Martin Zubeldia
A General-Purpose Theorem for High-Probability Bounds of Stochastic Approximation with Polyak Averaging
May 27, 2025Abstract:Polyak-Ruppert averaging is a widely used technique to achieve the optimal asymptotic variance of stochastic approximation (SA) algorithms, yet its high-probability performance guarantees remain underexplored in general settings. In this paper, we present a general framework for establishing non-asymptotic concentration bounds for the error of averaged SA iterates. Our approach assumes access to individual concentration bounds for the unaveraged iterates and yields a sharp bound on the averaged iterates. We also construct an example, showing the tightness of our result up to constant multiplicative factors. As direct applications, we derive tight concentration bounds for contractive SA algorithms and for algorithms such as temporal difference learning and Q-learning with averaging, obtaining new bounds in settings where traditional analysis is challenging.
Concentration of Contractive Stochastic Approximation: Additive and Multiplicative Noise
Mar 28, 2023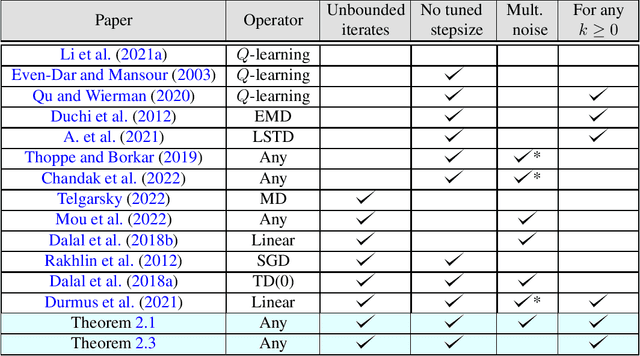
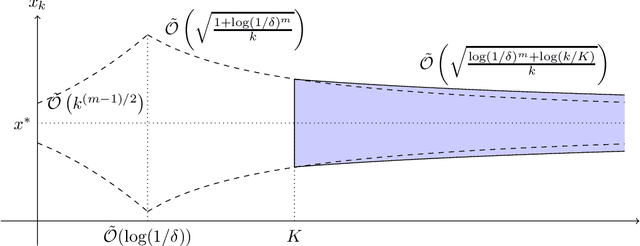
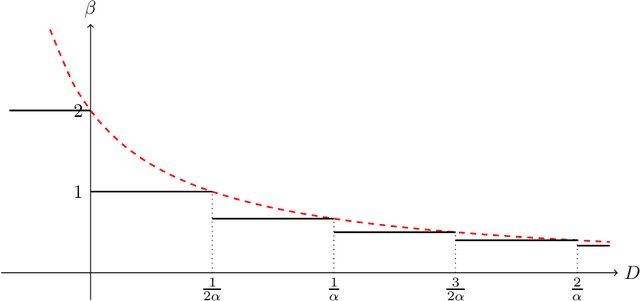
Abstract:In this work, we study the concentration behavior of a stochastic approximation (SA) algorithm under a contractive operator with respect to an arbitrary norm. We consider two settings where the iterates are potentially unbounded: (1) bounded multiplicative noise, and (2) additive sub-Gaussian noise. We obtain maximal concentration inequalities on the convergence errors, and show that these errors have sub-Gaussian tails in the additive noise setting, and super-polynomial tails (faster than polynomial decay) in the multiplicative noise setting. In addition, we provide an impossibility result showing that it is in general not possible to achieve sub-exponential tails for SA with multiplicative noise. To establish these results, we develop a novel bootstrapping argument that involves bounding the moment generating function of the generalized Moreau envelope of the error and the construction of an exponential supermartingale to enable using Ville's maximal inequality. To demonstrate the applicability of our theoretical results, we use them to provide maximal concentration bounds for a large class of reinforcement learning algorithms, including but not limited to on-policy TD-learning with linear function approximation, off-policy TD-learning with generalized importance sampling factors, and $Q$-learning. To the best of our knowledge, super-polynomial concentration bounds for off-policy TD-learning have not been established in the literature due to the challenge of handling the combination of unbounded iterates and multiplicative noise.
Collaboratively Learning the Best Option, Using Bounded Memory
Mar 06, 2018
Abstract:We consider multi-armed bandit problems in social groups wherein each individual has bounded memory and shares the common goal of learning the best arm/option. We say an individual learns the best option if eventually (as $t \to \infty$) it pulls only the arm with the highest average reward. While this goal is provably impossible for an isolated individual, we show that, in social groups, this goal can be achieved easily with the aid of social persuasion, i.e., communication. Specifically, we study the learning dynamics wherein an individual sequentially decides on which arm to pull next based on not only its private reward feedback but also the suggestions provided by randomly chosen peers. Our learning dynamics are hard to analyze via explicit probabilistic calculations due to the stochastic dependency induced by social interaction. Instead, we employ the mean-field approximation method from statistical physics and we show: (1) With probability $\to 1$ as the social group size $N \to \infty $, every individual in the social group learns the best option. (2) Over an arbitrary finite time horizon $[0, T]$, with high probability (in $N$), the fraction of individuals that prefer the best option grows to 1 exponentially fast as $t$ increases ($t\in [0, T]$). A major innovation of our mean-filed analysis is a simple yet powerful technique to deal with absorbing states in the interchange of limits $N \to \infty$ and $t \to \infty $. The mean-field approximation method allows us to approximate the probabilistic sample paths of our learning dynamics by a deterministic and smooth trajectory that corresponds to the unique solution of a well-behaved system of ordinary differential equations (ODEs). Such an approximation is desired because the analysis of a system of ODEs is relatively easier than that of the original stochastic system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge