Marco Grosso
AI-Assisted Diagnosis for Covid-19 CXR Screening: From Data Collection to Clinical Validation
May 19, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we present the major results from the Covid Radiographic imaging System based on AI (Co.R.S.A.) project, which took place in Italy. This project aims to develop a state-of-the-art AI-based system for diagnosing Covid-19 pneumonia from Chest X-ray (CXR) images. The contributions of this work are manyfold: the release of the public CORDA dataset, a deep learning pipeline for Covid-19 detection, and the clinical validation of the developed solution by expert radiologists. The proposed detection model is based on a two-step approach that, paired with state-of-the-art debiasing, provides reliable results. Most importantly, our investigation includes the actual usage of the diagnosis aid tool by radiologists, allowing us to assess the real benefits in terms of accuracy and time efficiency. Project homepage: https://corsa.di.unito.it/
Exploiting Liver CT scans in Colorectal Carcinoma genomics mutation classification
Jan 25, 2024



Abstract:The liver is the most involved organ by distant metastasis in colon-rectal cancer (CRC) patients and it comes necessary to be aware of the mutational status of the lesions to correctly design the best individual treatment. So far, efforts have been made in order to develop non-invasive and real-time methods that permit the analysis of the whole tumor, using new artificial intelligence tools to analyze the tumor's image obtained by Computed Tomography (CT) scan. In order to address the current medical workflow, that is biopsy analysis-based, we propose the first DeepLearning-based exploration, to our knowledge, of such classification approach from the patient medical imaging. We propose i) a solid pipeline for managing undersized datasets of available CT scans and ii) a baseline study for genomics mutation diagnosis support for preemptive patient follow-up. Our method is able to identify CRC RAS mutation family from CT images with 0.73 F1 score.
Lung nodules segmentation from CT with DeepHealth toolkit
Aug 01, 2022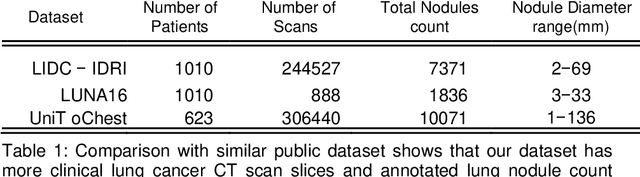
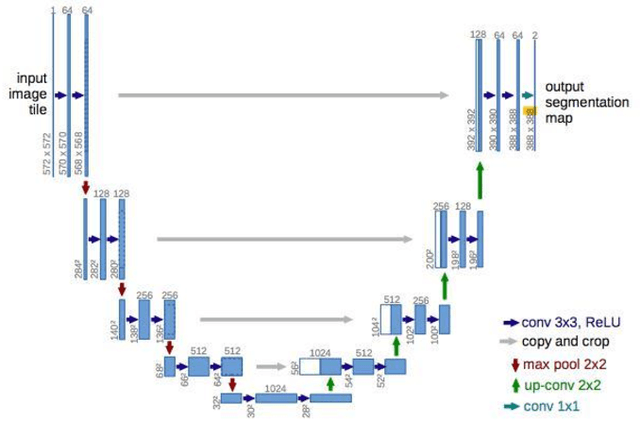

Abstract:The accurate and consistent border segmentation plays an important role in the tumor volume estimation and its treatment in the field of Medical Image Segmentation. Globally, Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of death and the early detection of lung nodules is essential for the early cancer diagnosis and survival rate of patients. The goal of this study was to demonstrate the feasibility of Deephealth toolkit including PyECVL and PyEDDL libraries to precisely segment lung nodules. Experiments for lung nodules segmentation has been carried out on UniToChest using PyECVL and PyEDDL, for data pre-processing as well as neural network training. The results depict accurate segmentation of lung nodules across a wide diameter range and better accuracy over a traditional detection approach. The datasets and the code used in this paper are publicly available as a baseline reference.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge