Mehrnoush Shamsfard
A Parallel Cross-Lingual Benchmark for Multimodal Idiomaticity Understanding
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Potentially idiomatic expressions (PIEs) construe meanings inherently tied to the everyday experience of a given language community. As such, they constitute an interesting challenge for assessing the linguistic (and to some extent cultural) capabilities of NLP systems. In this paper, we present XMPIE, a parallel multilingual and multimodal dataset of potentially idiomatic expressions. The dataset, containing 34 languages and over ten thousand items, allows comparative analyses of idiomatic patterns among language-specific realisations and preferences in order to gather insights about shared cultural aspects. This parallel dataset allows to evaluate model performance for a given PIE in different languages and whether idiomatic understanding in one language can be transferred to another. Moreover, the dataset supports the study of PIEs across textual and visual modalities, to measure to what extent PIE understanding in one modality transfers or implies in understanding in another modality (text vs. image). The data was created by language experts, with both textual and visual components crafted under multilingual guidelines, and each PIE is accompanied by five images representing a spectrum from idiomatic to literal meanings, including semantically related and random distractors. The result is a high-quality benchmark for evaluating multilingual and multimodal idiomatic language understanding.
FarsEval-PKBETS: A new diverse benchmark for evaluating Persian large language models
Apr 20, 2025Abstract:Research on evaluating and analyzing large language models (LLMs) has been extensive for resource-rich languages such as English, yet their performance in languages such as Persian has received considerably less attention. This paper introduces FarsEval-PKBETS benchmark, a subset of FarsEval project for evaluating large language models in Persian. This benchmark consists of 4000 questions and answers in various formats, including multiple choice, short answer and descriptive responses. It covers a wide range of domains and tasks,including medicine, law, religion, Persian language, encyclopedic knowledge, human preferences, social knowledge, ethics and bias, text generation, and respecting others' rights. This bechmark incorporates linguistics, cultural, and local considerations relevant to the Persian language and Iran. To ensure the questions are challenging for current LLMs, three models -- Llama3-70B, PersianMind, and Dorna -- were evaluated using this benchmark. Their average accuracy was below 50%, meaning they provided fully correct answers to fewer than half of the questions. These results indicate that current language models are still far from being able to solve this benchmark
Formality Style Transfer in Persian
Jun 02, 2024Abstract:This study explores the formality style transfer in Persian, particularly relevant in the face of the increasing prevalence of informal language on digital platforms, which poses challenges for existing Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools. The aim is to transform informal text into formal while retaining the original meaning, addressing both lexical and syntactic differences. We introduce a novel model, Fa-BERT2BERT, based on the Fa-BERT architecture, incorporating consistency learning and gradient-based dynamic weighting. This approach improves the model's understanding of syntactic variations, balancing loss components effectively during training. Our evaluation of Fa-BERT2BERT against existing methods employs new metrics designed to accurately measure syntactic and stylistic changes. Results demonstrate our model's superior performance over traditional techniques across various metrics, including BLEU, BERT score, Rouge-l, and proposed metrics underscoring its ability to adeptly navigate the complexities of Persian language style transfer. This study significantly contributes to Persian language processing by enhancing the accuracy and functionality of NLP models and thereby supports the development of more efficient and reliable NLP applications, capable of handling language style transformation effectively, thereby streamlining content moderation, enhancing data mining results, and facilitating cross-cultural communication.
RFBES at SemEval-2024 Task 8: Investigating Syntactic and Semantic Features for Distinguishing AI-Generated and Human-Written Texts
Feb 19, 2024



Abstract:Nowadays, the usage of Large Language Models (LLMs) has increased, and LLMs have been used to generate texts in different languages and for different tasks. Additionally, due to the participation of remarkable companies such as Google and OpenAI, LLMs are now more accessible, and people can easily use them. However, an important issue is how we can detect AI-generated texts from human-written ones. In this article, we have investigated the problem of AI-generated text detection from two different aspects: semantics and syntax. Finally, we presented an AI model that can distinguish AI-generated texts from human-written ones with high accuracy on both multilingual and monolingual tasks using the M4 dataset. According to our results, using a semantic approach would be more helpful for detection. However, there is a lot of room for improvement in the syntactic approach, and it would be a good approach for future work.
FaBERT: Pre-training BERT on Persian Blogs
Feb 09, 2024Abstract:We introduce FaBERT, a Persian BERT-base model pre-trained on the HmBlogs corpus, encompassing both informal and formal Persian texts. FaBERT is designed to excel in traditional Natural Language Understanding (NLU) tasks, addressing the intricacies of diverse sentence structures and linguistic styles prevalent in the Persian language. In our comprehensive evaluation of FaBERT on 12 datasets in various downstream tasks, encompassing Sentiment Analysis (SA), Named Entity Recognition (NER), Natural Language Inference (NLI), Question Answering (QA), and Question Paraphrasing (QP), it consistently demonstrated improved performance, all achieved within a compact model size. The findings highlight the importance of utilizing diverse and cleaned corpora, such as HmBlogs, to enhance the performance of language models like BERT in Persian Natural Language Processing (NLP) applications. FaBERT is openly accessible at https://huggingface.co/sbunlp/fabert
Developing an Informal-Formal Persian Corpus
Aug 10, 2023Abstract:Informal language is a style of spoken or written language frequently used in casual conversations, social media, weblogs, emails and text messages. In informal writing, the language faces some lexical and/or syntactic changes varying among different languages. Persian is one of the languages with many differences between its formal and informal styles of writing, thus developing informal language processing tools for this language seems necessary. Such a converter needs a large aligned parallel corpus of colloquial-formal sentences which can be useful for linguists to extract a regulated grammar and orthography for colloquial Persian as is done for the formal language. In this paper we explain our methodology in building a parallel corpus of 50,000 sentence pairs with alignments in the word/phrase level. The sentences were attempted to cover almost all kinds of lexical and syntactic changes between informal and formal Persian, therefore both methods of exploring and collecting from the different resources of informal scripts and following the phonological and morphological patterns of changes were applied to find as much instances as possible. The resulting corpus has about 530,000 alignments and a dictionary containing 49,397 word and phrase pairs.
Stacked Cross-modal Feature Consolidation Attention Networks for Image Captioning
Feb 08, 2023Abstract:Recently, the attention-enriched encoder-decoder framework has aroused great interest in image captioning due to its overwhelming progress. Many visual attention models directly leverage meaningful regions to generate image descriptions. However, seeking a direct transition from visual space to text is not enough to generate fine-grained captions. This paper exploits a feature-compounding approach to bring together high-level semantic concepts and visual information regarding the contextual environment fully end-to-end. Thus, we propose a stacked cross-modal feature consolidation (SCFC) attention network for image captioning in which we simultaneously consolidate cross-modal features through a novel compounding function in a multi-step reasoning fashion. Besides, we jointly employ spatial information and context-aware attributes (CAA) as the principal components in our proposed compounding function, where our CAA provides a concise context-sensitive semantic representation. To make better use of consolidated features potential, we further propose an SCFC-LSTM as the caption generator, which can leverage discriminative semantic information through the caption generation process. The experimental results indicate that our proposed SCFC can outperform various state-of-the-art image captioning benchmarks in terms of popular metrics on the MSCOCO and Flickr30K datasets.
Improving Persian Relation Extraction Models by Data Augmentation
Mar 29, 2022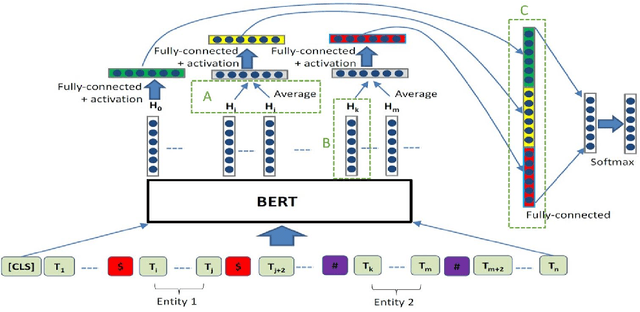

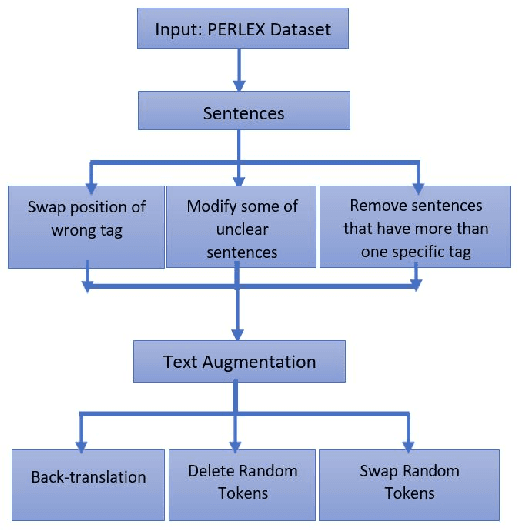
Abstract:Relation extraction that is the task of predicting semantic relation type between entities in a sentence or document is an important task in natural language processing. Although there are many researches and datasets for English, Persian suffers from sufficient researches and comprehensive datasets. The only available Persian dataset for this task is PERLEX, which is a Persian expert-translated version of the SemEval-2010-Task-8 dataset. In this paper, we present our augmented dataset and the results and findings of our system, participated in the Persian relation Extraction shared task of NSURL 2021 workshop. We use PERLEX as the base dataset and enhance it by applying some text preprocessing steps and by increasing its size via data augmentation techniques to improve the generalization and robustness of applied models. We then employ two different models including ParsBERT and multilingual BERT for relation extraction on the augmented PERLEX dataset. Our best model obtained 64.67% of Macro-F1 on the test phase of the contest and it achieved 83.68% of Macro-F1 on the test set of PERLEX.
* 5 pages, 6 images
HmBlogs: A big general Persian corpus
Nov 03, 2021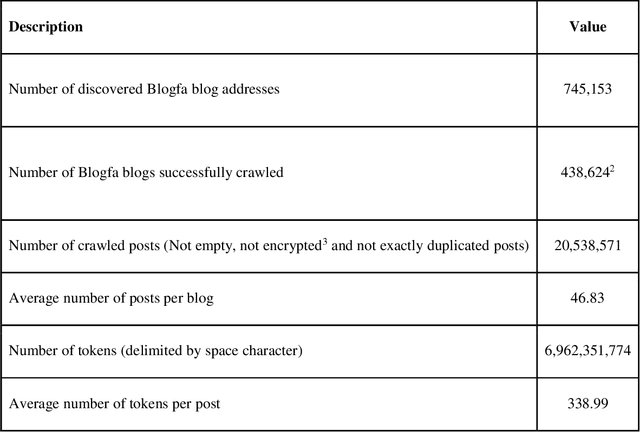
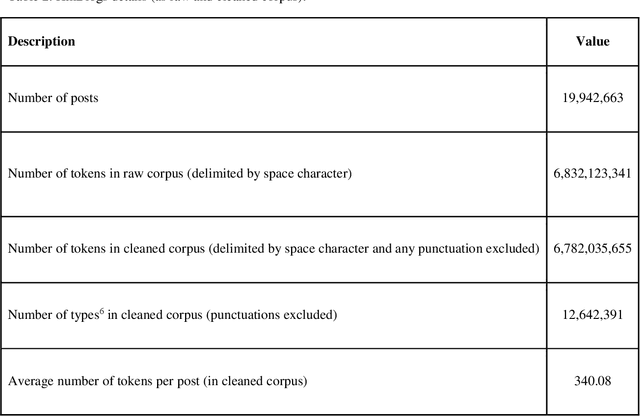
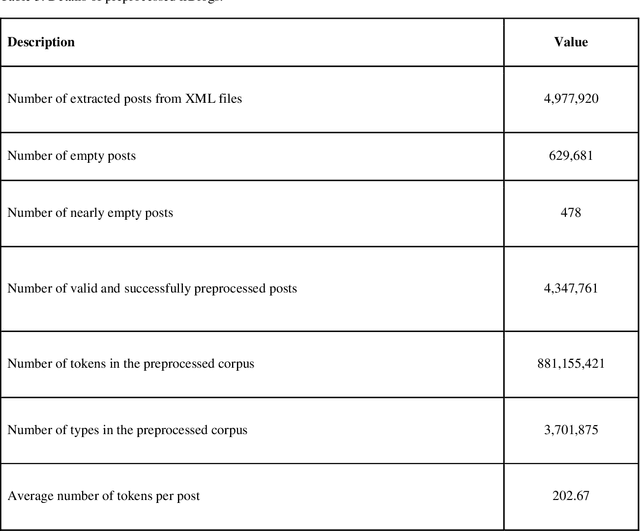
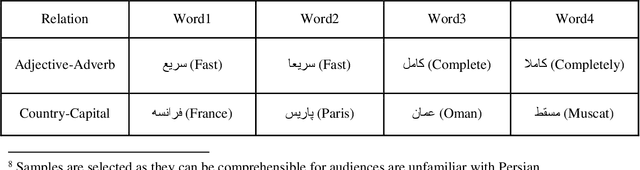
Abstract:This paper introduces the hmBlogs corpus for Persian, as a low resource language. This corpus has been prepared based on a collection of nearly 20 million blog posts over a period of about 15 years from a space of Persian blogs and includes more than 6.8 billion tokens. It can be claimed that this corpus is currently the largest Persian corpus that has been prepared independently for the Persian language. This corpus is presented in both raw and preprocessed forms, and based on the preprocessed corpus some word embedding models are produced. By the provided models, the hmBlogs is compared with some of the most important corpora available in Persian, and the results show the superiority of the hmBlogs corpus over the others. These evaluations also present the importance and effects of corpora, evaluation datasets, model production methods, different hyperparameters and even the evaluation methods. In addition to evaluating the corpus and its produced language models, this research also presents a semantic analogy dataset.
Offensive Language Detection with BERT-based models, By Customizing Attention Probabilities
Oct 11, 2021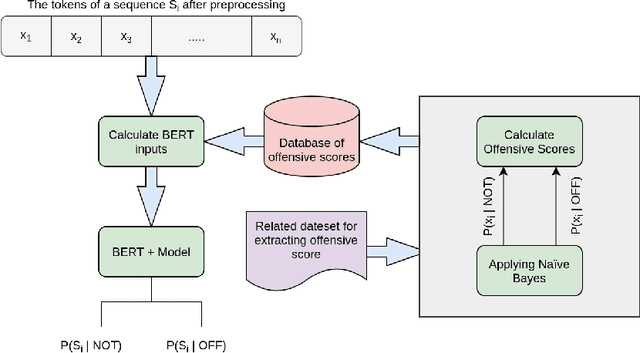
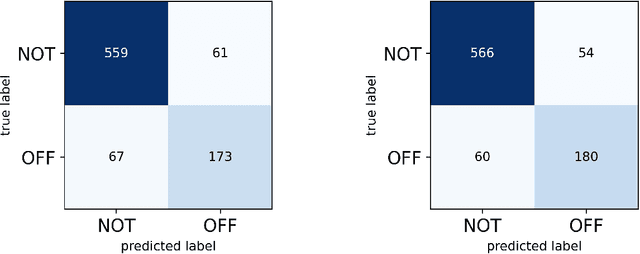
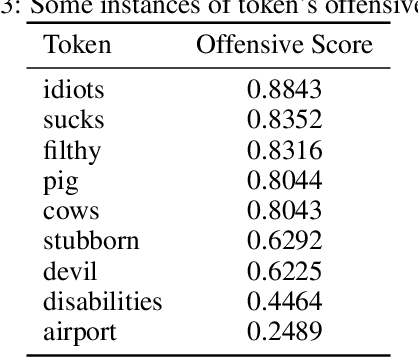
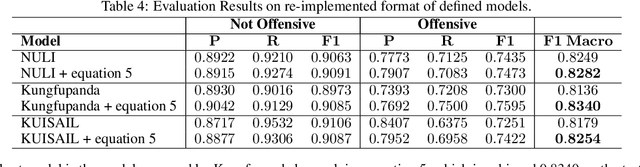
Abstract:This paper describes a novel study on using `Attention Mask' input in transformers and using this approach for detecting offensive content in both English and Persian languages. The paper's principal focus is to suggest a methodology to enhance the performance of the BERT-based models on the `Offensive Language Detection' task. Therefore, we customize attention probabilities by changing the `Attention Mask' input to create more efficacious word embeddings. To do this, we firstly tokenize the training set of the exploited datasets (by BERT tokenizer). Then, we apply Multinomial Naive Bayes to map these tokens to two probabilities. These probabilities indicate the likelihood of making a text non-offensive or offensive, provided that it contains that token. Afterwards, we use these probabilities to define a new term, namely Offensive Score. Next, we create two separate (because of the differences in the types of the employed datasets) equations based on Offensive Scores for each language to re-distribute the `Attention Mask' input for paying more attention to more offensive phrases. Eventually, we put the F1-macro score as our evaluation metric and fine-tune several combinations of BERT with ANNs, CNNs and RNNs to examine the effect of using this methodology on various combinations. The results indicate that all models will enhance with this methodology. The most improvement was 2% and 10% for English and Persian languages, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge