Marius Zoellner
Cycle-Consistent World Models for Domain Independent Latent Imagination
Oct 02, 2021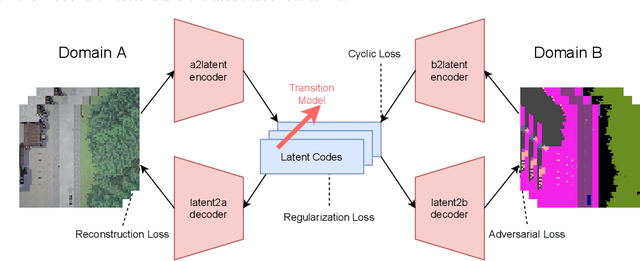

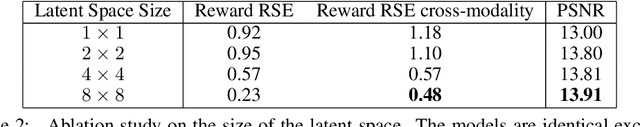
Abstract:End-to-end autonomous driving seeks to solve the perception, decision, and control problems in an integrated way, which can be easier to generalize at scale and be more adapting to new scenarios. However, high costs and risks make it very hard to train autonomous cars in the real world. Simulations can therefore be a powerful tool to enable training. Due to slightly different observations, agents trained and evaluated solely in simulation often perform well there but have difficulties in real-world environments. To tackle this problem, we propose a novel model-based reinforcement learning approach called Cycleconsistent World Models. Contrary to related approaches, our model can embed two modalities in a shared latent space and thereby learn from samples in one modality (e.g., simulated data) and be used for inference in different domain (e.g., real-world data). Our experiments using different modalities in the CARLA simulator showed that this enables CCWM to outperform state-of-the-art domain adaptation approaches. Furthermore, we show that CCWM can decode a given latent representation into semantically coherent observations in both modalities.
MultiNet: Real-time Joint Semantic Reasoning for Autonomous Driving
May 08, 2018
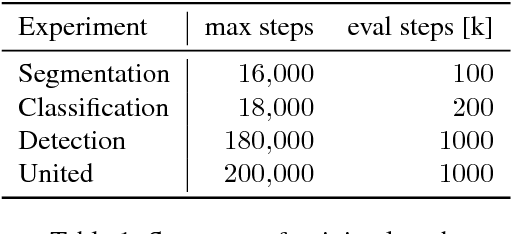
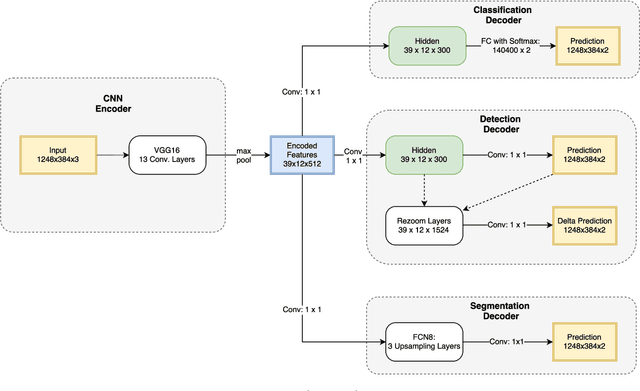
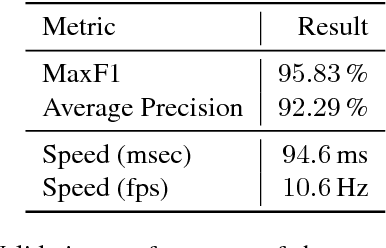
Abstract:While most approaches to semantic reasoning have focused on improving performance, in this paper we argue that computational times are very important in order to enable real time applications such as autonomous driving. Towards this goal, we present an approach to joint classification, detection and semantic segmentation via a unified architecture where the encoder is shared amongst the three tasks. Our approach is very simple, can be trained end-to-end and performs extremely well in the challenging KITTI dataset, outperforming the state-of-the-art in the road segmentation task. Our approach is also very efficient, taking less than 100 ms to perform all tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge