Lun-Pin Yuan
Recomposition vs. Prediction: A Novel Anomaly Detection for Discrete Events Based On Autoencoder
Dec 27, 2020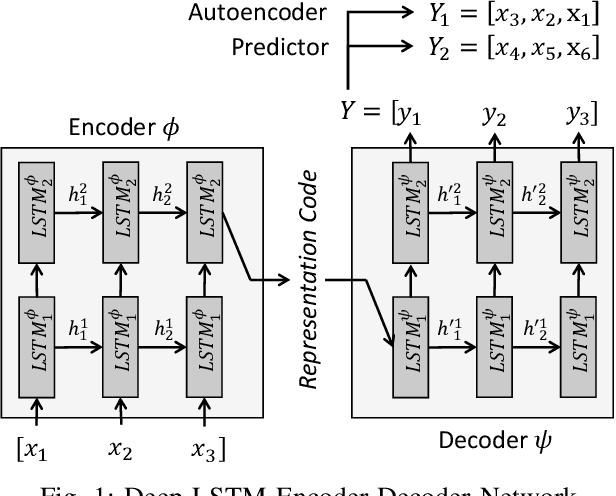
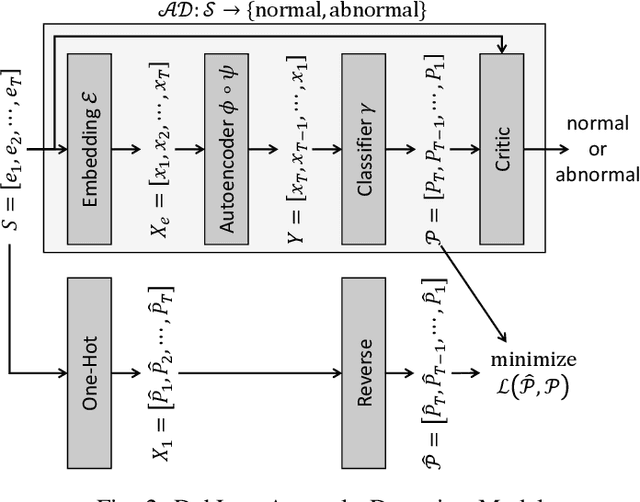
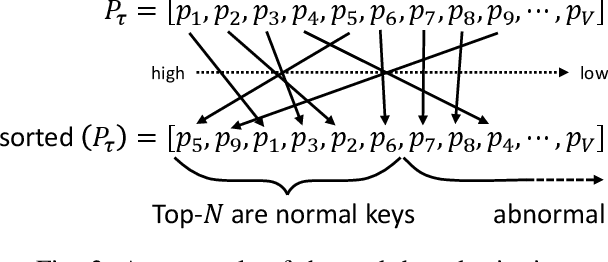
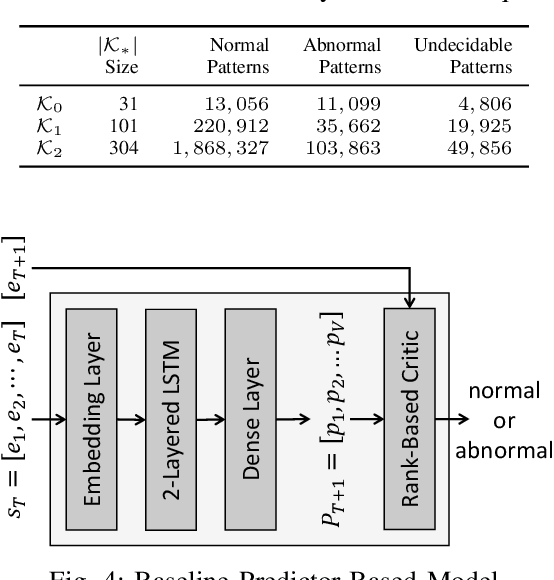
Abstract:One of the most challenging problems in the field of intrusion detection is anomaly detection for discrete event logs. While most earlier work focused on applying unsupervised learning upon engineered features, most recent work has started to resolve this challenge by applying deep learning methodology to abstraction of discrete event entries. Inspired by natural language processing, LSTM-based anomaly detection models were proposed. They try to predict upcoming events, and raise an anomaly alert when a prediction fails to meet a certain criterion. However, such a predict-next-event methodology has a fundamental limitation: event predictions may not be able to fully exploit the distinctive characteristics of sequences. This limitation leads to high false positives (FPs) and high false negatives (FNs). It is also critical to examine the structure of sequences and the bi-directional causality among individual events. To this end, we propose a new methodology: Recomposing event sequences as anomaly detection. We propose DabLog, a Deep Autoencoder-Based anomaly detection method for discrete event Logs. The fundamental difference is that, rather than predicting upcoming events, our approach determines whether a sequence is normal or abnormal by analyzing (encoding) and reconstructing (decoding) the given sequence. Our evaluation results show that our new methodology can significantly reduce the numbers of FPs and FNs, hence achieving a higher $F_1$ score.
Time-Window Group-Correlation Support vs. Individual Features: A Detection of Abnormal Users
Dec 27, 2020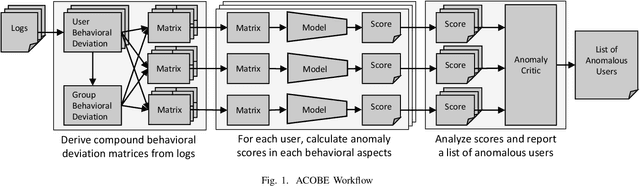
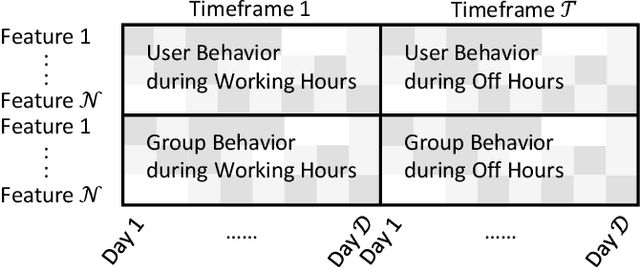
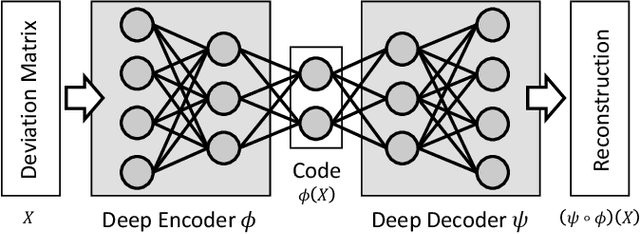
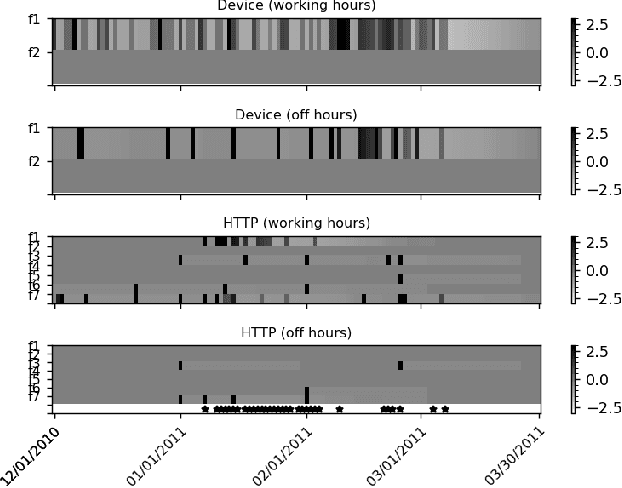
Abstract:Autoencoder-based anomaly detection methods have been used in identifying anomalous users from large-scale enterprise logs with the assumption that adversarial activities do not follow past habitual patterns. Most existing approaches typically build models by reconstructing single-day and individual-user behaviors. However, without capturing long-term signals and group-correlation signals, the models cannot identify low-signal yet long-lasting threats, and will wrongly report many normal users as anomalies on busy days, which, in turn, lead to high false positive rate. In this paper, we propose ACOBE, an Anomaly detection method based on COmpound BEhavior, which takes into consideration long-term patterns and group behaviors. ACOBE leverages a novel behavior representation and an ensemble of deep autoencoders and produces an ordered investigation list. Our evaluation shows that ACOBE outperforms prior work by a large margin in terms of precision and recall, and our case study demonstrates that ACOBE is applicable in practice for cyberattack detection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge