Man-Ki Yoon
Novelty Detection via Network Saliency in Visual-based Deep Learning
Jun 09, 2019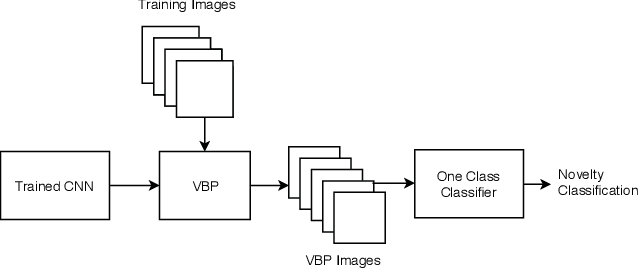
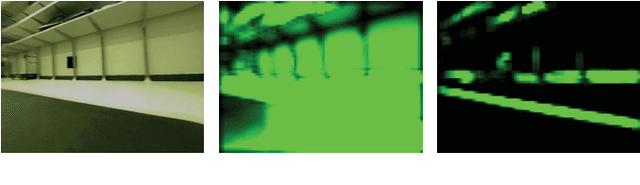


Abstract:Machine-learning driven safety-critical autonomous systems, such as self-driving cars, must be able to detect situations where its trained model is not able to make a trustworthy prediction. Often viewed as a black-box, it is non-obvious to determine when a model will make a safe decision and when it will make an erroneous, perhaps life-threatening one. Prior work on novelty detection deal with highly structured data and do not translate well to dynamic, real-world situations. This paper proposes a multi-step framework for the detection of novel scenarios in vision-based autonomous systems by leveraging information learned by the trained prediction model and a new image similarity metric. We demonstrate the efficacy of this method through experiments on a real-world driving dataset as well as on our in-house indoor racing environment.
Grouped Convolutional Neural Networks for Multivariate Time Series
May 31, 2018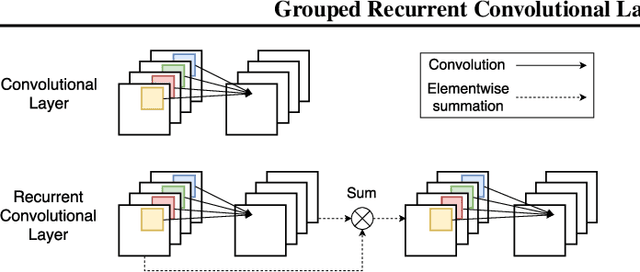
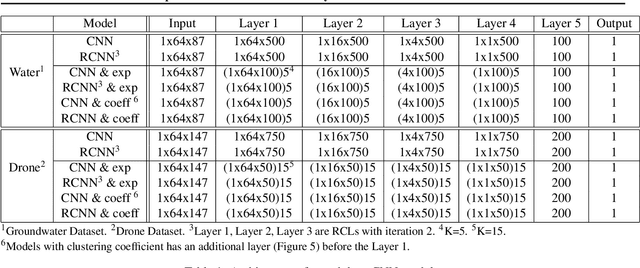
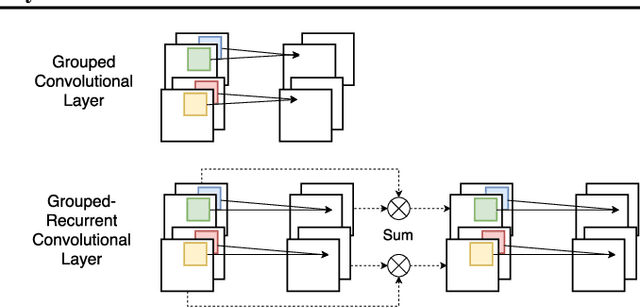
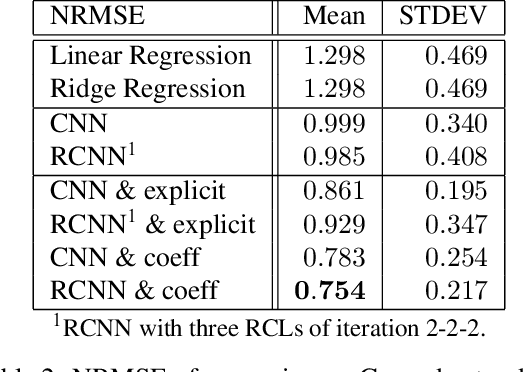
Abstract:Analyzing multivariate time series data is important for many applications such as automated control, fault diagnosis and anomaly detection. One of the key challenges is to learn latent features automatically from dynamically changing multivariate input. In visual recognition tasks, convolutional neural networks (CNNs) have been successful to learn generalized feature extractors with shared parameters over the spatial domain. However, when high-dimensional multivariate time series is given, designing an appropriate CNN model structure becomes challenging because the kernels may need to be extended through the full dimension of the input volume. To address this issue, we present two structure learning algorithms for deep CNN models. Our algorithms exploit the covariance structure over multiple time series to partition input volume into groups. The first algorithm learns the group CNN structures explicitly by clustering individual input sequences. The second algorithm learns the group CNN structures implicitly from the error backpropagation. In experiments with two real-world datasets, we demonstrate that our group CNNs outperform existing CNN based regression methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge