Maarten G. Poirot
Split Learning for collaborative deep learning in healthcare
Dec 27, 2019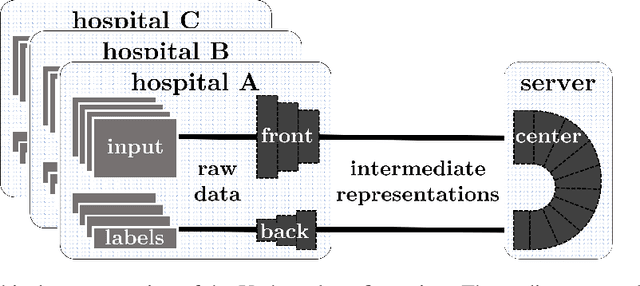
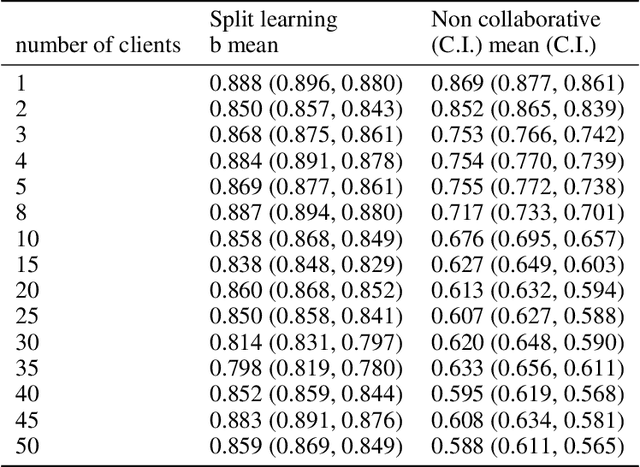
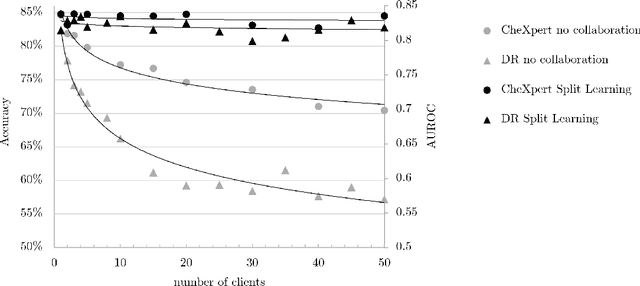
Abstract:Shortage of labeled data has been holding the surge of deep learning in healthcare back, as sample sizes are often small, patient information cannot be shared openly, and multi-center collaborative studies are a burden to set up. Distributed machine learning methods promise to mitigate these problems. We argue for a split learning based approach and apply this distributed learning method for the first time in the medical field to compare performance against (1) centrally hosted and (2) non collaborative configurations for a range of participants. Two medical deep learning tasks are used to compare split learning to conventional single and multi center approaches: a binary classification problem of a data set of 9000 fundus photos, and multi-label classification problem of a data set of 156,535 chest X-rays. The several distributed learning setups are compared for a range of 1-50 distributed participants. Performance of the split learning configuration remained constant for any number of clients compared to a single center study, showing a marked difference compared to the non collaborative configuration after 2 clients (p < 0.001) for both sets. Our results affirm the benefits of collaborative training of deep neural networks in health care. Our work proves the significant benefit of distributed learning in healthcare, and paves the way for future real-world implementations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge