Lukman Ismaila
A Survey on African Computer Vision Datasets, Topics and Researchers
Feb 04, 2024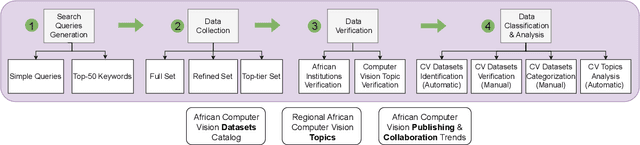


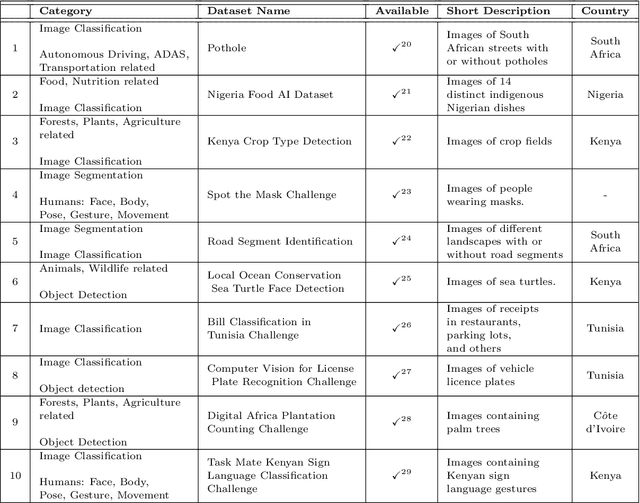
Abstract:Computer vision encompasses a range of tasks such as object detection, semantic segmentation, and 3D reconstruction. Despite its relevance to African communities, research in this field within Africa represents only 0.06% of top-tier publications over the past decade. This study undertakes a thorough analysis of 63,000 Scopus-indexed computer vision publications from Africa, spanning from 2012 to 2022. The aim is to provide a survey of African computer vision topics, datasets and researchers. A key aspect of our study is the identification and categorization of African Computer Vision datasets using large language models that automatically parse abstracts of these publications. We also provide a compilation of unofficial African Computer Vision datasets distributed through challenges or data hosting platforms, and provide a full taxonomy of dataset categories. Our survey also pinpoints computer vision topics trends specific to different African regions, indicating their unique focus areas. Additionally, we carried out an extensive survey to capture the views of African researchers on the current state of computer vision research in the continent and the structural barriers they believe need urgent attention. In conclusion, this study catalogs and categorizes Computer Vision datasets and topics contributed or initiated by African institutions and identifies barriers to publishing in top-tier Computer Vision venues. This survey underscores the importance of encouraging African researchers and institutions in advancing computer vision research in the continent. It also stresses on the need for research topics to be more aligned with the needs of African communities.
Toward more frugal models for functional cerebral networks automatic recognition with resting-state fMRI
Jul 04, 2023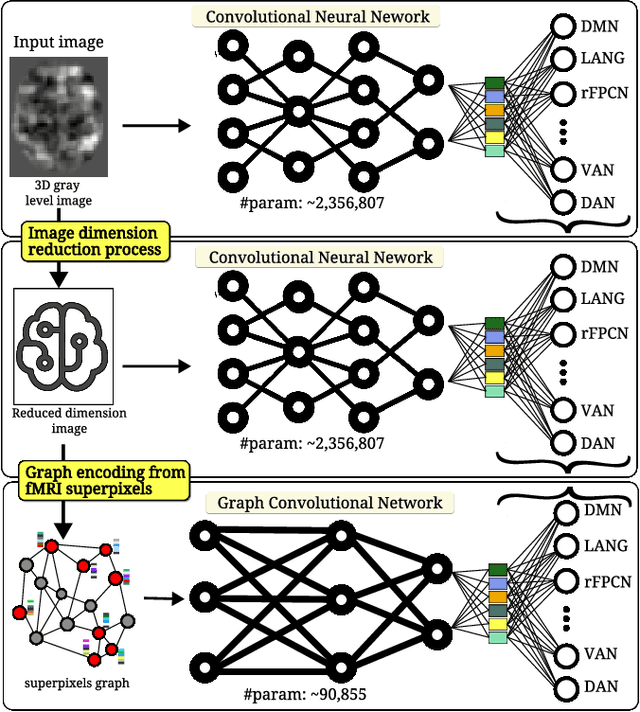
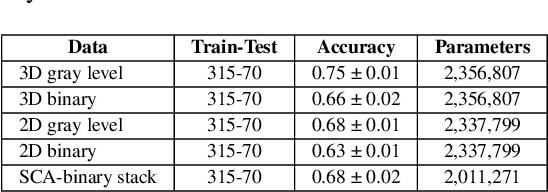
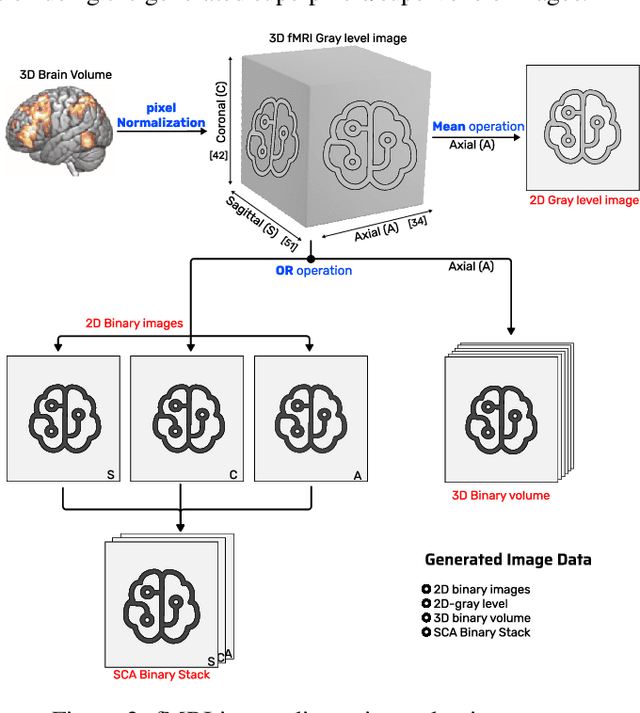
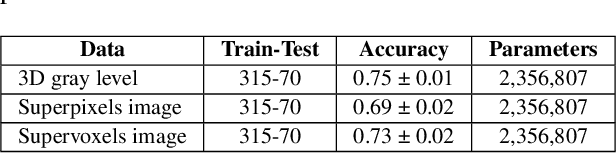
Abstract:We refer to a machine learning situation where models based on classical convolutional neural networks have shown good performance. We are investigating different encoding techniques in the form of supervoxels, then graphs to reduce the complexity of the model while tracking the loss of performance. This approach is illustrated on a recognition task of resting-state functional networks for patients with brain tumors. Graphs encoding supervoxels preserve activation characteristics of functional brain networks from images, optimize model parameters by 26 times while maintaining CNN model performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge