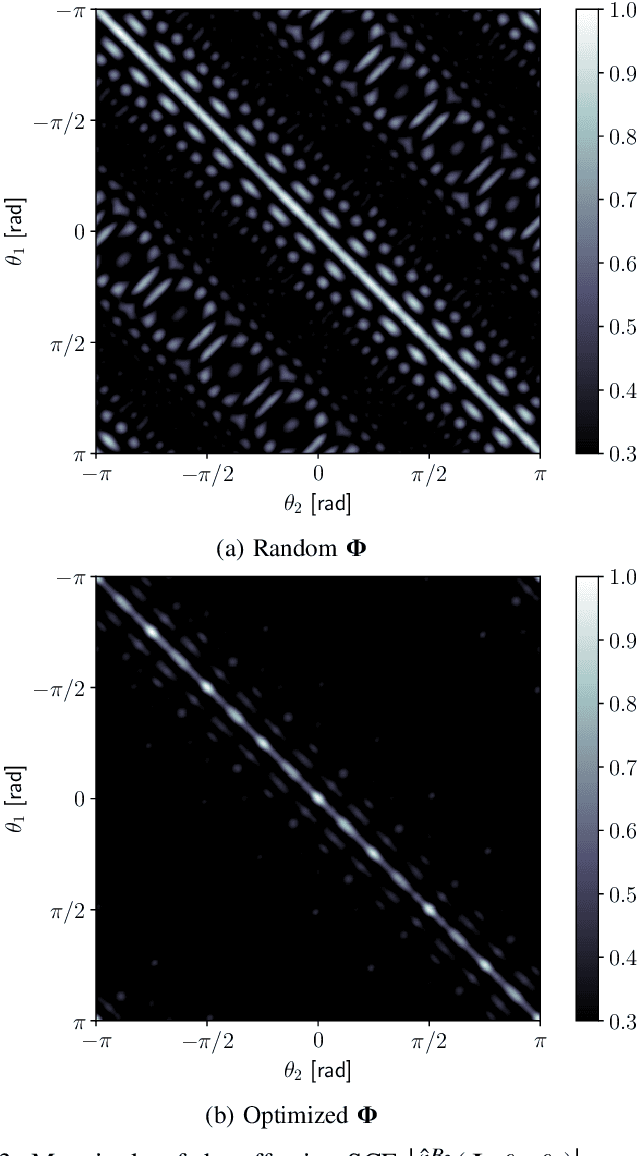
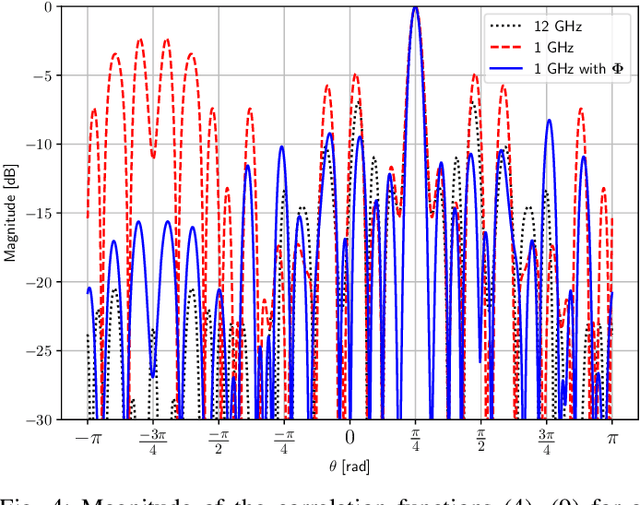
Abstract:The analysis of wireless communication channels at the mmWave, sub-THz and THz bands gives rise to difficulties in the construction of antenna arrays due to the small maximum inter-element spacing constraints at these frequencies. Arrays with uniform spacing greater than half the wavelength for a certain carrier frequency exhibit aliasing side-lobes in the angular domain, prohibiting non-ambiguous estimates of a propagating wave-front's angle of arrival. In this paper, we present how wide-band modelling of the array response is useful in mitigating this spatial aliasing effect. This approach aims to reduce the grating lobes by exploiting the angle- and frequency-dependent phase-shifts observed in the response of the array to a planar wave-front travelling across it. Furthermore, we propose a method by which the spatial correlation characteristics of an array operating at 33 GHz carrier frequency with an instantaneous bandwidth of 1 GHz can be improved such that the angular-domain side-lobes are reduced by 5-10 dB. This method, applicable to arbitrary antenna array manifolds, makes use of a linear operator that is applied to the base-band samples of the channel transfer function measured in space and frequency domains. By means of synthetically simulated arrays, we show that when operating with a bandwidth of 1 GHz, the use of a derived linear operator applied to the array output results in the spatial correlation characteristics approaching those of the array operating at a bandwidth of 12 GHz. Hence, non-ambiguous angle estimates can be obtained in the field without the use of expensive high-bandwidth RF front-end components.
Estimating Multi-Modal Dense Multipath Components using Auto-Encoders
Dec 05, 2022Abstract:We present a maximum-likelihood estimation algorithm for radio channel measurements exhibiting a mixture of independent Dense Multipath Components. The novelty of our approach is in the algorithms initialization using a deep learning architecture. Currently, available approaches can only deal with scenarios where a single mode is present. However, in measurements, two or more modes are often observed. This much more challenging multi-modal setting bears two important questions: How many modes are there, and how can we estimate those? To this end, we propose a Neural Net-architecture that can reliably estimate the number of modes present in the data and also provide an initial assessment of their shape. These predictions are used to initialize for gradient- and model-based optimization algorithm to further refine the estimates. We demonstrate numerically how the presented architecture performs on measurement data and analytically study its influence on the estimation of specular paths in a setting where the single-modal approach fails.
* https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9909796
Estimation of Signal Parameters using Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
Nov 09, 2022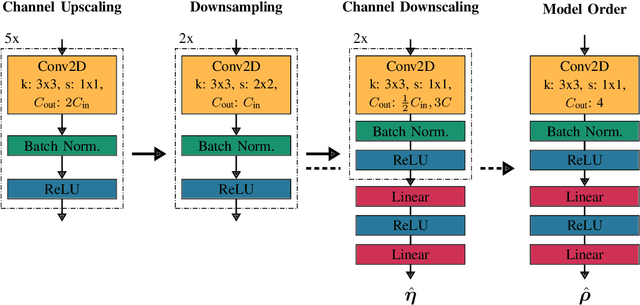
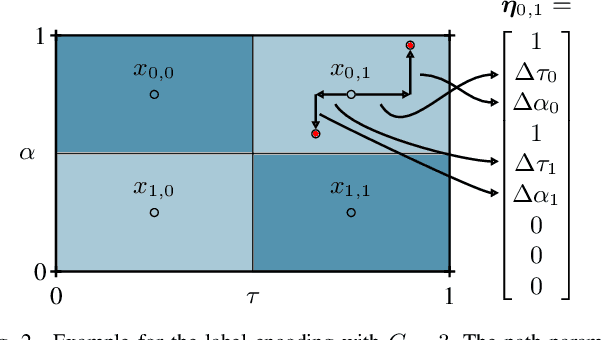
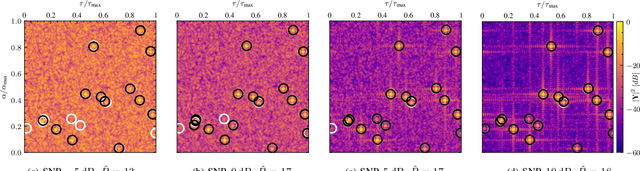
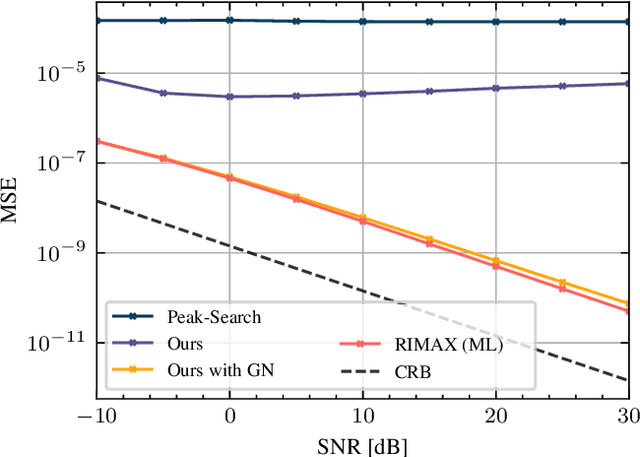
Abstract:This paper introduces a Deep Learning approach for signal parameter estimation in the context of wireless channel modeling. Our work is capable of multidimensional parameter estimation from a signal containing an unknown number of paths. The signal parameters are estimated relative to a predefined grid, providing quasi grid-free, hence, more accurate estimates than previous grid-limited approaches. It requires no prior knowledge of the number of paths, giving it an advantage in terms of complexity compared to existing solutions. Along with the description, we provide an initial performance analysis and a comparison with State-of-the-Art techniques and discuss future research directions.
Measurement Testbed for Radar and Emitter Localization of UAV at 3.75 GHz
Oct 13, 2022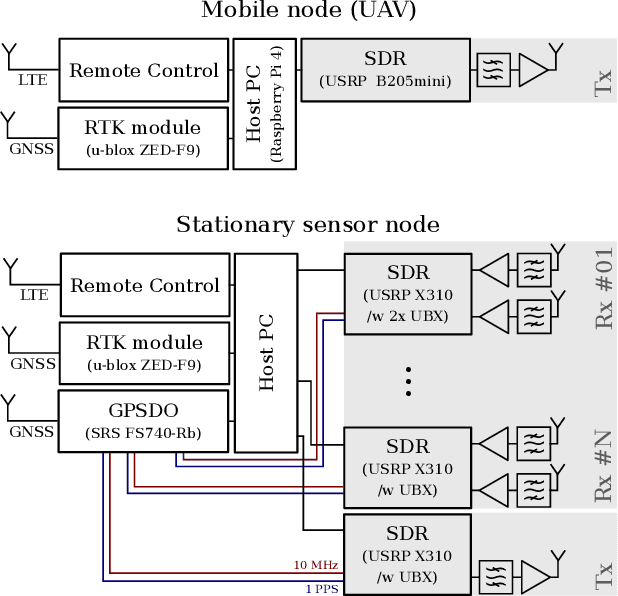
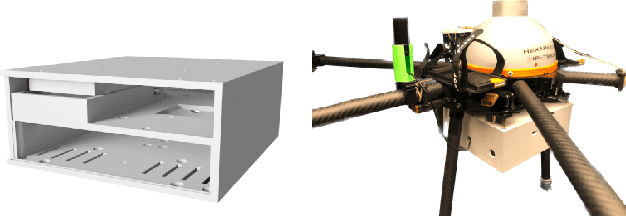
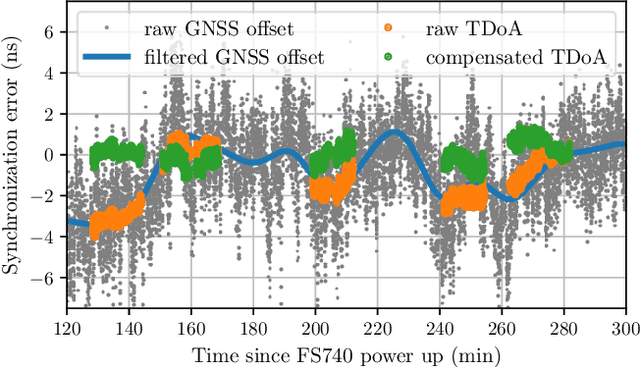
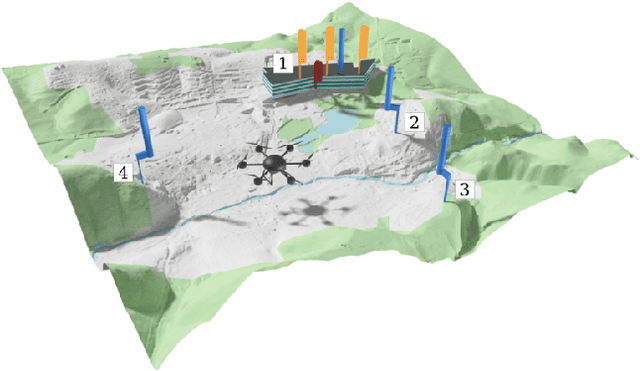
Abstract:This paper presents an experimental measurement platform for the research and development of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) localization algorithms using radio emission and reflectivity. We propose a cost-effective, flexible testbed made from commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) devices to allow academic research regarding the upcoming integration of UAV surveillance in existing mobile radio networks in terms of integrated sensing and communication (ISAC). The system enables nanosecond-level synchronization accuracy and centimeter-level positioning accuracy for multiple distributed sensor nodes and a mobile UAV-mounted node. Results from a real-world measurement in a 16 km2 urban area demonstrate the system's performance with both emitter localization as well as with the radar setup.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge