Martin Kersner
Temporal Knowledge Distillation for On-device Audio Classification
Oct 27, 2021



Abstract:Improving the performance of on-device audio classification models remains a challenge given the computational limits of the mobile environment. Many studies leverage knowledge distillation to boost predictive performance by transferring the knowledge from large models to on-device models. However, most lack the essence of the temporal information which is crucial to audio classification tasks, or similar architecture is often required. In this paper, we propose a new knowledge distillation method designed to incorporate the temporal knowledge embedded in attention weights of large models to on-device models. Our distillation method is applicable to various types of architectures, including the non-attention-based architectures such as CNNs or RNNs, without any architectural change during inference. Through extensive experiments on both an audio event detection dataset and a noisy keyword spotting dataset, we show that our proposed method improves the predictive performance across diverse on-device architectures.
MarioNETte: Few-shot Face Reenactment Preserving Identity of Unseen Targets
Nov 19, 2019
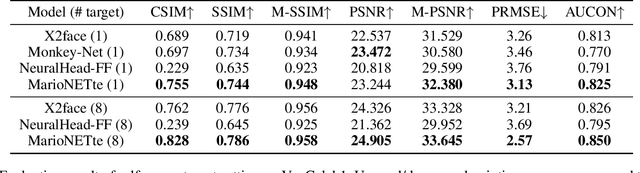
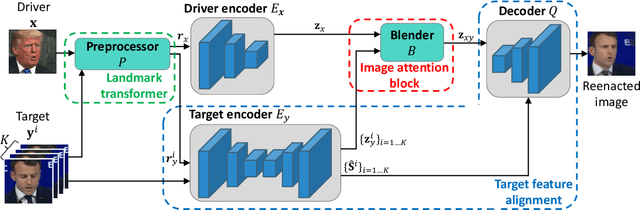

Abstract:When there is a mismatch between the target identity and the driver identity, face reenactment suffers severe degradation in the quality of the result, especially in a few-shot setting. The identity preservation problem, where the model loses the detailed information of the target leading to a defective output, is the most common failure mode. The problem has several potential sources such as the identity of the driver leaking due to the identity mismatch, or dealing with unseen large poses. To overcome such problems, we introduce components that address the mentioned problem: image attention block, target feature alignment, and landmark transformer. Through attending and warping the relevant features, the proposed architecture, called MarioNETte, produces high-quality reenactments of unseen identities in a few-shot setting. In addition, the landmark transformer dramatically alleviates the identity preservation problem by isolating the expression geometry through landmark disentanglement. Comprehensive experiments are performed to verify that the proposed framework can generate highly realistic faces, outperforming all other baselines, even under a significant mismatch of facial characteristics between the target and the driver.
Towards Real-Time Automatic Portrait Matting on Mobile Devices
Apr 08, 2019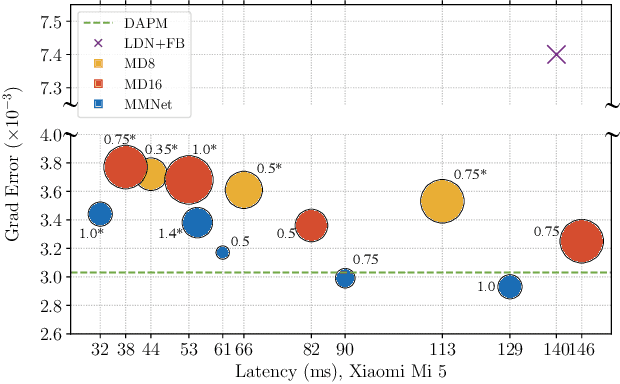
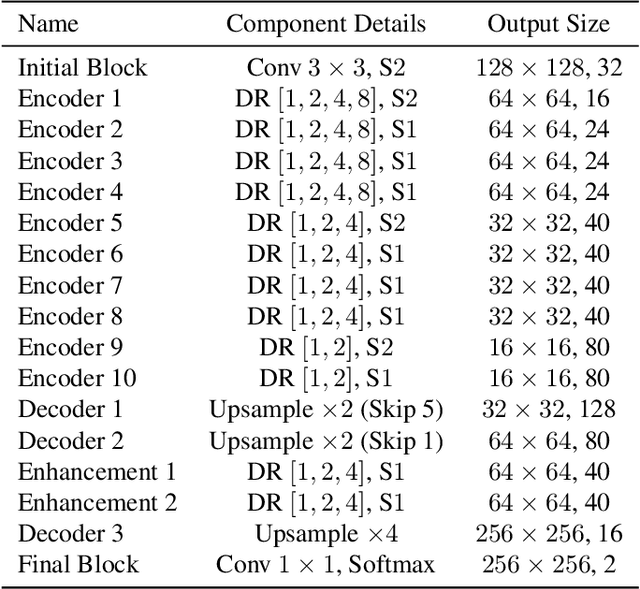
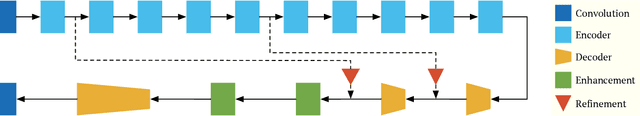
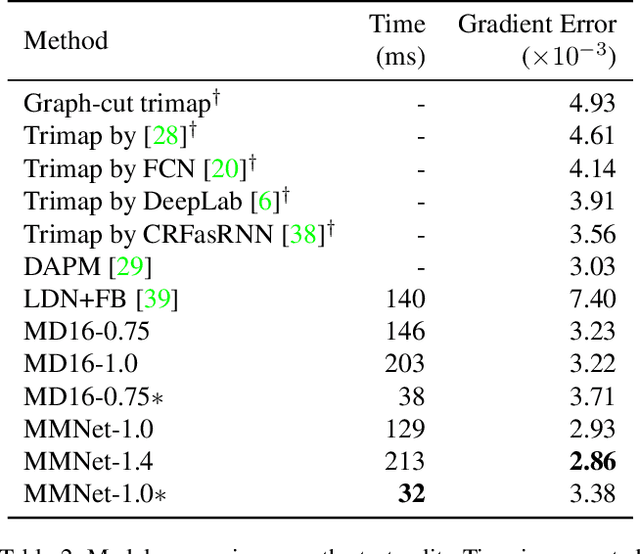
Abstract:We tackle the problem of automatic portrait matting on mobile devices. The proposed model is aimed at attaining real-time inference on mobile devices with minimal degradation of model performance. Our model MMNet, based on multi-branch dilated convolution with linear bottleneck blocks, outperforms the state-of-the-art model and is orders of magnitude faster. The model can be accelerated four times to attain 30 FPS on Xiaomi Mi 5 device with moderate increase in the gradient error. Under the same conditions, our model has an order of magnitude less number of parameters and is faster than Mobile DeepLabv3 while maintaining comparable performance. The accompanied implementation can be found at \url{https://github.com/hyperconnect/MMNet}.
Temporal Convolution for Real-time Keyword Spotting on Mobile Devices
Apr 08, 2019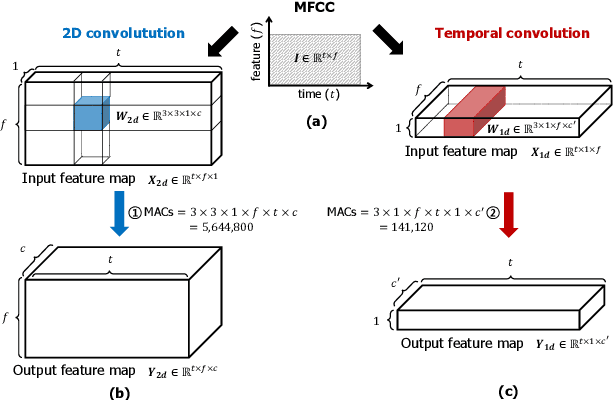
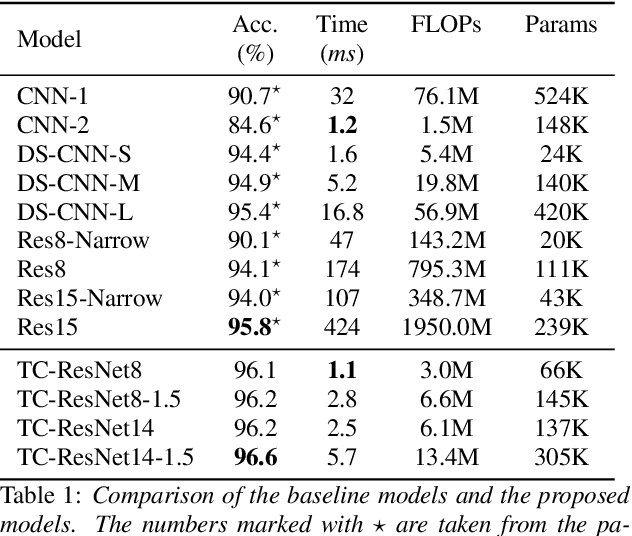
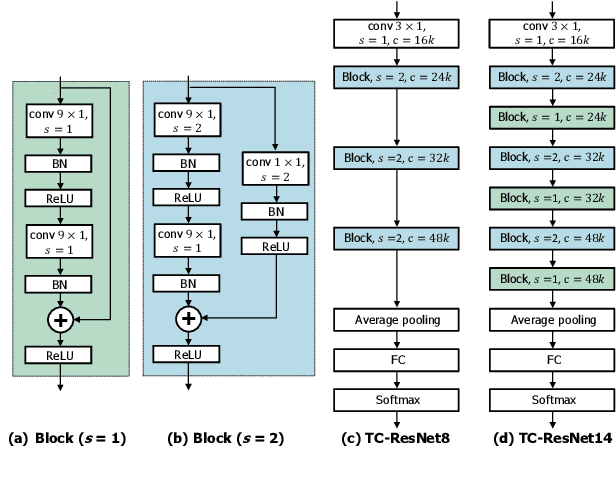
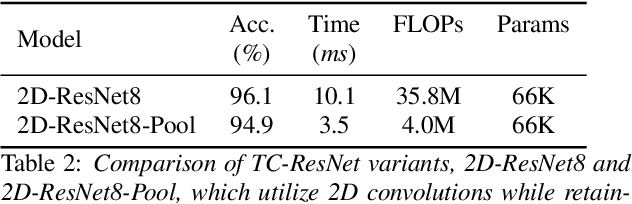
Abstract:Keyword spotting (KWS) plays a critical role in enabling speech-based user interactions on smart devices. Recent developments in the field of deep learning have led to wide adoption of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) in KWS systems due to their exceptional accuracy and robustness. The main challenge faced by KWS systems is the trade-off between high accuracy and low latency. Unfortunately, there has been little quantitative analysis of the actual latency of KWS models on mobile devices. This is especially concerning since conventional convolution-based KWS approaches are known to require a large number of operations to attain an adequate level of performance. In this paper, we propose a temporal convolution for real-time KWS on mobile devices. Unlike most of the 2D convolution-based KWS approaches that require a deep architecture to fully capture both low- and high-frequency domains, we exploit temporal convolutions with a compact ResNet architecture. In Google Speech Command Dataset, we achieve more than \textbf{385x} speedup on Google Pixel 1 and surpass the accuracy compared to the state-of-the-art model. In addition, we release the implementation of the proposed and the baseline models including an end-to-end pipeline for training models and evaluating them on mobile devices.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge