Mayuresh Anand
Composite Re-Ranking for Efficient Document Search with BERT
Mar 12, 2021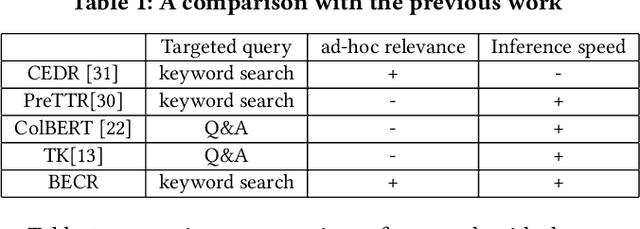
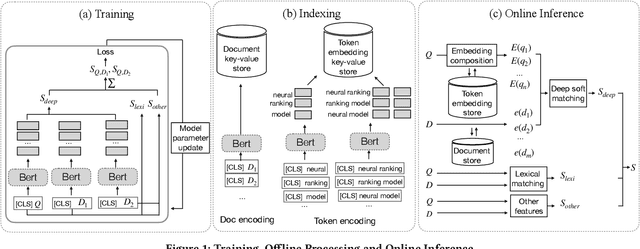
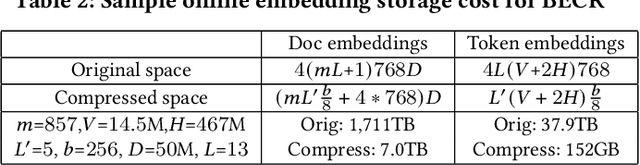
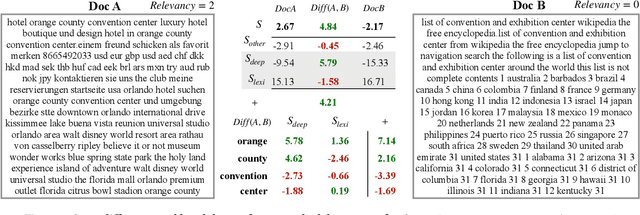
Abstract:Although considerable efforts have been devoted to transformer-based ranking models for document search, the relevance-efficiency tradeoff remains a critical problem for ad-hoc ranking. To overcome this challenge, this paper presents BECR (BERT-based Composite Re-Ranking), a composite re-ranking scheme that combines deep contextual token interactions and traditional lexical term-matching features. In particular, BECR exploits a token encoding mechanism to decompose the query representations into pre-computable uni-grams and skip-n-grams. By applying token encoding on top of a dual-encoder architecture, BECR separates the attentions between a query and a document while capturing the contextual semantics of a query. In contrast to previous approaches, this framework does not perform expensive BERT computations during online inference. Thus, it is significantly faster, yet still able to achieve high competitiveness in ad-hoc ranking relevance. Finally, an in-depth comparison between BECR and other start-of-the-art neural ranking baselines is described using the TREC datasets, thereby further demonstrating the enhanced relevance and efficiency of BECR.
Causal-BERT : Language models for causality detection between events expressed in text
Dec 10, 2020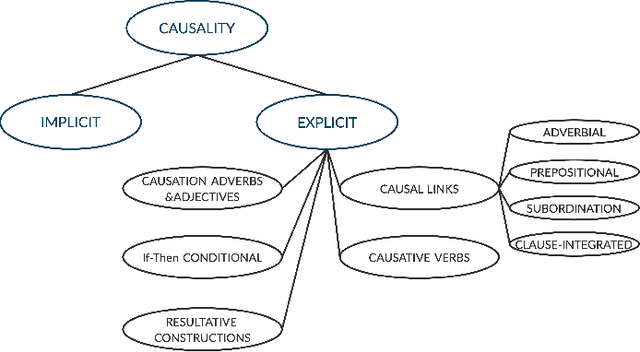
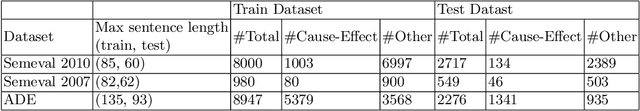
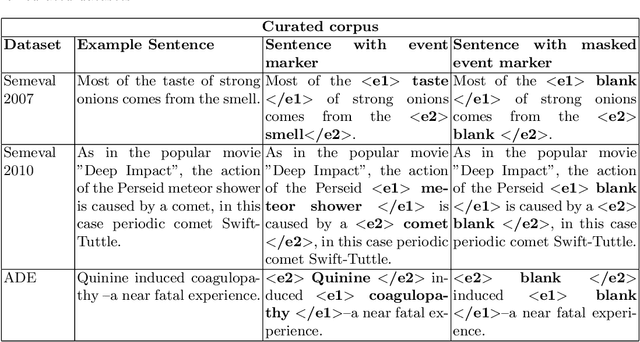

Abstract:Causality understanding between events is a critical natural language processing task that is helpful in many areas, including health care, business risk management and finance. On close examination, one can find a huge amount of textual content both in the form of formal documents or in content arising from social media like Twitter, dedicated to communicating and exploring various types of causality in the real world. Recognizing these "Cause-Effect" relationships between natural language events continues to remain a challenge simply because it is often expressed implicitly. Implicit causality is hard to detect through most of the techniques employed in literature and can also, at times be perceived as ambiguous or vague. Also, although well-known datasets do exist for this problem, the examples in them are limited in the range and complexity of the causal relationships they depict especially when related to implicit relationships. Most of the contemporary methods are either based on lexico-semantic pattern matching or are feature-driven supervised methods. Therefore, as expected these methods are more geared towards handling explicit causal relationships leading to limited coverage for implicit relationships and are hard to generalize. In this paper, we investigate the language model's capabilities for causal association among events expressed in natural language text using sentence context combined with event information, and by leveraging masked event context with in-domain and out-of-domain data distribution. Our proposed methods achieve the state-of-art performance in three different data distributions and can be leveraged for extraction of a causal diagram and/or building a chain of events from unstructured text.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge