Masoud Nosrati
Practical Issues of Action-conditioned Next Image Prediction
Feb 08, 2018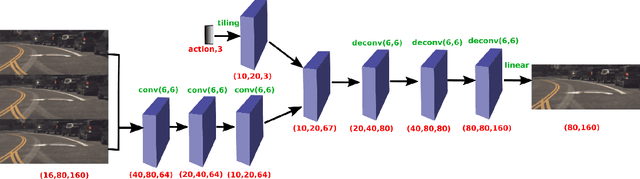
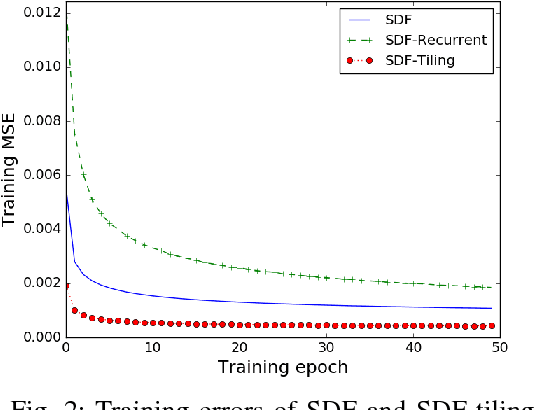
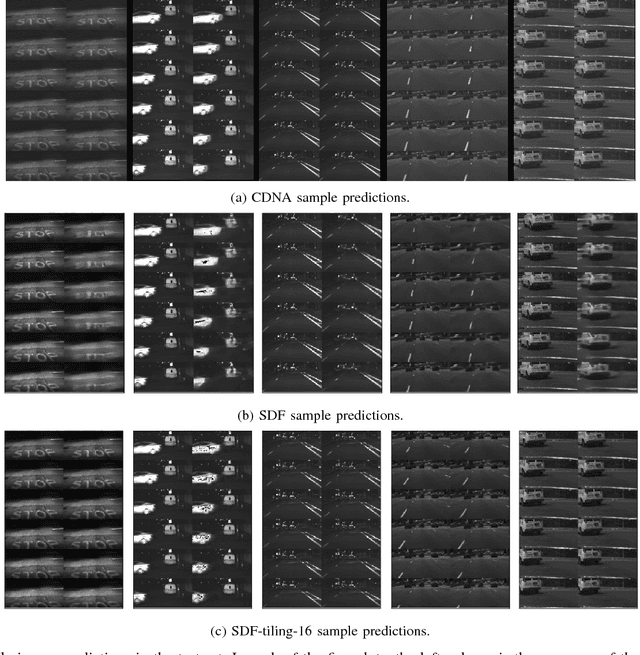
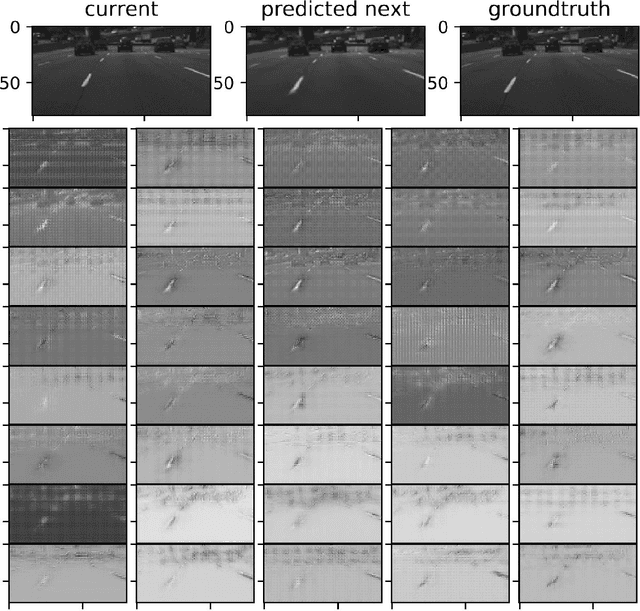
Abstract:The problem of action-conditioned image prediction is to predict the expected next frame given the current camera frame the robot observes and an action selected by the robot. We provide the first comparison of two recent popular models, especially for image prediction on cars. Our major finding is that action tiling encoding is the most important factor leading to the remarkable performance of the CDNA model. We present a light-weight model by action tiling encoding which has a single-decoder feedforward architecture same as [action_video_prediction_honglak]. On a real driving dataset, the CDNA model achieves ${0.3986} \times 10^{-3}$ MSE and ${0.9846}$ Structure SIMilarity (SSIM) with a network size of about {\bfseries ${12.6}$ million} parameters. With a small network of fewer than {\bfseries ${1}$ million} parameters, our new model achieves a comparable performance to CDNA at ${0.3613} \times 10^{-3}$ MSE and ${0.9633}$ SSIM. Our model requires less memory, is more computationally efficient and is advantageous to be used inside self-driving vehicles.
Language free character recognition using character sketch and center of gravity shifting
Aug 03, 2016



Abstract:In this research, we present a heuristic method for character recognition. For this purpose, a sketch is constructed from the image that contains the character to be recognized. This sketch contains the most important pixels of image that are representatives of original image. These points are the most probable points in pixel-by-pixel matching of image that adapt to target image. Furthermore, a technique called gravity shifting is utilized for taking over the problem of elongation of characters. The consequence of combining sketch and gravity techniques leaded to a language free character recognition method. This method can be implemented independently for real-time uses or in combination of other classifiers as a feature extraction algorithm. Low complexity and acceptable performance are the most impressive features of this method that let it to be simply implemented in mobile and battery-limited computing devices. Results show that in the best case 86% of accuracy is obtained and in the worst case 28% of recognized characters are accurate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge