Max Witjes
Quantifying the effect of speech pathology on automatic and human speaker verification
Jun 10, 2024



Abstract:This study investigates how surgical intervention for speech pathology (specifically, as a result of oral cancer surgery) impacts the performance of an automatic speaker verification (ASV) system. Using two recently collected Dutch datasets with parallel pre and post-surgery audio from the same speaker, NKI-OC-VC and SPOKE, we assess the extent to which speech pathology influences ASV performance, and whether objective/subjective measures of speech severity are correlated with the performance. Finally, we carry out a perceptual study to compare judgements of ASV and human listeners. Our findings reveal that pathological speech negatively affects ASV performance, and the severity of the speech is negatively correlated with the performance. There is a moderate agreement in perceptual and objective scores of speaker similarity and severity, however, we could not clearly establish in the perceptual study, whether the same phenomenon also exists in human perception.
Manipulation of oral cancer speech using neural articulatory synthesis
Mar 31, 2022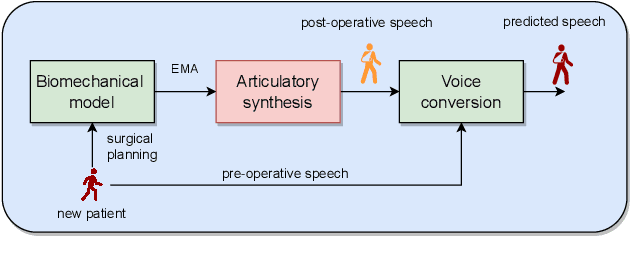
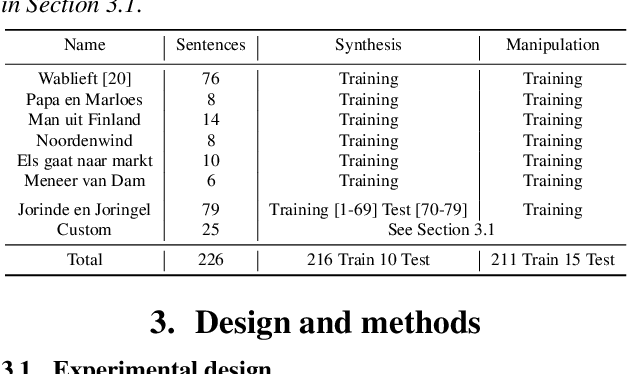
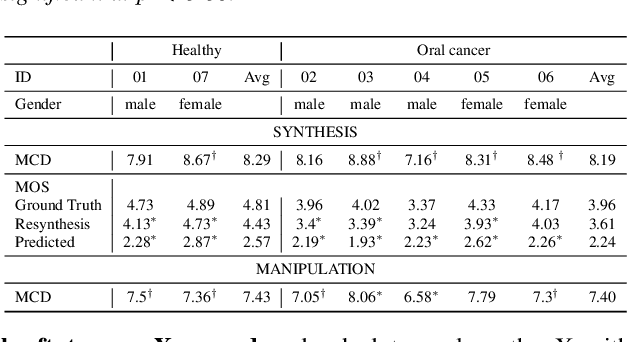
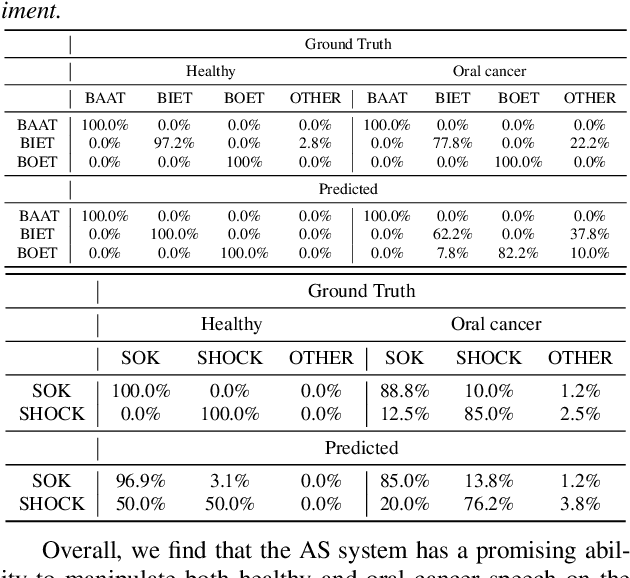
Abstract:We present an articulatory synthesis framework for the synthesis and manipulation of oral cancer speech for clinical decision making and alleviation of patient stress. Objective and subjective evaluations demonstrate that the framework has acceptable naturalness and is worth further investigation. A subsequent subjective vowel and consonant identification experiment showed that the articulatory synthesis system can manipulate the articulatory trajectories so that the synthesised speech reproduces problems present in the ground truth oral cancer speech.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge