Mark Sammons
Open-Domain Frame Semantic Parsing Using Transformers
Oct 23, 2020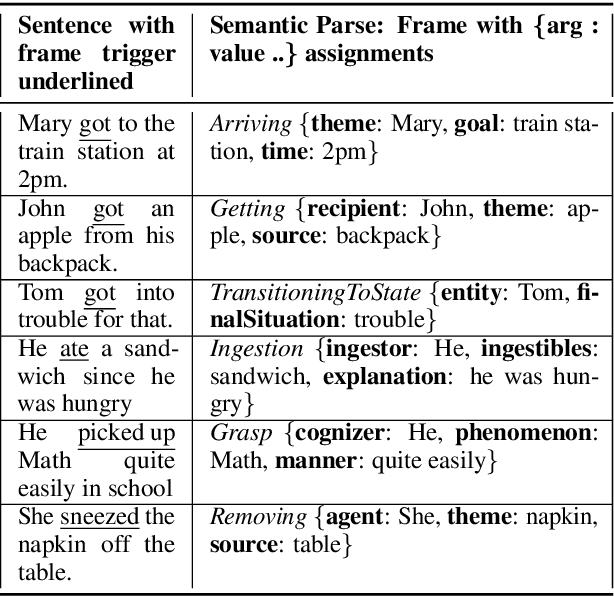
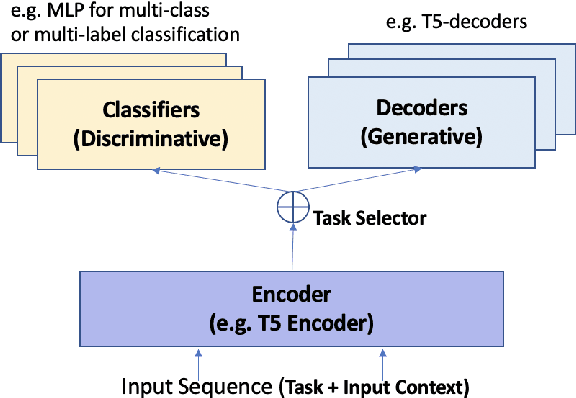
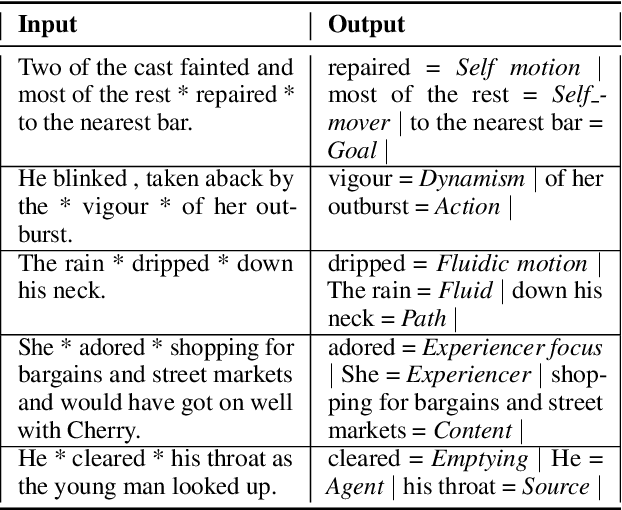
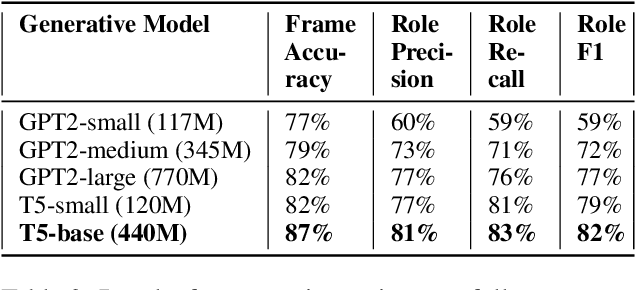
Abstract:Frame semantic parsing is a complex problem which includes multiple underlying subtasks. Recent approaches have employed joint learning of subtasks (such as predicate and argument detection), and multi-task learning of related tasks (such as syntactic and semantic parsing). In this paper, we explore multi-task learning of all subtasks with transformer-based models. We show that a purely generative encoder-decoder architecture handily beats the previous state of the art in FrameNet 1.7 parsing, and that a mixed decoding multi-task approach achieves even better performance. Finally, we show that the multi-task model also outperforms recent state of the art systems for PropBank SRL parsing on the CoNLL 2012 benchmark.
On the Strength of Character Language Models for Multilingual Named Entity Recognition
Sep 20, 2018



Abstract:Character-level patterns have been widely used as features in English Named Entity Recognition (NER) systems. However, to date there has been no direct investigation of the inherent differences between name and non-name tokens in text, nor whether this property holds across multiple languages. This paper analyzes the capabilities of corpus-agnostic Character-level Language Models (CLMs) in the binary task of distinguishing name tokens from non-name tokens. We demonstrate that CLMs provide a simple and powerful model for capturing these differences, identifying named entity tokens in a diverse set of languages at close to the performance of full NER systems. Moreover, by adding very simple CLM-based features we can significantly improve the performance of an off-the-shelf NER system for multiple languages.
* 5 pages, EMNLP 2018 short paper
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge