Madalina Olteanu
CEREMADE
Meta-survey on outlier and anomaly detection
Dec 12, 2023



Abstract:The impact of outliers and anomalies on model estimation and data processing is of paramount importance, as evidenced by the extensive body of research spanning various fields over several decades: thousands of research papers have been published on the subject. As a consequence, numerous reviews, surveys, and textbooks have sought to summarize the existing literature, encompassing a wide range of methods from both the statistical and data mining communities. While these endeavors to organize and summarize the research are invaluable, they face inherent challenges due to the pervasive nature of outliers and anomalies in all data-intensive applications, irrespective of the specific application field or scientific discipline. As a result, the resulting collection of papers remains voluminous and somewhat heterogeneous. To address the need for knowledge organization in this domain, this paper implements the first systematic meta-survey of general surveys and reviews on outlier and anomaly detection. Employing a classical systematic survey approach, the study collects nearly 500 papers using two specialized scientific search engines. From this comprehensive collection, a subset of 56 papers that claim to be general surveys on outlier detection is selected using a snowball search technique to enhance field coverage. A meticulous quality assessment phase further refines the selection to a subset of 25 high-quality general surveys. Using this curated collection, the paper investigates the evolution of the outlier detection field over a 20-year period, revealing emerging themes and methods. Furthermore, an analysis of the surveys sheds light on the survey writing practices adopted by scholars from different communities who have contributed to this field. Finally, the paper delves into several topics where consensus has emerged from the literature. These include taxonomies of outlier types, challenges posed by high-dimensional data, the importance of anomaly scores, the impact of learning conditions, difficulties in benchmarking, and the significance of neural networks. Non-consensual aspects are also discussed, particularly the distinction between local and global outliers and the challenges in organizing detection methods into meaningful taxonomies.
Challenges in anomaly and change point detection
Dec 27, 2022Abstract:This paper presents an introduction to the state-of-the-art in anomaly and change-point detection. On the one hand, the main concepts needed to understand the vast scientific literature on those subjects are introduced. On the other, a selection of important surveys and books, as well as two selected active research topics in the field, are presented.
On-line relational SOM for dissimilarity data
Dec 27, 2012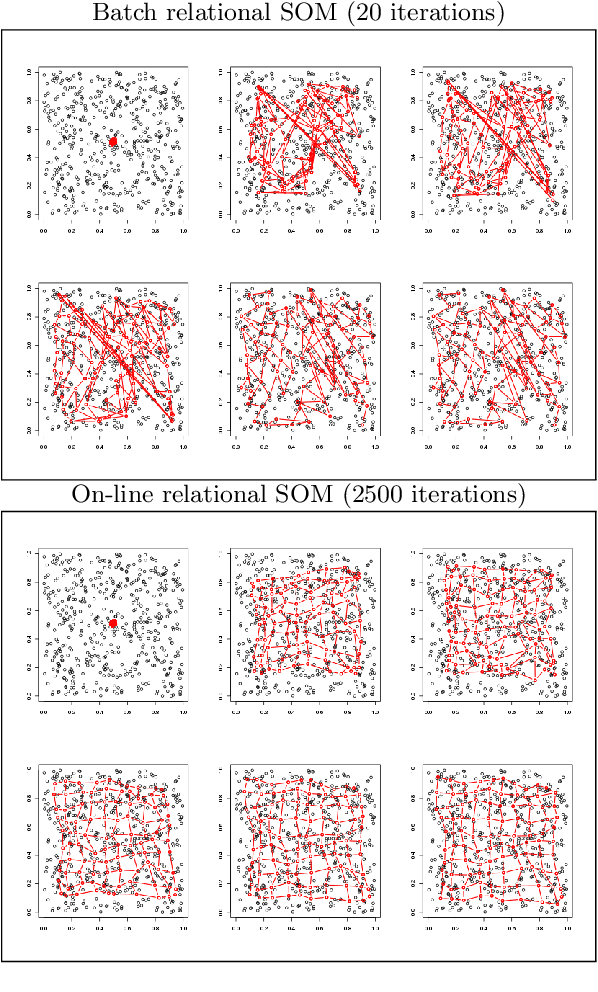
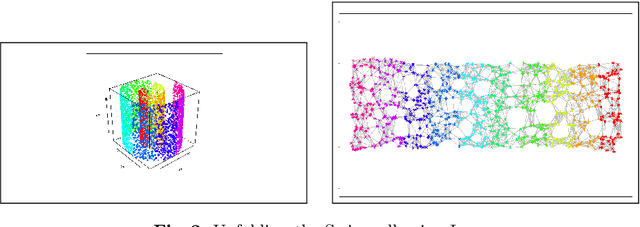
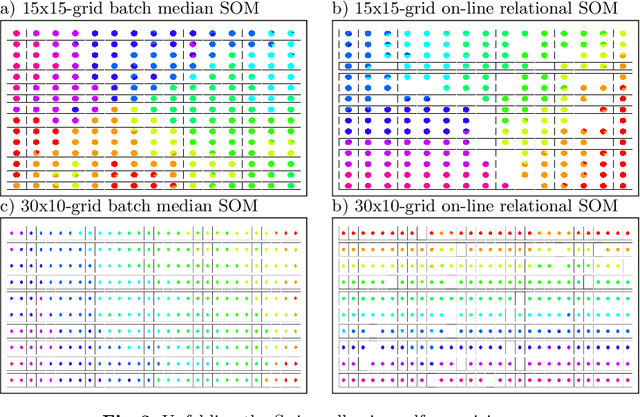
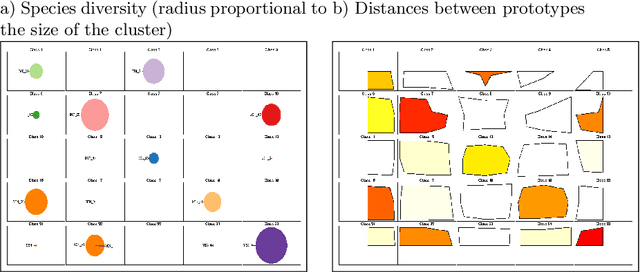
Abstract:In some applications and in order to address real world situations better, data may be more complex than simple vectors. In some examples, they can be known through their pairwise dissimilarities only. Several variants of the Self Organizing Map algorithm were introduced to generalize the original algorithm to this framework. Whereas median SOM is based on a rough representation of the prototypes, relational SOM allows representing these prototypes by a virtual combination of all elements in the data set. However, this latter approach suffers from two main drawbacks. First, its complexity can be large. Second, only a batch version of this algorithm has been studied so far and it often provides results having a bad topographic organization. In this article, an on-line version of relational SOM is described and justified. The algorithm is tested on several datasets, including categorical data and graphs, and compared with the batch version and with other SOM algorithms for non vector data.
Neural Networks for Complex Data
Oct 24, 2012
Abstract:Artificial neural networks are simple and efficient machine learning tools. Defined originally in the traditional setting of simple vector data, neural network models have evolved to address more and more difficulties of complex real world problems, ranging from time evolving data to sophisticated data structures such as graphs and functions. This paper summarizes advances on those themes from the last decade, with a focus on results obtained by members of the SAMM team of Universit\'e Paris 1
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge