Matej Moravčík
DeepStack: Expert-Level Artificial Intelligence in No-Limit Poker
Mar 03, 2017Abstract:Artificial intelligence has seen several breakthroughs in recent years, with games often serving as milestones. A common feature of these games is that players have perfect information. Poker is the quintessential game of imperfect information, and a longstanding challenge problem in artificial intelligence. We introduce DeepStack, an algorithm for imperfect information settings. It combines recursive reasoning to handle information asymmetry, decomposition to focus computation on the relevant decision, and a form of intuition that is automatically learned from self-play using deep learning. In a study involving 44,000 hands of poker, DeepStack defeated with statistical significance professional poker players in heads-up no-limit Texas hold'em. The approach is theoretically sound and is shown to produce more difficult to exploit strategies than prior approaches.
AIVAT: A New Variance Reduction Technique for Agent Evaluation in Imperfect Information Games
Jan 19, 2017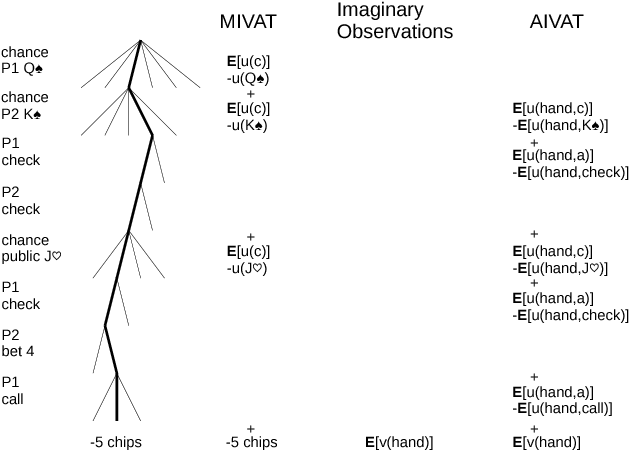
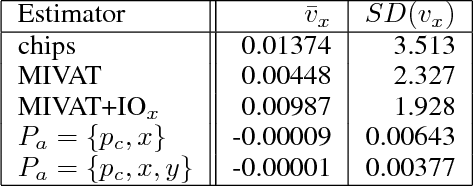
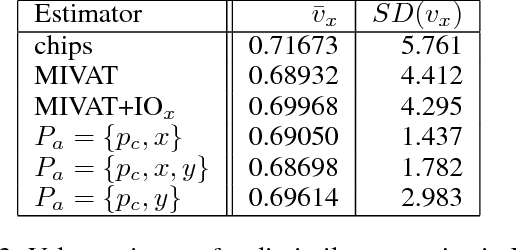
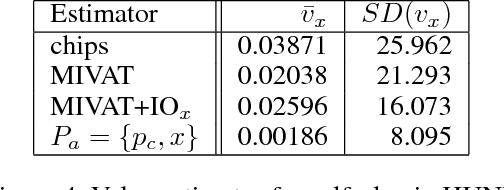
Abstract:Evaluating agent performance when outcomes are stochastic and agents use randomized strategies can be challenging when there is limited data available. The variance of sampled outcomes may make the simple approach of Monte Carlo sampling inadequate. This is the case for agents playing heads-up no-limit Texas hold'em poker, where man-machine competitions have involved multiple days of consistent play and still not resulted in statistically significant conclusions even when the winner's margin is substantial. In this paper, we introduce AIVAT, a low variance, provably unbiased value assessment tool that uses an arbitrary heuristic estimate of state value, as well as the explicit strategy of a subset of the agents. Unlike existing techniques which reduce the variance from chance events, or only consider game ending actions, AIVAT reduces the variance both from choices by nature and by players with a known strategy. The resulting estimator in no-limit poker can reduce the number of hands needed to draw statistical conclusions by more than a factor of 10.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge