Marina Fernandez Garcia
Towards contrast- and pathology-agnostic clinical fetal brain MRI segmentation using SynthSeg
Apr 14, 2025



Abstract:Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has played a crucial role in fetal neurodevelopmental research. Structural annotations of MR images are an important step for quantitative analysis of the developing human brain, with Deep learning providing an automated alternative for this otherwise tedious manual process. However, segmentation performances of Convolutional Neural Networks often suffer from domain shift, where the network fails when applied to subjects that deviate from the distribution with which it is trained on. In this work, we aim to train networks capable of automatically segmenting fetal brain MRIs with a wide range of domain shifts pertaining to differences in subject physiology and acquisition environments, in particular shape-based differences commonly observed in pathological cases. We introduce a novel data-driven train-time sampling strategy that seeks to fully exploit the diversity of a given training dataset to enhance the domain generalizability of the trained networks. We adapted our sampler, together with other existing data augmentation techniques, to the SynthSeg framework, a generator that utilizes domain randomization to generate diverse training data, and ran thorough experimentations and ablation studies on a wide range of training/testing data to test the validity of the approaches. Our networks achieved notable improvements in the segmentation quality on testing subjects with intense anatomical abnormalities (p < 1e-4), though at the cost of a slighter decrease in performance in cases with fewer abnormalities. Our work also lays the foundation for future works on creating and adapting data-driven sampling strategies for other training pipelines.
Synthesis of realistic fetal MRI with conditional Generative Adversarial Networks
Sep 20, 2022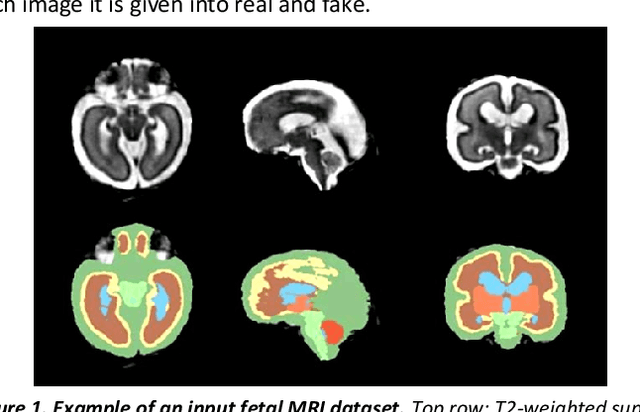
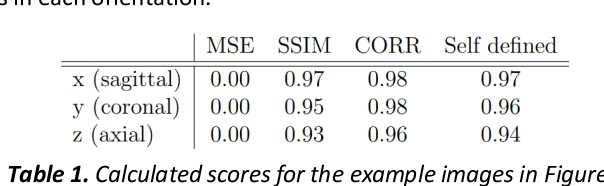
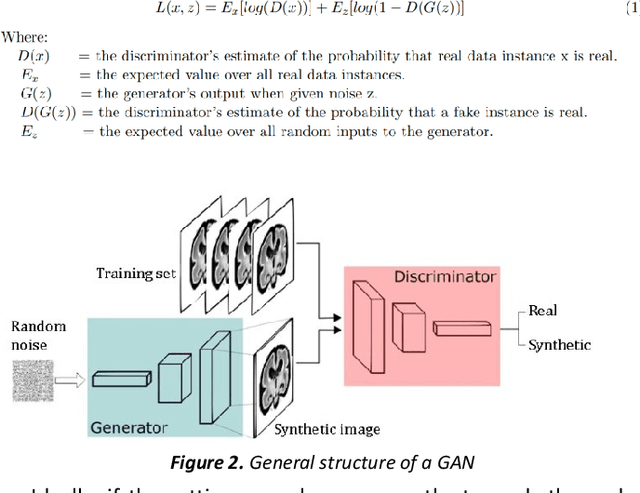
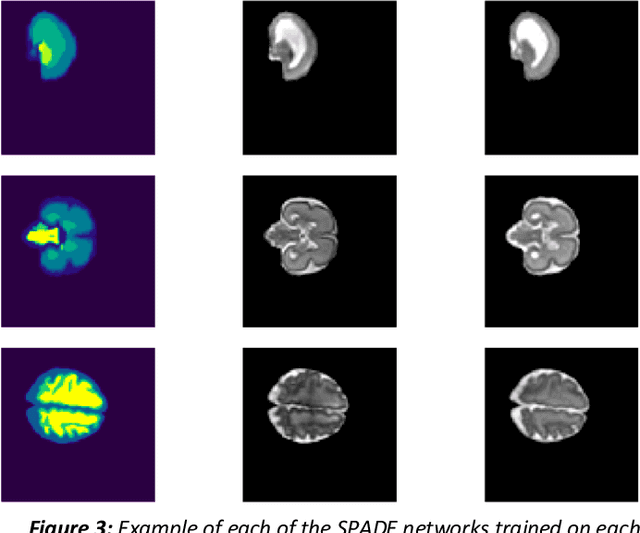
Abstract:Fetal brain magnetic resonance imaging serves as an emerging modality for prenatal counseling and diagnosis in disorders affecting the brain. Machine learning based segmentation plays an important role in the quantification of brain development. However, a limiting factor is the lack of sufficiently large, labeled training data. Our study explored the application of SPADE, a conditional general adversarial network (cGAN), which learns the mapping from the label to the image space. The input to the network was super-resolution T2-weighted cerebral MRI data of 120 fetuses (gestational age range: 20-35 weeks, normal and pathological), which were annotated for 7 different tissue categories. SPADE networks were trained on 256*256 2D slices of the reconstructed volumes (image and label pairs) in each orthogonal orientation. To combine the generated volumes from each orientation into one image, a simple mean of the outputs of the three networks was taken. Based on the label maps only, we synthesized highly realistic images. However, some finer details, like small vessels were not synthesized. A structural similarity index (SSIM) of 0.972+-0.016 and correlation coefficient of 0.974+-0.008 were achieved. To demonstrate the capacity of the cGAN to create new anatomical variants, we artificially dilated the ventricles in the segmentation map and created synthetic MRI of different degrees of fetal hydrocephalus. cGANs, such as the SPADE algorithm, allow the generation of hypothetically unseen scenarios and anatomical configurations in the label space, which data in turn can be utilized for training various machine learning algorithms. In the future, this algorithm would be used for generating large, synthetic datasets representing fetal brain development. These datasets would potentially improve the performance of currently available segmentation networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge