Maria Edwards
Generating Diverse Indoor Furniture Arrangements
Jun 20, 2022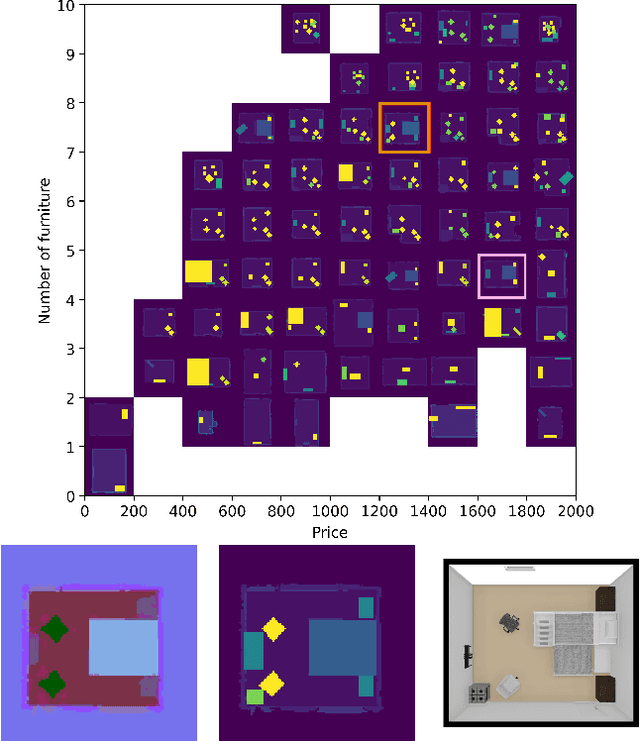

Abstract:We present a method for generating arrangements of indoor furniture from human-designed furniture layout data. Our method creates arrangements that target specified diversity, such as the total price of all furniture in the room and the number of pieces placed. To generate realistic furniture arrangement, we train a generative adversarial network (GAN) on human-designed layouts. To target specific diversity in the arrangements, we optimize the latent space of the GAN via a quality diversity algorithm to generate a diverse arrangement collection. Experiments show our approach discovers a set of arrangements that are similar to human-designed layouts but varies in price and number of furniture pieces.
Exploring open-ended gameplay features with Micro RollerCoaster Tycoon
May 10, 2021
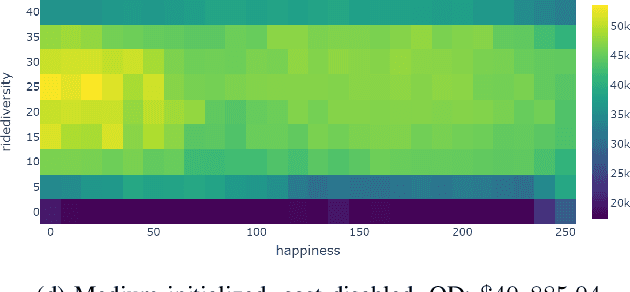
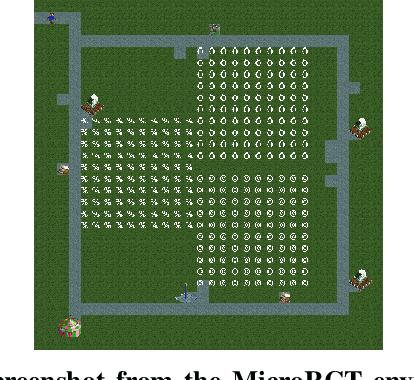
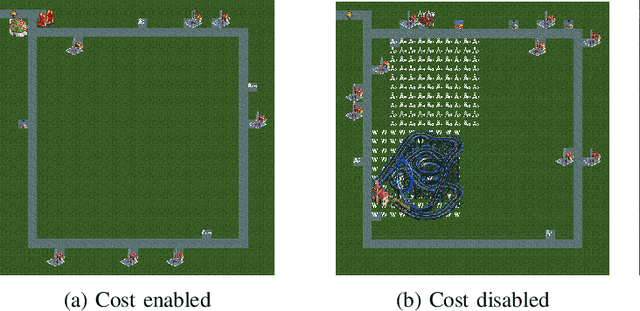
Abstract:This paper introduces MicroRCT, a novel open source simulator inspired by the theme park sandbox game RollerCoaster Tycoon. The goal in MicroRCT is to place rides and shops in an amusement park to maximize profit earned from park guests. Thus, the challenges for game AI include both selecting high-earning attractions and placing them in locations that are convenient to guests. In this paper, the MAP-Elites algorithm is used to generate a diversity of park layouts, exploring two theoretical questions about evolutionary algorithms and game design: 1) Is there a benefit to starting from a minimal starting point for evolution and complexifying incrementally? and 2) What are the effects of resource limitations on creativity and optimization? Results indicate that building from scratch with no costs results in the widest diversity of high-performing designs.
Learning Controllable Content Generators
May 06, 2021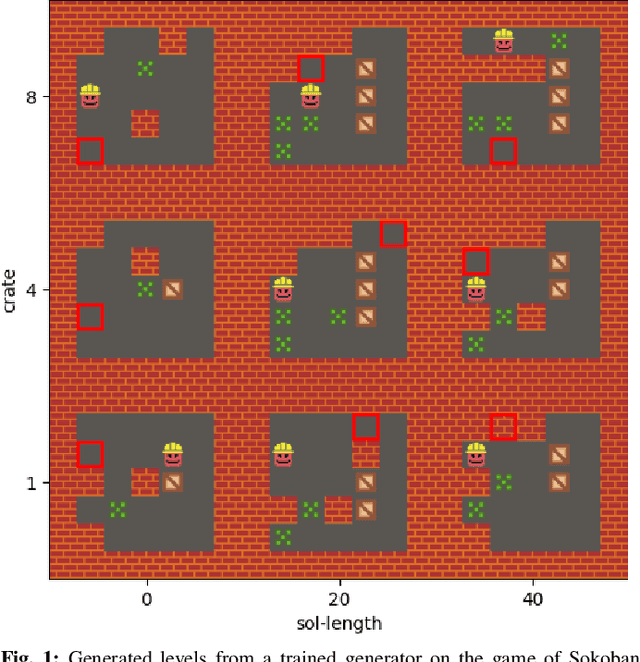

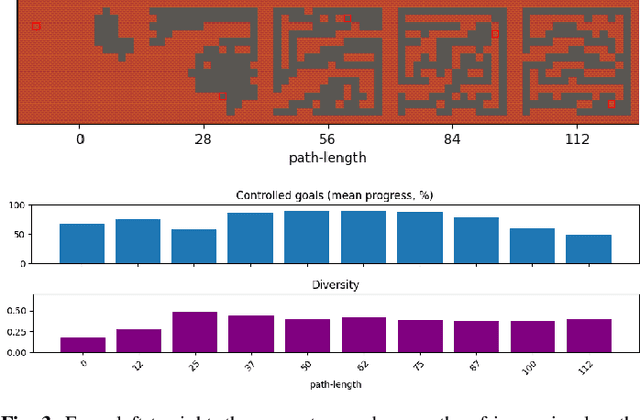
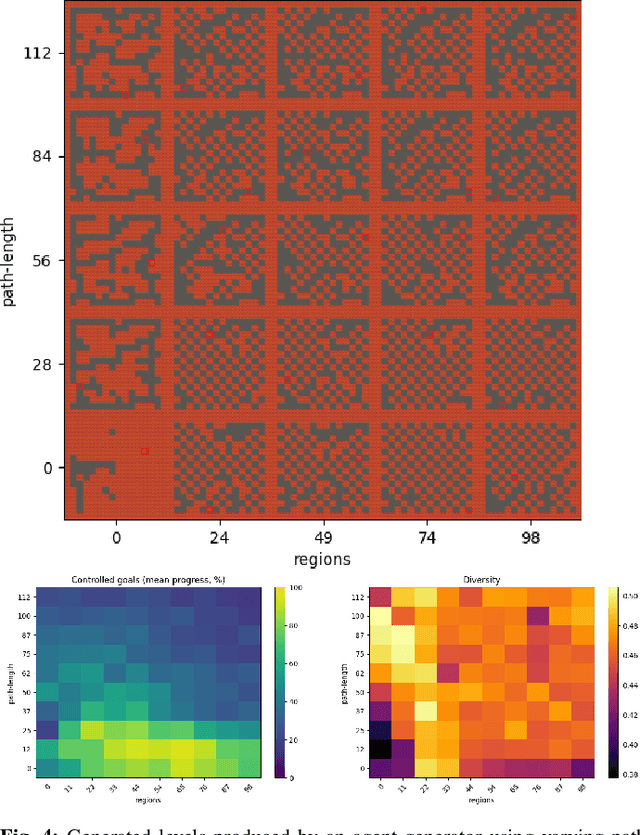
Abstract:It has recently been shown that reinforcement learning can be used to train generators capable of producing high-quality game levels, with quality defined in terms of some user-specified heuristic. To ensure that these generators' output is sufficiently diverse (that is, not amounting to the reproduction of a single optimal level configuration), the generation process is constrained such that the initial seed results in some variance in the generator's output. However, this results in a loss of control over the generated content for the human user. We propose to train generators capable of producing controllably diverse output, by making them "goal-aware." To this end, we add conditional inputs representing how close a generator is to some heuristic, and also modify the reward mechanism to incorporate that value. Testing on multiple domains, we show that the resulting level generators are capable of exploring the space of possible levels in a targeted, controllable manner, producing levels of comparable quality as their goal-unaware counterparts, that are diverse along designer-specified dimensions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge