Mehak Preet Dhaliwal
A Shocking Amount of the Web is Machine Translated: Insights from Multi-Way Parallelism
Jan 11, 2024
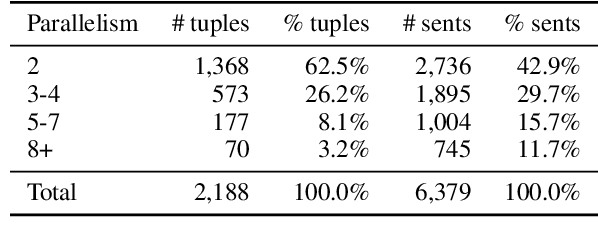
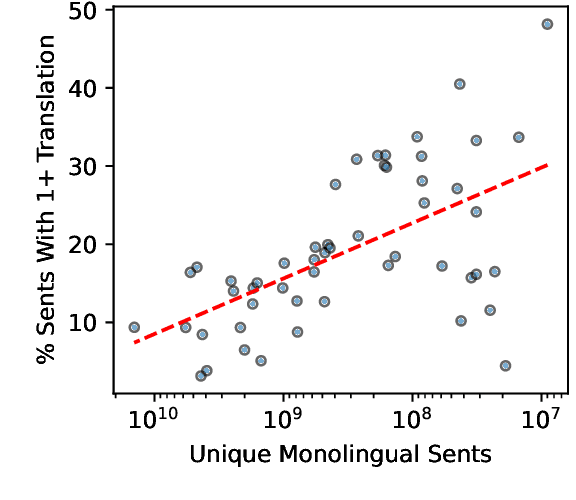
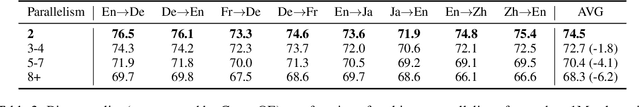
Abstract:We show that content on the web is often translated into many languages, and the low quality of these multi-way translations indicates they were likely created using Machine Translation (MT). Multi-way parallel, machine generated content not only dominates the translations in lower resource languages; it also constitutes a large fraction of the total web content in those languages. We also find evidence of a selection bias in the type of content which is translated into many languages, consistent with low quality English content being translated en masse into many lower resource languages, via MT. Our work raises serious concerns about training models such as multilingual large language models on both monolingual and bilingual data scraped from the web.
Infinite Recommendation Networks: A Data-Centric Approach
Jun 03, 2022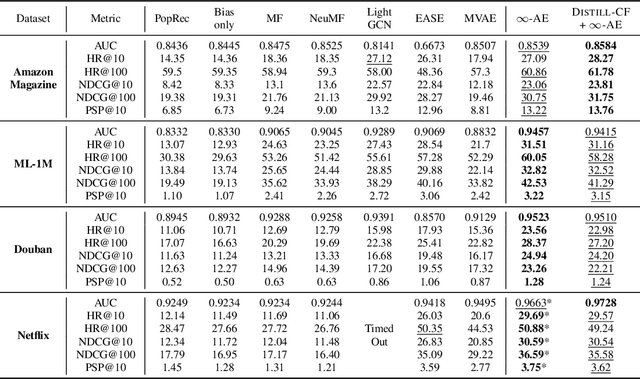
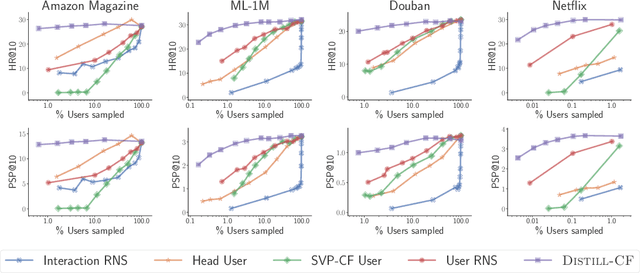
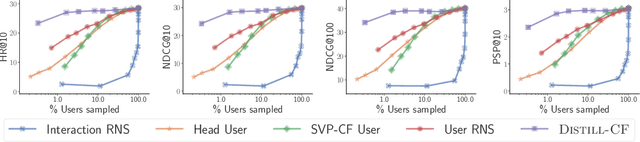
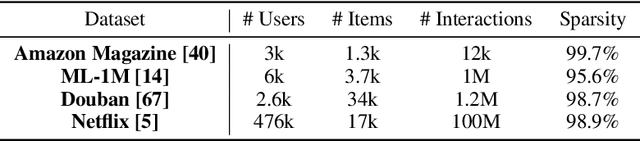
Abstract:We leverage the Neural Tangent Kernel and its equivalence to training infinitely-wide neural networks to devise $\infty$-AE: an autoencoder with infinitely-wide bottleneck layers. The outcome is a highly expressive yet simplistic recommendation model with a single hyper-parameter and a closed-form solution. Leveraging $\infty$-AE's simplicity, we also develop Distill-CF for synthesizing tiny, high-fidelity data summaries which distill the most important knowledge from the extremely large and sparse user-item interaction matrix for efficient and accurate subsequent data-usage like model training, inference, architecture search, etc. This takes a data-centric approach to recommendation, where we aim to improve the quality of logged user-feedback data for subsequent modeling, independent of the learning algorithm. We particularly utilize the concept of differentiable Gumbel-sampling to handle the inherent data heterogeneity, sparsity, and semi-structuredness, while being scalable to datasets with hundreds of millions of user-item interactions. Both of our proposed approaches significantly outperform their respective state-of-the-art and when used together, we observe 96-105% of $\infty$-AE's performance on the full dataset with as little as 0.1% of the original dataset size, leading us to explore the counter-intuitive question: Is more data what you need for better recommendation?
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge