Md Aminul Haque Palash
Incongruity Detection between Bangla News Headline and Body Content through Graph Neural Network
Oct 26, 2022Abstract:Incongruity between news headlines and the body content is a common method of deception used to attract readers. Profitable headlines pique readers' interest and encourage them to visit a specific website. This is usually done by adding an element of dishonesty, using enticements that do not precisely reflect the content being delivered. As a result, automatic detection of incongruent news between headline and body content using language analysis has gained the research community's attention. However, various solutions are primarily being developed for English to address this problem, leaving low-resource languages out of the picture. Bangla is ranked 7th among the top 100 most widely spoken languages, which motivates us to pay special attention to the Bangla language. Furthermore, Bangla has a more complex syntactic structure and fewer natural language processing resources, so it becomes challenging to perform NLP tasks like incongruity detection and stance detection. To tackle this problem, for the Bangla language, we offer a graph-based hierarchical dual encoder (BGHDE) model that learns the content similarity and contradiction between Bangla news headlines and content paragraphs effectively. The experimental results show that the proposed Bangla graph-based neural network model achieves above 90% accuracy on various Bangla news datasets.
Brain Tumor Segmentation using Enhanced U-Net Model with Empirical Analysis
Oct 24, 2022Abstract:Cancer of the brain is deadly and requires careful surgical segmentation. The brain tumors were segmented using U-Net using a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). When looking for overlaps of necrotic, edematous, growing, and healthy tissue, it might be hard to get relevant information from the images. The 2D U-Net network was improved and trained with the BraTS datasets to find these four areas. U-Net can set up many encoder and decoder routes that can be used to get information from images that can be used in different ways. To reduce computational time, we use image segmentation to exclude insignificant background details. Experiments on the BraTS datasets show that our proposed model for segmenting brain tumors from MRI (MRI) works well. In this study, we demonstrate that the BraTS datasets for 2017, 2018, 2019, and 2020 do not significantly differ from the BraTS 2019 dataset's attained dice scores of 0.8717 (necrotic), 0.9506 (edema), and 0.9427 (enhancing).
A Survey of Recommender System Techniques and the Ecommerce Domain
Aug 15, 2022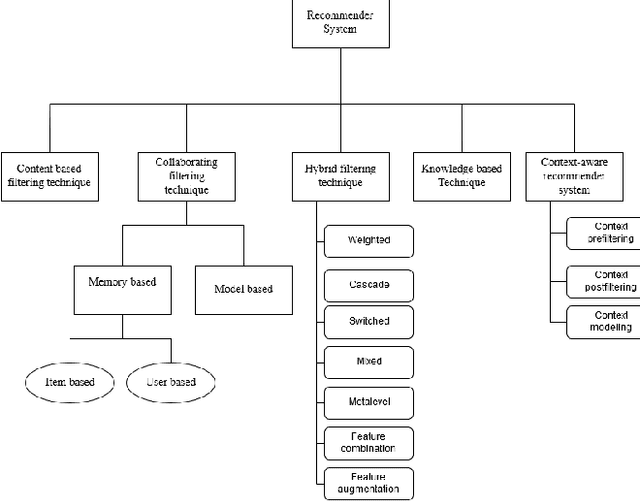

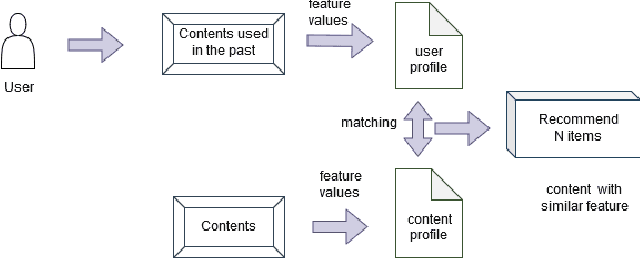
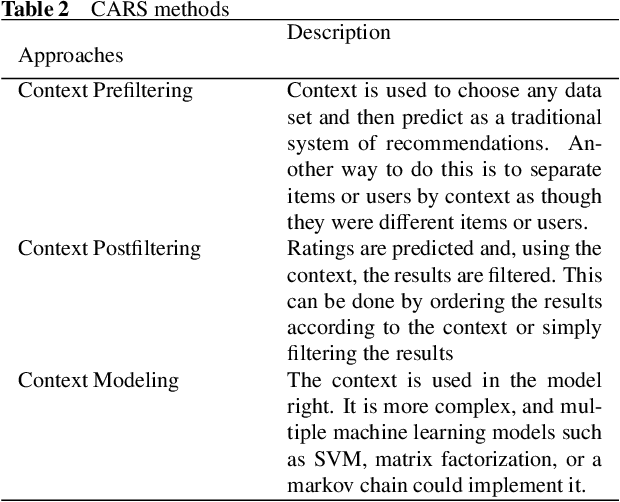
Abstract:In this big data era, it is hard for the current generation to find the right data from the huge amount of data contained within online platforms. In such a situation, there is a need for an information filtering system that might help them find the information they are looking for. In recent years, a research field has emerged known as recommender systems. Recommenders have become important as they have many real-life applications. This paper reviews the different techniques and developments of recommender systems in e-commerce, e-tourism, e-resources, e-government, e-learning, and e-library. By analyzing recent work on this topic, we will be able to provide a detailed overview of current developments and identify existing difficulties in recommendation systems. The final results give practitioners and researchers the necessary guidance and insights into the recommendation system and its application.
Bangla Image Caption Generation through CNN-Transformer based Encoder-Decoder Network
Oct 24, 2021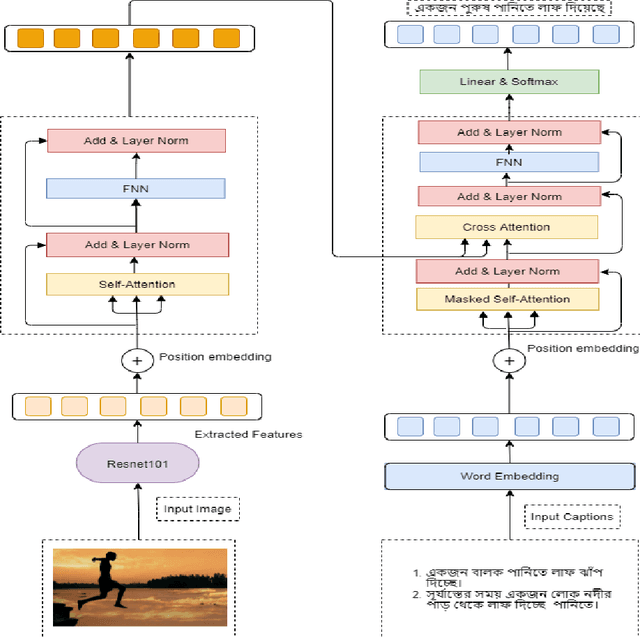
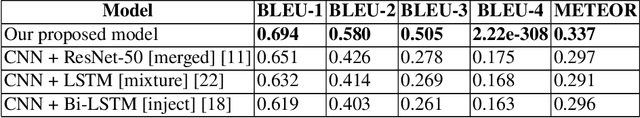
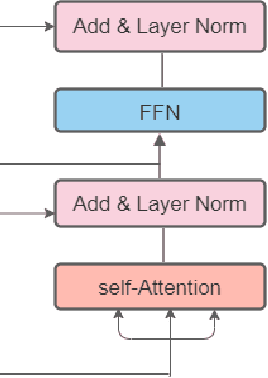
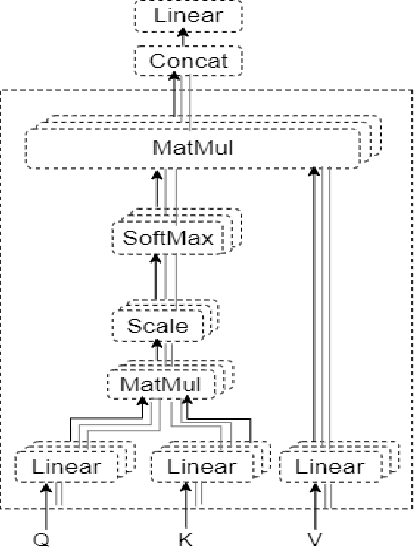
Abstract:Automatic Image Captioning is the never-ending effort of creating syntactically and validating the accuracy of textual descriptions of an image in natural language with context. The encoder-decoder structure used throughout existing Bengali Image Captioning (BIC) research utilized abstract image feature vectors as the encoder's input. We propose a novel transformer-based architecture with an attention mechanism with a pre-trained ResNet-101 model image encoder for feature extraction from images. Experiments demonstrate that the language decoder in our technique captures fine-grained information in the caption and, then paired with image features, produces accurate and diverse captions on the BanglaLekhaImageCaptions dataset. Our approach outperforms all existing Bengali Image Captioning work and sets a new benchmark by scoring 0.694 on BLEU-1, 0.630 on BLEU-2, 0.582 on BLEU-3, and 0.337 on METEOR.
Fine-Grained Image Generation from Bangla Text Description using Attentional Generative Adversarial Network
Sep 24, 2021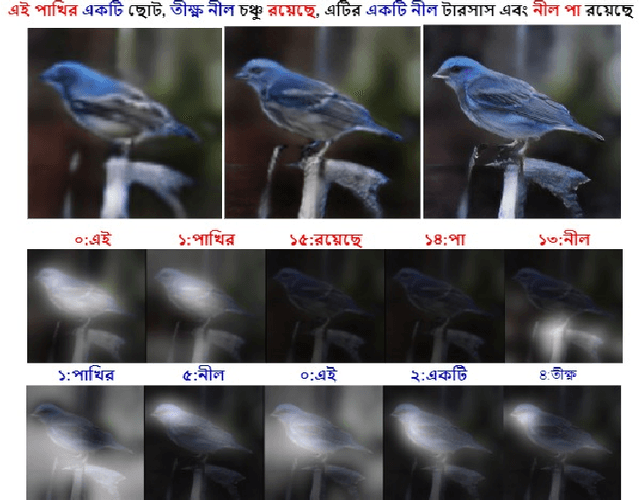
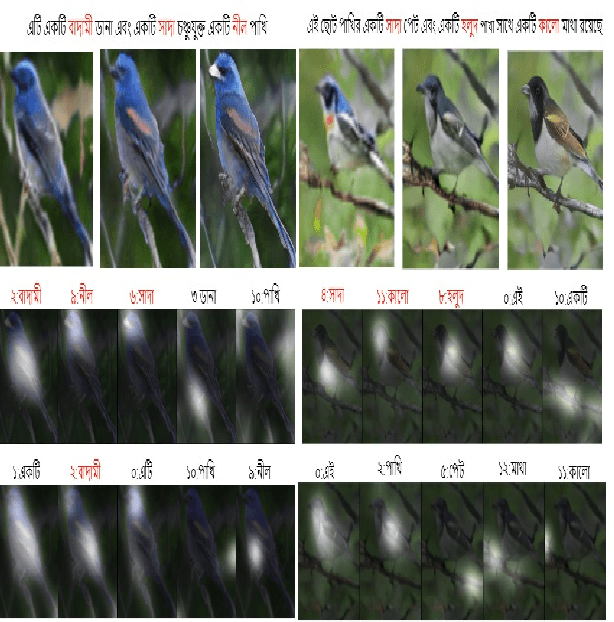
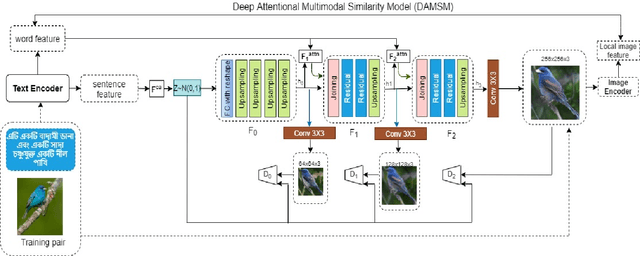


Abstract:Generating fine-grained, realistic images from text has many applications in the visual and semantic realm. Considering that, we propose Bangla Attentional Generative Adversarial Network (AttnGAN) that allows intensified, multi-stage processing for high-resolution Bangla text-to-image generation. Our model can integrate the most specific details at different sub-regions of the image. We distinctively concentrate on the relevant words in the natural language description. This framework has achieved a better inception score on the CUB dataset. For the first time, a fine-grained image is generated from Bangla text using attentional GAN. Bangla has achieved 7th position among 100 most spoken languages. This inspires us to explicitly focus on this language, which will ensure the inevitable need of many people. Moreover, Bangla has a more complex syntactic structure and less natural language processing resource that validates our work more.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge