Meghdeep Jana
SafeShift: Safety-Informed Distribution Shifts for Robust Trajectory Prediction in Autonomous Driving
Sep 16, 2023Abstract:As autonomous driving technology matures, safety and robustness of its key components, including trajectory prediction, is vital. Though real-world datasets, such as Waymo Open Motion, provide realistic recorded scenarios for model development, they often lack truly safety-critical situations. Rather than utilizing unrealistic simulation or dangerous real-world testing, we instead propose a framework to characterize such datasets and find hidden safety-relevant scenarios within. Our approach expands the spectrum of safety-relevance, allowing us to study trajectory prediction models under a safety-informed, distribution shift setting. We contribute a generalized scenario characterization method, a novel scoring scheme to find subtly-avoided risky scenarios, and an evaluation of trajectory prediction models in this setting. We further contribute a remediation strategy, achieving a 10% average reduction in prediction collision rates. To facilitate future research, we release our code to the public: github.com/cmubig/SafeShift
T2FPV: Constructing High-Fidelity First-Person View Datasets From Real-World Pedestrian Trajectories
Sep 22, 2022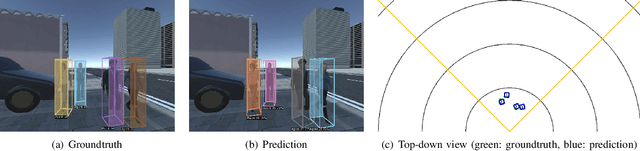
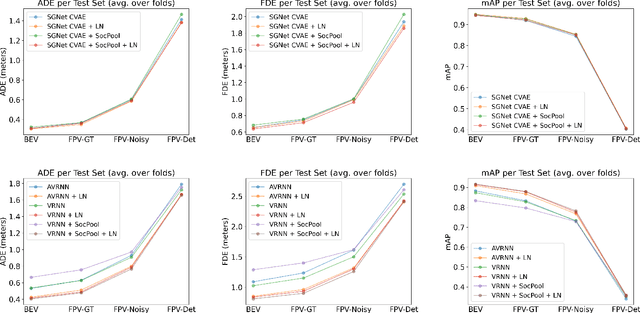
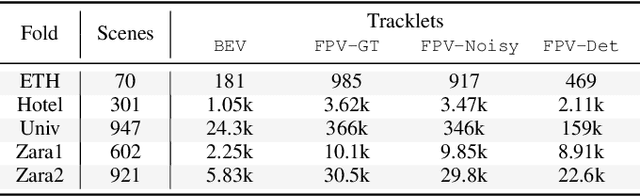
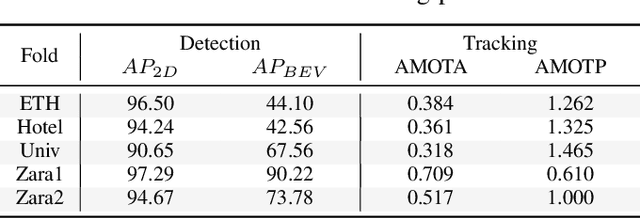
Abstract:Predicting pedestrian motion is essential for developing socially-aware robots that interact in a crowded environment. While the natural visual perspective for a social interaction setting is an egocentric view, the majority of existing work in trajectory prediction has been investigated purely in the top-down trajectory space. To support first-person view trajectory prediction research, we present T2FPV, a method for constructing high-fidelity first-person view datasets given a real-world, top-down trajectory dataset; we showcase our approach on the ETH/UCY pedestrian dataset to generate the egocentric visual data of all interacting pedestrians. We report that the bird's-eye view assumption used in the original ETH/UCY dataset, i.e., an agent can observe everyone in the scene with perfect information, does not hold in the first-person views; only a fraction of agents are fully visible during each 20-timestep scene used commonly in existing work. We evaluate existing trajectory prediction approaches under varying levels of realistic perception -- displacement errors suffer a 356% increase compared to the top-down, perfect information setting. To promote research in first-person view trajectory prediction, we release our T2FPV-ETH dataset and software tools.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge