Mainak Ghosh
Tracing the Flow of Knowledge From Science to Technology Using Deep Learning
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:We develop a language similarity model suitable for working with patents and scientific publications at the same time. In a horse race-style evaluation, we subject eight language (similarity) models to predict credible Patent-Paper Citations. We find that our Pat-SPECTER model performs best, which is the SPECTER2 model fine-tuned on patents. In two real-world scenarios (separating patent-paper-pairs and predicting patent-paper-pairs) we demonstrate the capabilities of the Pat-SPECTER. We finally test the hypothesis that US patents cite papers that are semantically less similar than in other large jurisdictions, which we posit is because of the duty of candor. The model is open for the academic community and practitioners alike.
PaECTER: Patent-level Representation Learning using Citation-informed Transformers
Feb 29, 2024Abstract:PaECTER is a publicly available, open-source document-level encoder specific for patents. We fine-tune BERT for Patents with examiner-added citation information to generate numerical representations for patent documents. PaECTER performs better in similarity tasks than current state-of-the-art models used in the patent domain. More specifically, our model outperforms the next-best patent specific pre-trained language model (BERT for Patents) on our patent citation prediction test dataset on two different rank evaluation metrics. PaECTER predicts at least one most similar patent at a rank of 1.32 on average when compared against 25 irrelevant patents. Numerical representations generated by PaECTER from patent text can be used for downstream tasks such as classification, tracing knowledge flows, or semantic similarity search. Semantic similarity search is especially relevant in the context of prior art search for both inventors and patent examiners. PaECTER is available on Hugging Face.
Logic Mill -- A Knowledge Navigation System
Dec 31, 2022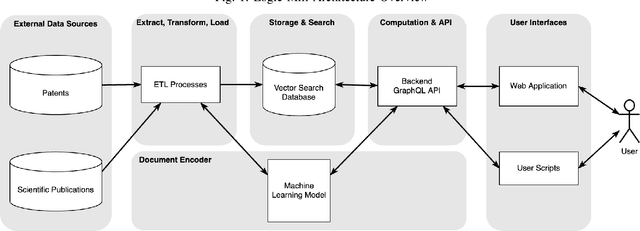
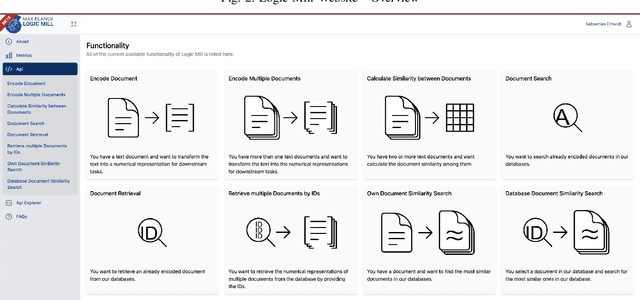
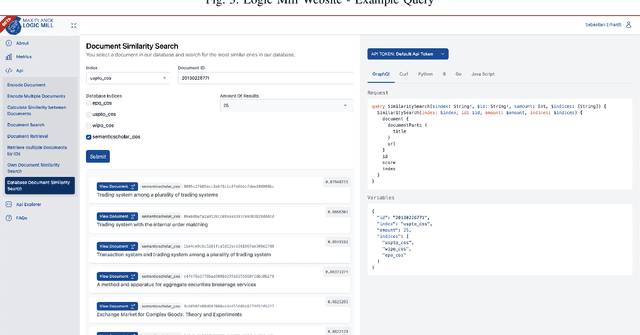
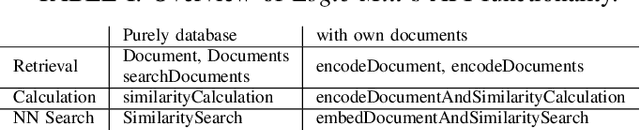
Abstract:Logic Mill is a scalable and openly accessible software system that identifies semantically similar documents within either one domain-specific corpus or multi-domain corpora. It uses advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to generate numerical representations of documents. Currently it leverages a large pre-trained language model to generate these document representations. The system focuses on scientific publications and patent documents and contains more than 200 million documents. It is easily accessible via a simple Application Programming Interface (API) or via a web interface. Moreover, it is continuously being updated and can be extended to text corpora from other domains. We see this system as a general-purpose tool for future research applications in the social sciences and other domains.
Forecasting SQL Query Cost at Twitter
Apr 12, 2022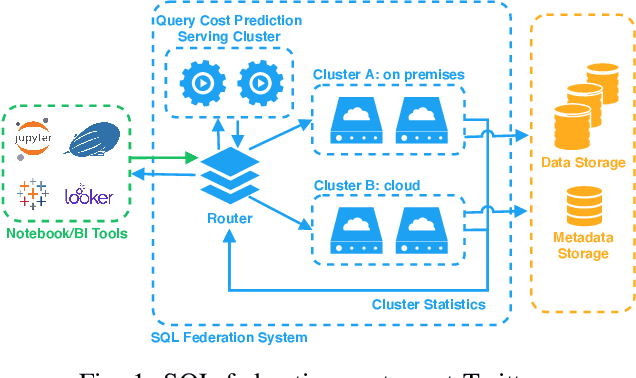
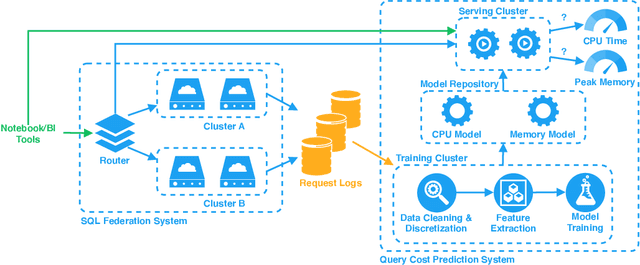
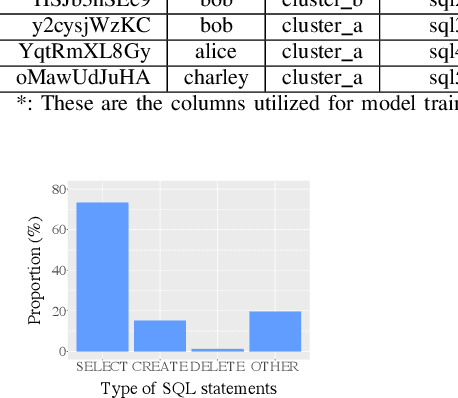
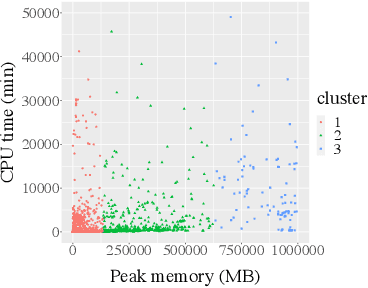
Abstract:With the advent of the Big Data era, it is usually computationally expensive to calculate the resource usages of a SQL query with traditional DBMS approaches. Can we estimate the cost of each query more efficiently without any computation in a SQL engine kernel? Can machine learning techniques help to estimate SQL query resource utilization? The answers are yes. We propose a SQL query cost predictor service, which employs machine learning techniques to train models from historical query request logs and rapidly forecasts the CPU and memory resource usages of online queries without any computation in a SQL engine. At Twitter, infrastructure engineers are maintaining a large-scale SQL federation system across on-premises and cloud data centers for serving ad-hoc queries. The proposed service can help to improve query scheduling by relieving the issue of imbalanced online analytical processing (OLAP) workloads in the SQL engine clusters. It can also assist in enabling preemptive scaling. Additionally, the proposed approach uses plain SQL statements for the model training and online prediction, indicating it is both hardware and software-agnostic. The method can be generalized to broader SQL systems and heterogeneous environments. The models can achieve 97.9\% accuracy for CPU usage prediction and 97\% accuracy for memory usage prediction.
SocialVisTUM: An Interactive Visualization Toolkit for Correlated Neural Topic Models on Social Media Opinion Mining
Oct 20, 2021



Abstract:Recent research in opinion mining proposed word embedding-based topic modeling methods that provide superior coherence compared to traditional topic modeling. In this paper, we demonstrate how these methods can be used to display correlated topic models on social media texts using SocialVisTUM, our proposed interactive visualization toolkit. It displays a graph with topics as nodes and their correlations as edges. Further details are displayed interactively to support the exploration of large text collections, e.g., representative words and sentences of topics, topic and sentiment distributions, hierarchical topic clustering, and customizable, predefined topic labels. The toolkit optimizes automatically on custom data for optimal coherence. We show a working instance of the toolkit on data crawled from English social media discussions about organic food consumption. The visualization confirms findings of a qualitative consumer research study. SocialVisTUM and its training procedures are accessible online.
* Demo paper accepted for publication on RANLP 2021; 8 pages, 5 figures, 1 table
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge