Mengliu Zhao
Detection and Longitudinal Tracking of Pigmented Skin Lesions in 3D Total-Body Skin Textured Meshes
May 02, 2021
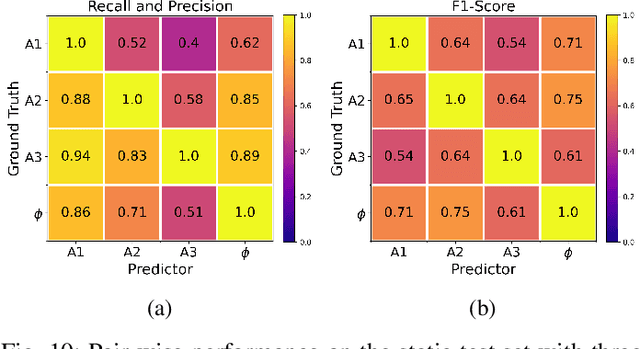
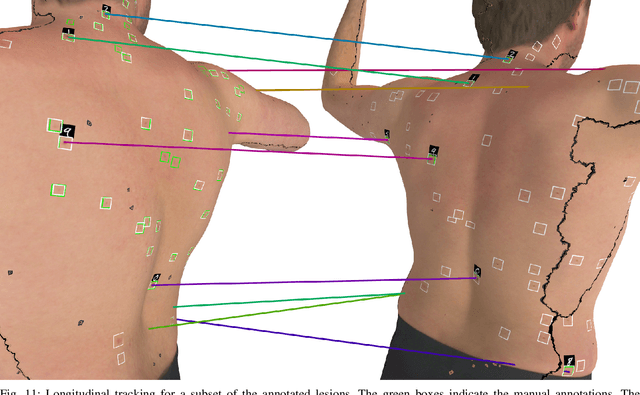

Abstract:We present an automated approach to detect and longitudinally track skin lesions on 3D total-body skin surfaces scans. The acquired 3D mesh of the subject is unwrapped to a 2D texture image, where a trained region convolutional neural network (R-CNN) localizes the lesions within the 2D domain. These detected skin lesions are mapped back to the 3D surface of the subject and, for subjects imaged multiple times, the anatomical correspondences among pairs of meshes and the geodesic distances among lesions are leveraged in our longitudinal lesion tracking algorithm. We evaluated the proposed approach using three sources of data. Firstly, we augmented the 3D meshes of human subjects from the public FAUST dataset with a variety of poses, textures, and images of lesions. Secondly, using a handheld structured light 3D scanner, we imaged a mannequin with multiple synthetic skin lesions at selected location and with varying shapes, sizes, and colours. Finally, we used 3DBodyTex, a publicly available dataset composed of 3D scans imaging the colored (textured) skin of 200 human subjects. We manually annotated locations that appeared to the human eye to contain a pigmented skin lesion as well as tracked a subset of lesions occurring on the same subject imaged in different poses. Our results, on test subjects annotated by three human annotators, suggest that the trained R-CNN detects lesions at a similar performance level as the human annotators. Our lesion tracking algorithm achieves an average accuracy of 80% when identifying corresponding pairs of lesions across subjects imaged in different poses. As there currently is no other large-scale publicly available dataset of 3D total-body skin lesions, we publicly release the 10 mannequin meshes and over 25,000 3DBodyTex manual annotations, which we hope will further research on total-body skin lesion analysis.
WhiteNNer-Blind Image Denoising via Noise Whiteness Priors
Aug 08, 2019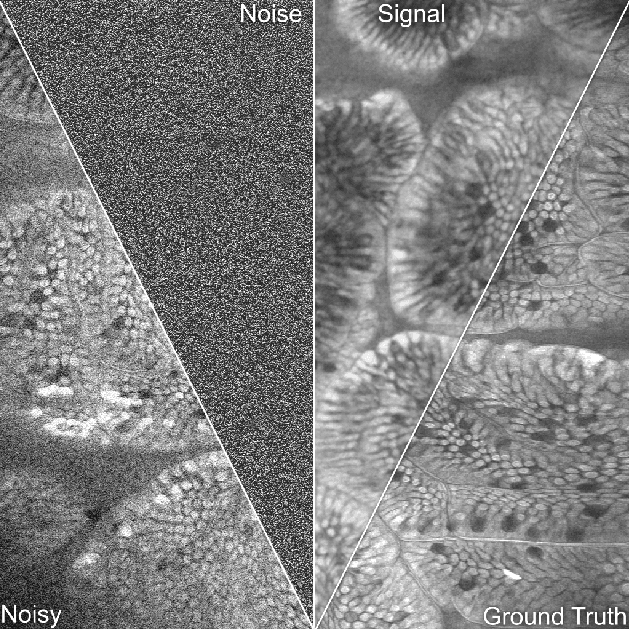
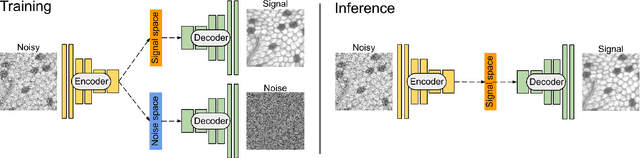
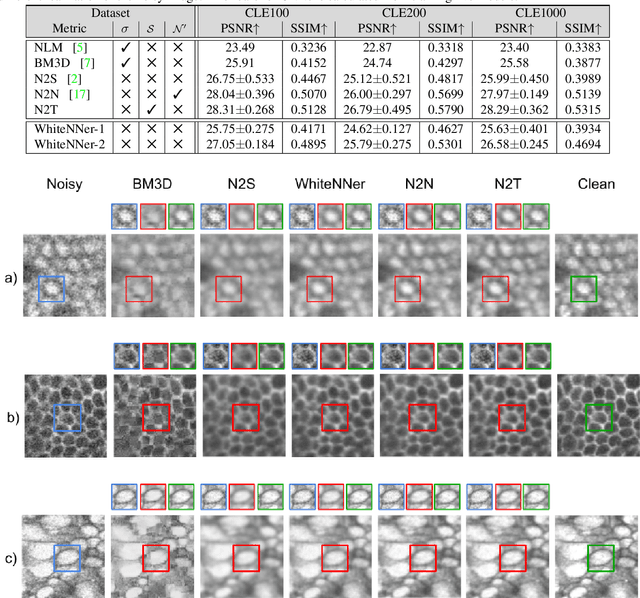
Abstract:The accuracy of medical imaging-based diagnostics is directly impacted by the quality of the collected images. A passive approach to improve image quality is one that lags behind improvements in imaging hardware, awaiting better sensor technology of acquisition devices. An alternative, active strategy is to utilize prior knowledge of the imaging system to directly post-process and improve the acquired images. Traditionally, priors about the image properties are taken into account to restrict the solution space. However, few techniques exploit the prior about the noise properties. In this paper, we propose a neural network-based model for disentangling the signal and noise components of an input noisy image, without the need for any ground truth training data. We design a unified loss function that encodes priors about signal as well as noise estimate in the form of regularization terms. Specifically, by using total variation and piecewise constancy priors along with noise whiteness priors such as auto-correlation and stationary losses, our network learns to decouple an input noisy image into the underlying signal and noise components. We compare our proposed method to Noise2Noise and Noise2Self, as well as non-local mean and BM3D, on three public confocal laser endomicroscopy datasets. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of our network compared to state-of-the-art in terms of PSNR and SSIM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge