Masafumi Takahashi
Motion Capture Dataset for Practical Use of AI-based Motion Editing and Stylization
Jun 15, 2023Abstract:In this work, we proposed a new style-diverse dataset for the domain of motion style transfer. The motion dataset uses an industrial-standard human bone structure and thus is industry-ready to be plugged into 3D characters for many projects. We claim the challenges in motion style transfer and encourage future work in this domain by releasing the proposed motion dataset to the public. We conduct a comprehensive study on motion style transfer in the experiment using the state-of-the-art method, and the results show the proposed dataset's validity for the motion style transfer task.
Spatial Data Augmentation with Simulated Room Impulse Responses for Sound Event Localization and Detection
Oct 13, 2021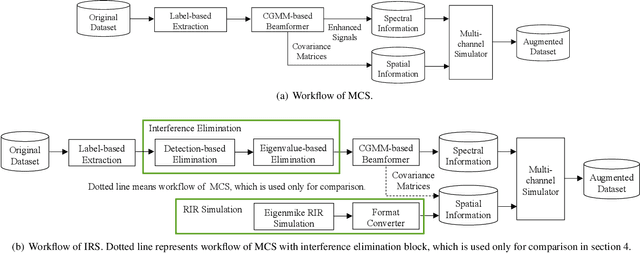
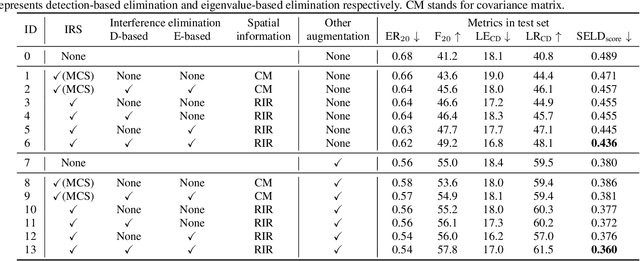

Abstract:Recording and annotating real sound events for a sound event localization and detection (SELD) task is time consuming, and data augmentation techniques are often favored when the amount of data is limited. However, how to augment the spatial information in a dataset, including unlabeled directional interference events, remains an open research question. Furthermore, directional interference events make it difficult to accurately extract spatial characteristics from target sound events. To address this problem, we propose an impulse response simulation framework (IRS) that augments spatial characteristics using simulated room impulse responses (RIR). RIRs corresponding to a microphone array assumed to be placed in various rooms are accurately simulated, and the source signals of the target sound events are extracted from a mixture. The simulated RIRs are then convolved with the extracted source signals to obtain an augmented multi-channel training dataset. Evaluation results obtained using the TAU-NIGENS Spatial Sound Events 2021 dataset show that the IRS contributes to improving the overall SELD performance. Additionally, we conducted an ablation study to discuss the contribution and need for each component within the IRS.
Ensemble of ACCDOA- and EINV2-based Systems with D3Nets and Impulse Response Simulation for Sound Event Localization and Detection
Jun 21, 2021
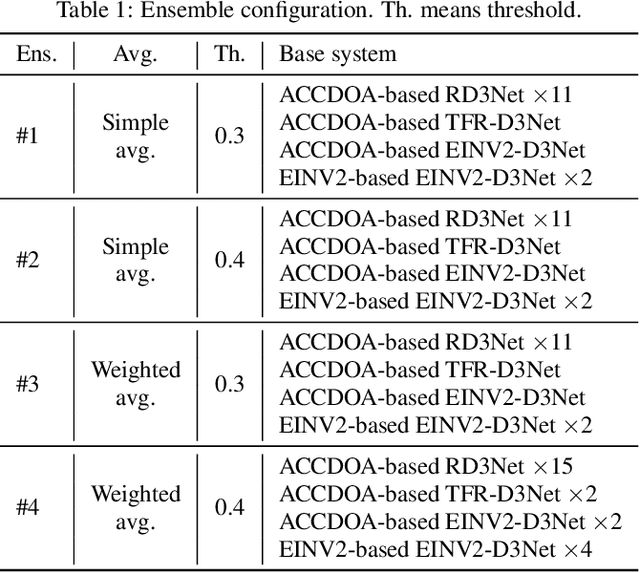


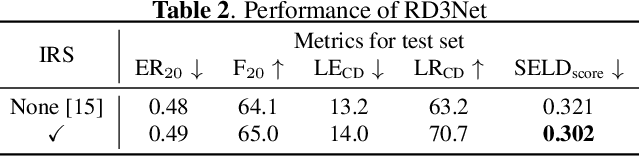
Abstract:This report describes our systems submitted to the DCASE2021 challenge task 3: sound event localization and detection (SELD) with directional interference. Our previous system based on activity-coupled Cartesian direction of arrival (ACCDOA) representation enables us to solve a SELD task with a single target. This ACCDOA-based system with efficient network architecture called RD3Net and data augmentation techniques outperformed state-of-the-art SELD systems in terms of localization and location-dependent detection. Using the ACCDOA-based system as a base, we perform model ensembles by averaging outputs of several systems trained with different conditions such as input features, training folds, and model architectures. We also use the event independent network v2 (EINV2)-based system to increase the diversity of the model ensembles. To generalize the models, we further propose impulse response simulation (IRS), which generates simulated multi-channel signals by convolving simulated room impulse responses (RIRs) with source signals extracted from the original dataset. Our systems significantly improved over the baseline system on the development dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge